
In the botanical classification of plants, Aeridinae Pfitzer is a subtribe of the tribe Vandeae whose representatives all have a monopodial growth habit and do not possess pseudobulbs.

Brassia is a genus of orchids classified in the subtribe Oncidiinae. It is native to Mexico, Central America, the West Indies, and northern South America, with one species extending into Florida.

Aganisia is a small South American genus in the orchid family (Orchidaceae), subfamily Epidendroideae.
Angostylis is a genus of flowering plants in the family Euphorbiaceae, first described in 1854. The genus is native to northern South America.

Bletia is a genus of about 30 species of orchids, almost all of which are terrestrial; some are occasionally lithophytic or epiphytic. It is named after Spanish botanist and pharmacist Don Luis Blet. The genus is widespread across Florida, Mexico, Central America, the West Indies, and South America as far south as Argentina.

Blepharocalyx is a genus of plant in family Myrtaceae first described as a genus in 1854. It is native to South America and the West Indies.
- Blepharocalyx cruckshanksii(Hook. & Arn.) Nied. - Chile
- Blepharocalyx eggersii(Kiaerskou) L.R.Landrum - Lesser Antilles, Venezuela, Guyana, Peru, Brazil
- Blepharocalyx myriophyllus Mattos - Minas Gerais
- Blepharocalyx salicifolius(Kunth.) O.Berg - Brazil, Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Paraguay, Uruguay, N Argentina

The genus Arachnis, abbreviated as Arach in horticultural trade, is a member of the orchid family (Orchidaceae), consisting of more than 20 species native to China, India, Southeast Asia, Indonesia, the Philippines, New Guinea, and the Solomon Islands.
Trigonidium, abbreviated as Trgdm in horticultural trade, was a formerly accepted genus of orchids comprising roughly twenty species found from Mexico to Brazil. As of 2023, it was considered a synonym of Maxillaria.

Epidendrum secundum, one of the crucifix orchids, is a poorly understood reed stemmed species, which Dressler (1989) describes as "the Epidendrum secundum complex." According to Dressler, there are dozens of varieties, some of which appear to deserve species rank. Arditti and Ghani note that E. secundum has the distinction of bearing the longest seeds known in the Orchidaceae, 6.0 mm long. By comparison, the seeds of E. ibaguense are only 2.9 mm long.

Triphora is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It is native to South America, Central America, southern Mexico, the West Indies and eastern North America as far north as Ontario. Noddingcaps is a common name for plants in this genus.
- Triphora amazonicaSchltr. - Florida, Caribbean, south to Brazil
- Triphora carnosula(Rchb.f.) Schltr. - Brazil
- Triphora craigheadiiLuer - Florida
- Triphora debilis(Schltr.) Schltr. - southern Mexico, Costa Rica, Guatemala, Panama
- Triphora duckeiSchltr. - Brazil
- Triphora foldatsiiCarnevali - Venezuela
- Triphora gentianoides(Sw.) Nutt. ex Ames & Schltr. - Florida, Southern Mexico, Costa Rica, Veenzuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Bahamas, Greater Antilles
- Triphora hassleriana(Cogn. ex Chodat & Hassl.) Schltr. - from Mexico to Argentina
- Triphora heringeriPabst - Brazil
- Triphora miserrima(Cogn.) Acuña - Cuba, Hispaniola
- Triphora nitida(Schltr.) Schltr. - Costa Rica
- Triphora pusilla(Rchb.f. & Warm.) Schltr. - Brazil
- Triphora ravenii(L.O.Williams) Garay - Costa Rica, Panama
- Triphora santamariensisPortalet - Brazil
- Triphora surinamensis(Lindl. ex Benth.) Britton - West Indies south to Brazil
- Triphora trianthophoros(Sw.) Rydb. Ontario, Eastern United States, much of Mexico
- Triphora unifloraA.W.C.Ferreira, Baptista & Pansarin - Brazil
- Triphora wagneriSchltr. - from Mexico to Ecuador
- Triphora yucatanensisAmes - Florida and the Yucatán Peninsula

Psilochilus is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It is native to South America, Central America, Mexico and the West Indies.
- Psilochilus carinatusGaray - Colombia
- Psilochilus dusenianusKraenzl. ex Garay & Dunst. - Venezuela, Brazil
- Psilochilus macrophyllus(Lindl.) Ames - widespread from central Mexico and the West indies south to Peru
- Psilochilus maderoi(Schltr.) Schltr. - Colombia
- Psilochilus modestusBarb.Rodr. - Venezuela, Brazil
- Psilochilus mollisGaray - Ecuador
- Psilochilus physurifolius(Rchb.f.) Løjtnant - Venezuela, Guyana
- Psilochilus vallecaucanusKolan. & Szlach. - Colombia

Pteroceras is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It is native to China, the Indian Subcontinent, and Southeast Asia.

Sarcoglottis is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It is widespread across much of Latin America from Mexico to Argentina, with one species extending northward into Trinidad and the Windward Islands.
Maxillaria donaldeedodii, synonym Ornithidium donaldeedodii, is a species of orchid native to Haiti. It was "discovered" in April 2010 when DNA analysis showed that a wrongly labeled orchid at the University of California Botanical Garden in Berkeley, California, was actually a distinct new species. The "new" orchid, which had been mislabeled as Maxillaria croceorubens since the 1990s, was named after orchidologist Donald D. Dod (1912–2008), who collected the specimen in the 1980s in Haiti. The new orchid was officially described in Lankesteriana, an international journal on orchidology, by authors James Ackerman of the University of Puerto Rico and W. Mark Whitten of the Florida Museum of Natural History, as Ornithidium donaldeedodii. It was transferred to Maxillaria in 2011.

Maxillariinae is an orchid subtribe in the tribe Cymbidieae. It was formerly treated as the tribe Maxillarieae, and divided into a number of subtribes.
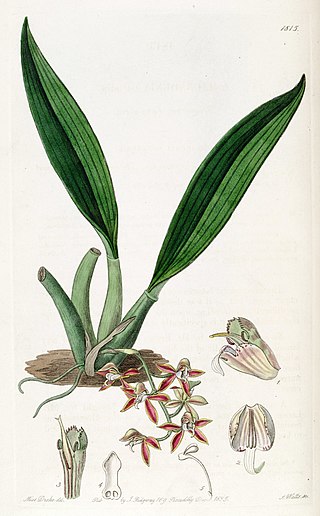
Macradenia lutescens is a species of epiphytic orchid known by the common name longgland orchid. It is native to South America, the West Indies, and southern Florida.

Maxillaria parviflora, the purple tiger orchid, is a species of epiphytic orchid native to Florida, the West Indies and through Latin America from Mexico to Bolivia.
Maxillaria petiolaris, synonym Hylaeorchis petiolaris, is a species of epiphytic orchids native to northwestern South America. When placed in the genus Hylaeorchis, it was the only species.
Kerbera is a genus of plants in the family Apocynaceae first established in 1885. It contains only one known species, Kerbera eichleri, endemic to Brazil.

Maxillaria obtusa, synonym Trigonidium obtusum, is an orchid native to tropical South America.















