Related Research Articles

Dravidian languages are a family of languages spoken by 220 million people, mainly in southern India and north-east Sri Lanka, with pockets elsewhere in South Asia. Since the colonial era, there have been small but significant immigrant communities outside the Indian subcontinent in Mauritius, Hong Kong, Singapore, Malaysia, Indonesia, Philippines, United Kingdom, Australia, France, Canada, Germany, South Africa, and the United States.

Tamil Nadu is a state in southern India. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. The state is the home of the Tamil people, whose Tamil language—one of the longest surviving classical languages in the world—is widely spoken in the state and serves as its official language.

Tamil is a Classical Dravidian language natively spoken by the Tamil people of South Asia. Tamil is an official language of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu, the sovereign nations of Sri Lanka and Singapore, and the Union Territory of Puducherry. Tamil is spoken by significant minorities in the four other South Indian states of Kerala, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana and the Union Territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. It is also spoken by the Tamil diaspora found in many countries, including Malaysia, Myanmar, South Africa, United Kingdom, United States, Canada, Australia and Mauritius. Tamil is also natively spoken by Sri Lankan Moors. One of 22 scheduled languages in the Constitution of India, Tamil was the first to be classified as a classical language of India.
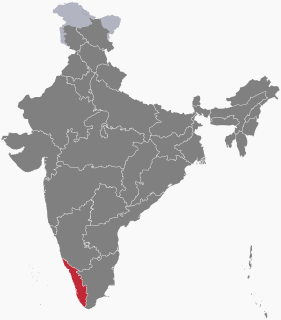
Malayalam is a Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry by the Malayali people. It is one of 22 scheduled languages of India and is spoken by 2.88% of Indians. Malayalam has official language status in Kerala, Lakshadweep and Puducherry (Mahé), and is spoken by 34 million people worldwide. Malayalam is also spoken by linguistic minorities in the neighbouring states; with significant number of speakers in the Kodagu and Dakshina Kannada districts of Karnataka, and Nilgiris and Kanyakumari, districts of Tamil Nadu. Due to Malayali expatriates in the Persian Gulf, Malayalam is also widely spoken in the Gulf countries.

Agastya was a revered Indian sage of Hinduism. In the Indian tradition, he is a noted recluse and an influential scholar in diverse languages of the Indian subcontinent. He and his wife Lopamudra are the celebrated authors of hymns 1.165 to 1.191 in the Sanskrit text Rigveda and other Vedic literature.

The Kingdom of Travancore (/ˈtrævənkɔːr/), also known as the Kingdom of Thiruvithamkoor, was an Indian kingdom from c. 1729 until 1949. It was ruled by the Travancore Royal Family from Padmanabhapuram, and later Thiruvananthapuram. At its zenith, the kingdom covered most of the south of modern-day Kerala, and the southernmost part of modern-day Tamil Nadu with the Thachudaya Kaimal's enclave of Irinjalakuda Koodalmanikyam temple in the neighbouring Kingdom of Cochin. However Tangasseri area of Kollam city and Anchuthengu near Attingal in Thiruvananthapuram district, were British colonies and were part of the Malabar District until 30 June 1927, and Tirunelveli district from 1 July 1927 onwards. Travancore merged with the erstwhile princely state of Cochin to form Travancore-Cochin in 1950. The five Tamil-majority Taluks of Vilavancode, Kalkulam, Thovalai, Agastheeswaram, and Sengottai were transferred from Travancore-Cochin to Madras State in 1956. The Malayalam-speaking regions of Travancore-Cochin merged with the Malabar District and the Kasaragod taluk of the South Canara district in Madras State to form the modern Malayalam-state of Kerala on 1 November 1956, according to the States Reorganisation Act, 1956 passed by the Government of India.

The Tamil people, also known as Tamilar, or simply Tamils, are a Dravidian ethno-linguistic group who trace their ancestry mainly to India’s southern state of Tamil Nadu, union territory of Puducherry and to Sri Lanka. Tamils constitute 5.9% of the population in India, 15% in Sri Lanka, 10% in Mauritius, 7% in Malaysia and 5% in Singapore.

Iyer is a caste of Hindu Brahmin communities of Tamil origin. Most Iyers are followers of the Advaita philosophy propounded by Adi Shankara and adhere to Smarta tradition. This is in contrast to the Iyengar caste, who are Vaishnavite Hindus. The majority of Iyers reside in Tamil Nadu, India.

The Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam is a social-democratic and Dravidianist political party in the state of Tamil Nadu and the union territory of Puducherry.

Velupillai Prabhakaran was a Sri Lankan Tamil guerrilla and the founder and leader of the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE), a militant organization that sought to create an independent Tamil state in the north and east of Sri Lanka. The LTTE waged war in Sri Lanka for more than 25 years, to create an independent state for the Sri Lankan Tamil people.

