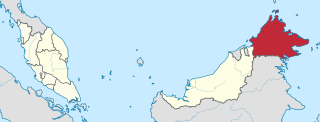
Sabah is a state of Malaysia located on the northern portion of Borneo, in the region of East Malaysia. Sabah has land borders with the Malaysian state of Sarawak to the southwest and Indonesia's North Kalimantan province to the south. The Federal Territory of Labuan is an island just off Sabah's west coast. Sabah shares maritime borders with Vietnam to the west and the Philippines to the north and east. Kota Kinabalu is the state capital and the economic centre of the state, and the seat of the Sabah State government. Other major towns in Sabah include Sandakan and Tawau. The 2020 census recorded a population of 3,418,785 in the state. It has an equatorial climate with tropical rainforests, abundant with animal and plant species. The state has long mountain ranges on the west side which forms part of the Crocker Range National Park. Kinabatangan River, the second longest river in Malaysia runs through Sabah. The highest point of Sabah, Mount Kinabalu is also the highest point of Malaysia.
The states and federal territories of Malaysia are the principal administrative divisions of Malaysia. Malaysia is a federation of 13 states (Negeri) and 3 federal territories.

The Murut, alternatively referred to as Tagol/Tahol, constitute an indigenous ethnic community comprising 29 distinct sub-ethnic groups dwelling within the northern inland territories of Borneo. Characterized by their rich cultural diversity, the Murutic languages form a linguistic family encompassing approximately half a dozen closely intertwined Austronesian languages. Murut populations exhibit dispersion in Malaysia's Sabah and the northern part of Sarawak, as well as in the country of Brunei and the Indonesian North Kalimantan Province. Furthermore, the Murut people have close connections with the Tidung, who historically inhabited Borneo's east coast region that underwent processes of Islamization and Malayalization,

The Ida'an people are an ethnic group residing primarily in the Lahad Datu and Tawau districts on the east coast of Sabah, Malaysia. Their current population is estimated to be around 6,000, but it appears that they once inhabited a much larger area along the east Sabah coast than present. For centuries, the Ida’an have owned exclusive rights to the collection of edible bird's nests in the limestone caves of the region, notably the Madai Caves. Most Ida'an are Sunni Muslims.

The Kwijau or Kuijau are an indigenous ethnic group residing in Sabah, eastern Malaysia on the island of Borneo. The Kwijau tribe claim descent from the Nunuk Ragang settlers who intermarried and assimilated with the native Muruts. They reside in the Keningau district of the Interior Division within a 12-mile radius to the west and north of Keningau town centre. Their population was estimated at 7,910 in the year 2000. They are considered a sub-group of the Kadazan-Dusun, as their language is on the Dusunic branch of the Austronesian language family. About 20% of the population embrace the Christian faith in denominations of evangelical Christianity and Roman Catholicism with large significant Muslim minorities, the remainder are animist practicing the ancient belief system called Momolianism. They are known for performing the Magunatip, an east Malaysian dance very strongly influenced by the Philippine tinikling. Performed by the young men and women, the dance involves jumping steps that manoeuvre the dancer's feet in and out, so as not to get their feet trapped by 2 moving bamboo poles that are held by another pair of dancers, who beat the poles together and over a shorter length of wood or bamboo, creating an interesting rhythm.

The Lotud people are an indigenous ethnic group residing in Sabah, eastern Malaysia on the island of Borneo. They reside mainly in the Tuaran district and also a portion of this tribe's population also reside in the village of Kampung Sukoli located in the Telipok suburban township of Kota Kinabalu city, all located in the West Coast Division of Sabah. Their population was estimated at 5,000 in the year 1985 but now believed to be more than 20,000. They are a sub-ethnic group of the Dusunic group, now also known as Kadazan-Dusun.
The Tambanuo people are an indigenous ethnic group residing in Sabah, Malaysia. They primarily reside in the Beluran district of the Sandakan Division as well as Kota Marudu and Pitas districts of Kudat Division of Sabah. Their population was estimated at 20,000 in the year 1990. They are considered a sub-group of the Orang Sungai, and their language belongs to the Paitanic branch of the Austronesian language family.
The Dumpas are an indigenous ethnic group residing in Sabah, Malaysia. They reside in the villages of Rancangan Nangoh and Perancangan of the Beluran district in the Sandakan Division. Their population was estimated at 1,078 in the year 2000. Their language belongs to the Paitanic branch of the Austronesian language family. The language is dying out as a result of intermarriage with other groups, and since native speakers also use Tambanuo in their daily conversation.
The Kimaragang or Maragang people are an indigenous ethnic group residing in Sabah, eastern Malaysia on the island of Borneo. They reside in the Kota Marudu and Pitas districts of Kudat Division. Their population was estimated at 10,000 in the year 1987. They are considered a sub-group of the Kadazan-Dusun, as their language belongs to the Dusunic branch of the Austronesian language family. They are primarily farmers, raising paddy rice, cocoa, and cash crops.
The Minokok are an indigenous ethnic group residing in Sabah, Malaysia. They reside near the headwaters of Kinabatangan River, in Sandakan Division. Their population was estimated at 2,000 in the year 1991. They are considered a sub-group of the Kadazan-Dusun, as their language belongs to the Dusunic branch of the Austronesian language family. About 35% of the population has been converted to evangelical Christianity, the remainder are animist.
The Rumanau are an indigenous ethnic group residing in Sabah, eastern Malaysia on the island of Borneo. They are known as the Lobu in the Keningau District near Lanas, and the Rumanau in the Masaum, Mangkawagu, Minusu areas of the Kinabatangan District along the Kinabatangan River, in Sandakan Division. Their population was estimated at 2,800 in the year 1991. They are a sub-group of the Kadazan-Dusun, although their language belongs to the Paitanic branch of the Austronesian language family.

