
Devanāgarī or Devanagari, also called Nāgarī, is a left-to-right abugida, based on the ancient Brāhmī script, used in the northern Indian subcontinent. It is one of the official scripts of the Republic of India and Nepal. It was developed and in regular use by the 7th century CE. The Devanāgarī script, composed of 48 primary characters, including 14 vowels and 34 consonants, is the fourth most widely adopted writing system in the world, being used for over 120 languages.
Transliteration is a type of conversion of a text from one script to another that involves swapping letters in predictable ways, such as Greek ⟨α⟩ → ⟨a⟩, Cyrillic ⟨д⟩ → ⟨d⟩, Greek ⟨χ⟩ → the digraph ⟨ch⟩, Armenian ⟨ն⟩ → ⟨n⟩ or Latin ⟨æ⟩ → ⟨ae⟩.
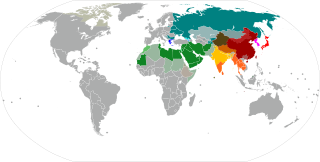
The Brahmic scripts, also known as Indic scripts, are a family of abugida writing systems. They are used throughout the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia and parts of East Asia. They are descended from the Brahmi script of ancient India and are used by various languages in several language families in South, East and Southeast Asia: Indo-Aryan, Dravidian, Tibeto-Burman, Mongolic, Austroasiatic, Austronesian, and Tai. They were also the source of the dictionary order (gojūon) of Japanese kana.

Malayalam script is a Brahmic script used commonly to write Malayalam, which is the principal language of Kerala, India, spoken by 45 million people in the world. It is a Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry by the Malayali people. It is one of the official scripts of the Indian Republic. Malayalam script is also widely used for writing Sanskrit texts in Kerala.

Romanization or romanisation, in linguistics, is the conversion of text from a different writing system to the Roman (Latin) script, or a system for doing so. Methods of romanization include transliteration, for representing written text, and transcription, for representing the spoken word, and combinations of both. Transcription methods can be subdivided into phonemic transcription, which records the phonemes or units of semantic meaning in speech, and more strict phonetic transcription, which records speech sounds with precision.
Devanagari is an Indic script used for many Indo-Aryan languages of North India and Nepal, including Hindi, Marathi and Nepali, which was the script used to write Classical Sanskrit. There are several somewhat similar methods of transliteration from Devanagari to the Roman script, including the influential and lossless IAST notation. Romanized Devanagari is also called Romanagari.
The National Library at Kolkata romanisation is a widely used transliteration scheme in dictionaries and grammars of Indic languages. This transliteration scheme is also known as (American) Library of Congress and is nearly identical to one of the possible ISO 15919 variants. The scheme is an extension of the IAST scheme that is used for transliteration of Sanskrit.
Indian Standard Code for Information Interchange (ISCII) is a coding scheme for representing various writing systems of India. It encodes the main Indic scripts and a Roman transliteration. The supported scripts are: Bengali–Assamese, Devanagari, Gujarati, Gurmukhi, Kannada, Malayalam, Oriya, Tamil, and Telugu. ISCII does not encode the writing systems of India that are based on Persian, but its writing system switching codes nonetheless provide for Kashmiri, Sindhi, Urdu, Persian, Pashto and Arabic. The Persian-based writing systems were subsequently encoded in the PASCII encoding.
The International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration (IAST) is a transliteration scheme that allows the lossless romanisation of Indic scripts as employed by Sanskrit and related Indic languages. It is based on a scheme that emerged during the 19th century from suggestions by Charles Trevelyan, William Jones, Monier Monier-Williams and other scholars, and formalised by the Transliteration Committee of the Geneva Oriental Congress, in September 1894. IAST makes it possible for the reader to read the Indic text unambiguously, exactly as if it were in the original Indic script. It is this faithfulness to the original scripts that accounts for its continuing popularity amongst scholars.

