
Botrytis cinerea is a necrotrophic fungus that affects many plant species, although its most notable hosts may be wine grapes. In viticulture, it is commonly known as "botrytis bunch rot"; in horticulture, it is usually called "grey mould" or "gray mold".

Magnaporthe grisea, also known as rice blast fungus, rice rotten neck, rice seedling blight, blast of rice, oval leaf spot of graminea, pitting disease, ryegrass blast, Johnson spot, neck blast, wheat blast and Imochi (稲熱), is a plant-pathogenic fungus and model organism that causes a serious disease affecting rice. It is now known that M. grisea consists of a cryptic species complex containing at least two biological species that have clear genetic differences and do not interbreed. Complex members isolated from Digitaria have been more narrowly defined as M. grisea. The remaining members of the complex isolated from rice and a variety of other hosts have been renamed Magnaporthe oryzae, within the same M. grisea complex. Confusion on which of these two names to use for the rice blast pathogen remains, as both are now used by different authors.

A sclerotium, is a compact mass of hardened fungal mycelium containing food reserves. One role of sclerotia is to survive environmental extremes. In some higher fungi such as ergot, sclerotia become detached and remain dormant until favorable growth conditions return. Sclerotia initially were mistaken for individual organisms and described as separate species until Louis René Tulasne proved in 1853 that sclerotia are only a stage in the life cycle of some fungi. Further investigation showed that this stage appears in many fungi belonging to many diverse groups. Sclerotia are important in the understanding of the life cycle and reproduction of fungi, as a food source, as medicine, and in agricultural blight management.

White onion or Allium cepa are a cultivar of dry onion which have a distinct light and mild flavour profile. Much like red onions, they have a high sugar and low sulphur content, and thus have a relatively short shelf life. White onions are used in a variety of dishes, such as those of Mexican and European origin. Their uses in dishes often relate to their mild nature, they are often included in dishes to provide a light, fresh and sour taste to dishes and are often added uncooked to dishes such as salads.

Cochliobolus miyabeanus is a fungus that causes brown spot disease in rice.
This is a glossary of some of the terms used in phytopathology.

Rhizoctonia solani is a species of fungus in the order Cantharellales. Basidiocarps are thin, effused, and web-like, but the fungus is more typically encountered in its anamorphic state, as hyphae and sclerotia. The name Rhizoctonia solani is currently applied to a complex of related species that await further research. In its wide sense, Rhizoctonia solani is a facultative plant pathogen with a wide host range and worldwide distribution. It causes various plant diseases such as root rot, damping off, and wire stem. It can also form mycorrhizal associations with orchids.
Alternaria triticina is a fungal plant pathogen that causes leaf blight on wheat. A. triticina is responsible for the largest leaf blight issue in wheat and also causes disease in other major cereal grain crops. It was first identified in India in 1962 and still causes significant yield loss to wheat crops on the Indian subcontinent. The disease is caused by a fungal pathogen and causes necrotic leaf lesions and in severe cases shriveling of the leaves.

Gibberella zeae, also known by the name of its anamorph Fusarium graminearum, is a fungal plant pathogen which causes fusarium head blight (FHB), a devastating disease on wheat and barley. The pathogen is responsible for billions of dollars in economic losses worldwide each year. Infection causes shifts in the amino acid composition of wheat, resulting in shriveled kernels and contaminating the remaining grain with mycotoxins, mainly deoxynivalenol (DON), which inhibits protein biosynthesis; and zearalenone, an estrogenic mycotoxin. These toxins cause vomiting, liver damage, and reproductive defects in livestock, and are harmful to humans through contaminated food. Despite great efforts to find resistance genes against F. graminearum, no completely resistant variety is currently available. Research on the biology of F. graminearum is directed towards gaining insight into more details about the infection process and reveal weak spots in the life cycle of this pathogen to develop fungicides that can protect wheat from scab infection.

Macrophomina phaseolina is a Botryosphaeriaceae plant pathogen fungus that causes damping off, seedling blight, collar rot, stem rot, charcoal rot, basal stem rot, and root rot on many plant species.

Alternaria solani is a fungal pathogen that produces a disease in tomato and potato plants called early blight. The pathogen produces distinctive "bullseye" patterned leaf spots and can also cause stem lesions and fruit rot on tomato and tuber blight on potato. Despite the name "early," foliar symptoms usually occur on older leaves. If uncontrolled, early blight can cause significant yield reductions. Primary methods of controlling this disease include preventing long periods of wetness on leaf surfaces and applying fungicides. Early blight can also be caused by Alternaria tomatophila, which is more virulent on stems and leaves of tomato plants than Alternaria solani.