Thiruvalluvar, commonly known as Valluvar, was a celebrated Tamil poet and philosopher. He is best known as the author of the Tirukkuṟaḷ, a collection of couplets on ethics, political and economical matters, and love. The text is considered an exceptional and widely cherished work of Tamil literature.

The Pandya dynasty, also known as the Pandyas of Madurai, was a dynasty of south India, one of the three famous Tamil lineages, the other two being the Chola and the Chera. Extant since at least the 4th to 3rd centuries BC, the dynasty passed through two periods of imperial dominance, the 6th to 10th centuries CE, and under the 'Later Pandyas'. The Pandyas ruled extensive territories, at times including the large portions of present-day south India and northern Sri Lanka through collateral branches subject to Madurai.

The Nayanars were a group of 63 poet-saints living in Tamil Nadu during the 3rd to 8th centuries CE who were devoted to the Hindu god Shiva. Along with the Alwars, their contemporaries who were devoted to Vishnu, they influenced the Bhakti movement in early medieval South India. The names of the Nayanars were first compiled by Sundarar. The list was expanded by Nambiyandar Nambi during his compilation of material by the poets for the Tirumurai collection, and would include Sundarar himself and Sundarar's parents.

A Divya Desam or Vaishnava Divya Desam is one of the 108 Vishnu temples that are mentioned in the works of the Alvars. Divya means "divine" and Desam indicates "place of abode" (temple). Of the 108 temples, 105 are in India, one is in Nepal, and the last two are believed to be outside the Earthly realms. In India, they are spread over states of Tamil Nadu (84), Kerala (11), Andhra Pradesh (2), Gujarat (1), Uttar Pradesh (4), and Uttarakhand (3). Muktinath, Saligramam is the only Divya Desam in Nepal. The Divya Desams are revered by the 12 Alvars in the Divya Prabandha, a collection of 4,000 Tamil verses. Divya Desams follow Thenkalai or Vadakalai modes of worship.

The Chola Dynasty was a Tamil thalassocratic empire of southern India, one of the longest-ruling dynasties in the world history. The earliest datable references to the Chola are in inscriptions from the 3rd century BCE left by Ashoka, of the Maurya Empire. As one of the Three Crowned Kings of Tamilakam, along with the Chera and Pandya, the dynasty continued to govern over varying territory until the 13th century CE. Despite these ancient origins, the period when it is appropriate to speak of a "Chola Empire" only begins with the medieval Cholas in the mid-9th century CE.

Sri Lankan Tamils, also known as Ceylon Tamils or Eelam Tamils, are Tamils native to the South Asian island state of Sri Lanka. Today, they constitute a majority in the Northern Province, live in significant numbers in the Eastern Province and are in the minority throughout the rest of the country. 70% of Sri Lankan Tamils in Sri Lanka live in the Northern and Eastern provinces.

Tamilakam refers to the geographical region inhabited by the ancient Tamil people. Tamilakam covered today's Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Puducherry, Lakshadweep and southern parts of Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka. Traditional accounts and Tolkāppiyam referred these territories as a single cultural area, where Tamil was the natural language and culture of all people. The ancient Tamil country was divided into kingdoms. The best known among them were the Cheras, Cholas, Pandyans and Pallavas. During the Sangam period, Tamil culture began to spread outside Tamilakam. Ancient Tamil settlements were also found in Sri Lanka and the Maldives (Giravarus).

Tamil-Brahmi, also known as Tamili or Damili, is a variant of the Brahmi script used to write inscriptions in the early form of Old Tamil. The Tamil-Brahmi script has been paleographically and stratigraphically dated between the third century BCE and the first century CE, and it constitutes the earliest known writing system evidenced in many parts of Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh and Sri Lanka. Tamil Brahmi inscriptions have been found on cave entrances, stone beds, potsherds, jar burials, coins, seals, and rings.

Pancha Bhoota Sthalam refers to five temples dedicated to Shiva, each representing a manifestation of the five prime elements of nature: earth, water, fire, air, and aether. Pancha indicates "five," Bhoota means "elements," and Sthala means "place." The temples are located in South India, four in Tamil Nadu and one in Andhra Pradesh. The five elements are believed to be enshrined in the five lingams of the temples, with each lingam named based on the element represented.
Thenpattinam Ponnuswamy Meenakshisundaram (1901–1980), popularly known as Te Po Meenkshisunadaranar, was an Indian scholar, writer of Tamil and English literature and the founder vice chancellor of Madurai Kamaraj University.
References
- ↑ Srinivasa-iyengar, P.T. (1929). History of the Tamils: from the earliest times to 600 A.D. New Delhi: Asian Educational Service. pp. 231–232. ISBN 81-206-0145-9.
- ↑ Zvelebil, Kamil (1973). The Smile of Murugan: On Tamil Literature of South India. Leiden: Brill. p. 47. ISBN 90-04-03591-5.