The Grantha script is a South Indian script, found particularly in Tamil Nadu and Kerala. Originating from the Pallava script, the Grantha script is related to the Tamil and the Vatteluttu scripts. The modern Malayalam script of Kerala is a direct descendant of the Grantha script. The Southeast Asian and Indonesian scripts such as Thai and Javanese respectively, as well as South Asian Tigalari and Sinhala scripts, are derived or closely related to Grantha through the early Pallava script. The Pallava script or Pallava Grantha, emerged in the 4th century CE and was used until the 7th century CE, in India. This early Grantha script was used to write Sanskrit texts, inscriptions on copper plates and stones of Hindu temples and monasteries. It was also used for classical Manipravalam – a language that is a blend of Sanskrit and Tamil. From it evolved Middle Grantha by the 7th century, and Transitional Grantha by about the 8th century, which remained in use until about the 14th century. Modern Grantha has been in use since the 14th century and into the modern era, to write classical texts in Sanskrit and Dravidian languages. It is also used to chant hymns and in traditional Vedic schools.
The Harvard-Kyoto Convention is a system for transliterating Sanskrit and other languages that use the Devanāgarī script into ASCII. It is predominantly used informally in e-mail, and for electronic texts.
ISO 15919 is one of a series of international standards for romanization by the International Organization for Standardization. It was published in 2001 and uses diacritics to map the much larger set of consonants and vowels in Brahmic and Nastaliq scripts to the Latin script.
The "Indian languages TRANSliteration" (ITRANS) is an ASCII transliteration scheme for Indic scripts, particularly for the Devanagari script.
There are several romanisation schemes for the Malayalam script, including ITRANS and ISO 15919.
Romanisation of Bengali is the representation of written Bengali language in the Latin script. Various romanisation systems for Bengali are used, most of which do not perfectly represent Bengali pronunciation. While different standards for romanisation have been proposed for Bengali, none has been adopted with the same degree of uniformity as Japanese or Sanskrit.
Indic Computing means "computing in Indic", i.e., Indian Scripts and Languages. It involves developing software in Indic Scripts/languages, Input methods, Localization of computer applications, web development, Database Management, Spell checkers, Speech to Text and Text to Speech applications and OCR in Indian languages.

WX notation is a transliteration scheme for representing Indian languages in ASCII. This scheme originated at IIT Kanpur for computational processing of Indian languages, and is widely used among the natural language processing (NLP) community in India. The notation is used, for example, in a textbook on NLP from IIT Kanpur. The salient features of this transliteration scheme are: Every consonant and every vowel has a single mapping into Roman. Hence it is a prefix code, advantageous from a computation point of view. Typically the small case letters are used for un-aspirated consonants and short vowels while the capital case letters are used for aspirated consonants and long vowels. While the retroflexed voiceless and voiced consonants are mapped to 't, T, d and D', the dentals are mapped to 'w, W, x and X'. Hence the name of the scheme "WX", referring to the idiosyncratic mapping. Ubuntu Linux provides a keyboard support for WX notation.
The Sanskrit Library Phonetic basic encoding scheme (SLP1) is an ASCII transliteration scheme for the Sanskrit language from and to the Devanagari script.
The Velthuis system of transliteration is an ASCII transliteration scheme for the Sanskrit language from and to the Devanagari script. It was developed in about 1983 by Frans Velthuis, a scholar living in Groningen, Netherlands, who created a popular, high-quality software package in LaTeX for typesetting Devanāgarī. The primary documentation for the scheme is the system's clearly-written software manual. It is based on using the ISO 646 repertoire to represent mnemonically the accents used in standard scholarly transliteration. It does not use diacritics as IAST does. It may optionally use capital letters in a manner similar but not identical to the Harvard-Kyoto or ITRANS schemes.manual para 4.1

Bharati Script is a constructed script, and an abugida created by a research team led by V. Srinivasa Chakravarthy at IIT Madras. It is designed to serve as a common script or link script for Indian languages.