The Kedayan are an ethnic group residing in Brunei, Federal Territory of Labuan, southwest of Sabah, and north of Sarawak on the island of Borneo. According to the Language and Literature Bureau of Brunei, the Kedayan language is spoken by about 30,000 people in Brunei, and it has been claimed that there are a further 46,500 speakers in Sabah and 37,000 in Sarawak. In Sabah, the Kedayan mainly live in the southern districts of Sipitang and Beaufort, where they are counted as a part of the local Malay populace. Whilst in Sarawak, the Kedayans mostly reside in the towns of Lawas, Limbang and Miri.

Malaysian nationality law details the conditions by which a person is a national of Malaysia. The primary law governing nationality requirements is the Constitution of Malaysia, which came into force on 27 August 1957.

Kadazan-Dusun are the largest ethnic group in Sabah, Malaysia, an amalgamation of the closely related indigenous Kadazan and Dusun peoples. They are also known as Mamasok Sabah, meaning "indigenous people of Sabah". Kadazan-Dusun tradition holds that they are the descendants of Nunuk Ragang. Kadazan-Dusun is recognised as an indigenous nation of Borneo with documented heritage by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) since 2004. Kadazan-Dusun is part of bumiputera group in Malaysia and has special rights concerning land, rivers, education and maintaining their own customs.
The Ida'an language is a Malayo-Polynesian language spoken by the Ida'an people on the east coast of Sabah, Malaysia.

The Tip of Borneo is the northernmost tip of Borneo located in Kudat District, Sabah, Malaysia. The tip marks the meeting point of the South China Sea and Sulu Sea.

Cocos Malays are a community that form the predominant group of the Cocos (Keeling) Islands, which is now a part of Australia. Today, most of the Cocos Malay can be found in the eastern coast of Sabah, Malaysia, because of diaspora originating from the 1950s during the British colonial period.
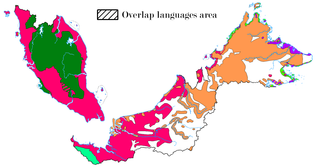
The indigenous languages of Malaysia belong to the Mon-Khmer and Malayo-Polynesian families. The national, or official, language is Malay which is the mother tongue of the majority Malay ethnic group. The main ethnic groups within Malaysia are the Malay people, Han Chinese people and Tamil people, with many other ethnic groups represented in smaller numbers, each with its own languages. The largest native languages spoken in East Malaysia are the Iban, Dusunic, and Kadazan languages. English is widely understood and spoken within the urban areas of the country; the English language is a compulsory subject in primary and secondary education. It is also the main medium of instruction within most private colleges and private universities. English may take precedence over Malay in certain official contexts as provided for by the National Language Act, especially in the states of Sabah and Sarawak, where it may be the official working language. Furthermore, the law of Malaysia is commonly taught and read in English, as the unwritten laws of Malaysia continue to be partially derived from pre-1957 English common law, which is a legacy of past British colonisation of the constituents forming Malaysia. In addition, authoritative versions of constitutional law and statutory law are continuously available in both Malay and English.

The Orang Asal are the indigenous peoples of Malaysia. The term is Malay for "Original People", used to refer to the aboriginals of Sabah, Sarawak, and Peninsular Malaysia. These groups are given the Bumiputera status in Malaysia.

Sabah is the third most populous state in Malaysia, with a population of 3,418,785 according to the 2020 Malaysian census. It also has the highest non-citizen population, at 810,443. Although Malaysia is one of the least densely populated countries in Asia, Sabah is particularly sparsely populated. Most of the population is concentrated along coastal areas, with towns and urban centers seeing the most population growth.