Didymella bryoniae, syn. Mycosphaerella melonis, is an ascomycete fungal plant pathogen that causes gummy stem blight on the family Cucurbitaceae, which includes cantaloupe, cucumber, muskmelon and watermelon plants. The anamorph/asexual stage for this fungus is called Phoma cucurbitacearum. When this pathogen infects the fruit of cucurbits it is called black rot.

Cercospora melongenae is a fungal plant pathogen that causes leaf spot on eggplant. It is a deuteromycete fungus that is primarily confined to eggplant species. Some other host species are Solanum aethiopicum and Solanum incanum. This plant pathogen only attacks leaves of eggplants and not the fruit. It is fairly common among the fungi that infect community gardens and home gardens of eggplant. Generally speaking, Cercospora melongenae attacks all local varieties of eggplants, but is most severe on the Philippine eggplant and less parasitic on a Siamese variety.

Southern corn leaf blight (SCLB) is a fungal disease of maize caused by the plant pathogen Bipolaris maydis.
Stromatinia cepivora is a fungus in the division Ascomycota. It is the teleomorph of Sclerotium cepivorum, the cause of white rot in onions, garlic, and leeks. The infective sclerotia remain viable in the soil for many years and are stimulated to germinate by the presence of a susceptible crop.
Gummy stem blight is a cucurbit-rot disease caused by the fungal plant pathogen Didymella bryoniae. Gummy stem blight can affect a host at any stage of growth in its development and affects all parts of the host including leaves, stems and fruits. Symptoms generally consist of circular dark tan lesions that blight the leaf, water soaked leaves, stem cankers, and gummy brown ooze that exudes from cankers, giving it the name gummy stem blight. Gummy stem blight reduces yields of edible cucurbits by devastating the vines and leaves and rotting the fruits. There are various methods to control gummy stem blight, including use of treated seed, crop rotation, using preventative fungicides, eradication of diseased material, and deep plowing previous debris.
Cladosporium fulvum is an Ascomycete called Passalora fulva, a non-obligate pathogen that causes the disease on tomatoes known as the tomato leaf mold. P. fulva only attacks tomato plants, especially the foliage, and it is a common disease in greenhouses, but can also occur in the field. The pathogen is likely to grow in humid and cool conditions. In greenhouses, this disease causes big problems during the fall, in the early winter and spring, due to the high relative humidity of air and the temperature, that are propitious for the leaf mold development. This disease was first described in the North Carolina, by Mordecai Cubitt Cooke (1883), on cultivated tomato, although it is originally from South and Central America. The causal fungus of tomato leaf mold may also be referred to as Cladosporium fulvum, a former name.
Gray leaf spot (GLS) is a foliar fungal disease that affects grasses. In grasses other than maize it is caused by Pyricularia grisea, which only infects perennial ryegrass, tall fescue, and St. Augustine grass in places with warm and rainy climates.

Alternaria leaf spot or Alternaria leaf blight are a group of fungal diseases in plants, that have a variety of hosts. The diseases infects common garden plants, such as cabbage, and are caused by several closely related species of fungi. Some of these fungal species target specific plants, while others have been known to target plant families. One commercially relevant plant genus that can be affected by Alternaria Leaf Spot is Brassica, as the cosmetic issues caused by symptomatic lesions can lead to rejection of crops by distributors and buyers. When certain crops such as cauliflower and broccoli are infected, the heads deteriorate and there is a complete loss of marketability. Secondary soft-rotting organisms can infect stored cabbage that has been affected by Alternaria Leaf Spot by entering through symptomatic lesions. Alternaria Leaf Spot diseases that affect Brassica species are caused by the pathogens Alternaria brassicae and Alternaria brassicicola.
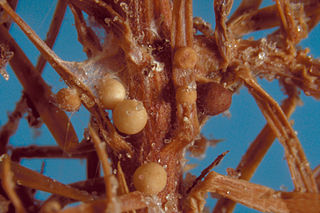
Agroathelia rolfsii is a corticioid fungus in the order Amylocorticiales. It is a facultative plant pathogen and is the causal agent of "southern blight" disease in crops.













