
A chordate is a deuterostomal bilaterian animal belonging to the phylum Chordata. All chordates possess, at some point during their larval or adult stages, five distinctive physical characteristics (synapomorphies) that distinguish them from other taxa. These five synapomorphies are a notochord, a hollow dorsal nerve cord, an endostyle or thyroid, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail.

A fossil is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the fossil record. Though the fossil record is incomplete, numerous studies have demonstrated that there is enough information available to give a good understanding of the pattern of diversification of life on Earth. In addition, the record can predict and fill gaps such as the discovery of Tiktaalik in the arctic of Canada.

Felidae is the family of mammals in the order Carnivora colloquially referred to as cats. A member of this family is also called a felid.
Panthera is a genus within the family Felidae, and one of two extant genera in the subfamily Pantherinae. It contains the largest living members of the cat family. There are five living species: the jaguar, leopard, lion, snow leopard and tiger, as well as a number of extinct species, including the cave lion and American lion.

A living fossil is an extant taxon that phenotypically resembles related species known only from the fossil record. To be considered a living fossil, the fossil species must be old relative to the time of origin of the extant clade. Living fossils commonly are of species-poor lineages, but they need not be. While the body plan of a living fossil remains superficially similar, it is never the same species as the remote relatives it resembles, because genetic drift would inevitably change its chromosomal structure.

The Glypheoidea, is a group of lobster-like decapod crustaceans which forms an important part of fossil faunas, such as the Solnhofen limestone. These fossils included taxa such as Glyphea, and Mecochirus, mostly with elongated chelipeds. This group of decapods is a good example of a living fossil, or a lazarus taxon, since until their discovery in the 1970s, the group was considered to have become extinct in the Eocene. The superfamily Glypheoidea comprises five families. The two extant species, Neoglyphea inopinata and Laurentaeglyphea neocaledonica, are both in the family Glypheidae.

Glypheidea is an infraorder of lobster-like decapod crustaceans, comprising a number of fossil forms and the two extant (living) genera Neoglyphea and Laurentaeglyphea: The infraorder was thought to be extinct until a living species, Neoglyphea inopinata, was discovered in 1975. They are now considered "living fossils", with over 256 fossil species discovered, and just two extant species.
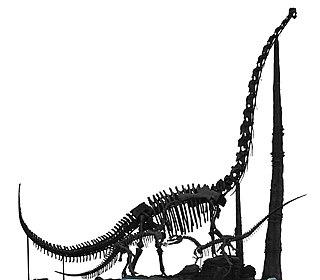
Chuanjiesaurus is a genus of sauropod dinosaurs from the middle Jurassic Period. They lived in what is now China. The type species, Chuanjiesaurus anaensis, was first described by Fang, Pang, Lü, Zhang, Pan, Wang, Li and Cheng in 2000. Fossils of the species were found in the village of Chuanjie, Lufeng County, Yunnan Province, and are named after the location where the fossils were discovered. Holtz gave a length of 25 meters.

Tremacebus is an extinct genus of New World monkeys from the Early Miocene. The type species is T. harringtoni.

Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, have myocytes and are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Animals form a clade, meaning that they arose from a single common ancestor. Over 1.5 million living animal species have been described, of which around 1.05 million are insects, over 85,000 are molluscs, and around 65,000 are vertebrates. It has been estimated there are as many as 7.77 million animal species on Earth. Animal body lengths range from 8.5 μm (0.00033 in) to 33.6 m (110 ft). They have complex ecologies and interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology, and the study of animal behaviour is known as ethology.

Boselaphini is a tribe of bovines. It contains only two extant genera, each with a single extant species.

Mecochirus is an extinct genus of lobster-like decapod crustaceans, containing 17 species. The Maxberg Specimen of Archaeopteryx was initially assigned to the type species, Mecochirus longimanatus before it was realised that it belonged to Archaeopteryx lithographica.

Qianichthyosaurus is an extinct genus of ichthyosaur from the Ladinian and Carnian stages of the Late Triassic epoch. Its fossils have been found in southeastern China, in Carnian rocks of the Falang Formation near Huangtutang, Guizhou. The type species is Qianichthyosaurus zhoui, named by Chun Li in 1999. A second species, Qianichthyosaurus xingyiensis, was named from older (Ladinian) deposits in the Falang Formation in 2013 by Pengfei Yang and colleagues. Complete Qianichthyosaurus fossils are common in the Xiaowa Formation, with both juveniles and pregnant specimens being known; its larger contemporaries, Guizhouichthyosaurus and Guanlingsaurus, are rarer.
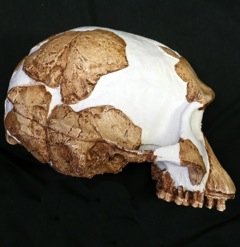
Homo gautengensis is a species name proposed by anthropologist Darren Curnoe in 2010 for South African hominin fossils otherwise attributed to H. habilis, H. ergaster, or, in some cases, Australopithecus or Paranthropus. The fossils assigned to the species by Curnoe cover a vast temporal range, from about 1.8 million years ago to potentially as late as 0.8 million years ago, meaning that if the species is considered valid, H. gautengensis would be both one of the earliest and one of the longest lived species of Homo.
Iaceornis is a genus of marine ornithuran dinosaurs closely related to modern birds. It was endemic to North America during the Late Cretaceous, living about 83.5 million years ago. It is known from a single fossil specimen found in Gove County, Kansas, and consisting of a partial skeleton lacking a skull.

Palaeomedusa testa is an extinct species of thalassochelydian turtle from the Tithonian of the Late Jurassic. It was first described by the German palaeontologist Christian Erich Hermann von Meyer in 1860. It is the only species classified under the genus Palaeomedusa.
Qantas is a genus of trematosauroid temnospondyl from the Early Triassic. Fossils have been found from the Kamennyi Yar Formation in Borsky District, Samara Oblast. The type species Qantas samarensis was named in 2012 and placed in the family Benthosuchidae, as it was viewed as a close relative of Benthosuchus. The subfamily Qantasinae was established to include Qantas, and possibly the genus Tirraturhinus. Qantas is named after the Australian airline Qantas, which supported the original study of the fossils.

Vulpes skinneri is a species of extinct fox in the genus Vulpes from the early Pleistocene, identified based on fossil remains dated to about 2 million years ago. The species is known from a single partial skeleton discovered in the Malapa Fossil Site at the Cradle of Humankind World Heritage Site in South Africa and is associated with the fossil hominin remains of Australopithecus sediba. The fossils have been dated to between 1.977 and 1.980 million years ago. Hartstone-Rose and colleagues described the remains as a newly discovered species of fox, which they named skinneri after the African mammalogist John Skinner.

Tasbacka is an extinct genus of sea turtle containing several species.
Dionysopithecidae is an extinct family of fossil catarrhines and the earliest-known and most primitive members of the Pliopithecoidea superfamily, with fossils in Sihong in China dating to 18–17 million years ago for species Dionysopithecus shuangouensis and Platodontopithecus jianghuaiensis.















