
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids. In addition to carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, alkaloids may also contain oxygen, sulfur and, more rarely, other elements such as chlorine, bromine, and phosphorus.

Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies. It is mainly used as a pain medication, and is also commonly used recreationally, or to make other illicit opioids. There are numerous methods used to administer morphine: oral; sublingual; via inhalation; injection into a muscle; by injection under the skin; intravenously; injection into the space around the spinal cord; transdermal; or via rectal suppository. It acts directly on the central nervous system (CNS) to induce analgesia and alter perception and emotional response to pain. Physical and psychological dependence and tolerance may develop with repeated administration. It can be taken for both acute pain and chronic pain and is frequently used for pain from myocardial infarction, kidney stones, and during labor. Its maximum effect is reached after about 20 minutes when administered intravenously and 60 minutes when administered by mouth, while the duration of its effect is 3–7 hours. Long-acting formulations of morphine are available as MS-Contin, Kadian, and other brand names as well as generically.

Opium is dried latex obtained from the seed capsules of the opium poppy Papaver somniferum. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid morphine, which is processed chemically to produce heroin and other synthetic opioids for medicinal use and for the illegal drug trade. The latex also contains the closely related opiates codeine and thebaine, and non-analgesic alkaloids such as papaverine and noscapine. The traditional, labor-intensive method of obtaining the latex is to scratch ("score") the immature seed pods (fruits) by hand; the latex leaks out and dries to a sticky yellowish residue that is later scraped off and dehydrated. The word meconium historically referred to related, weaker preparations made from other parts of the opium poppy or different species of poppies.

Thebaine (paramorphine), also known as codeine methyl enol ether, is an opiate alkaloid, its name coming from the Greek Θῆβαι, Thēbai (Thebes), an ancient city in Upper Egypt. A minor constituent of opium, thebaine is chemically similar to both morphine and codeine, but has stimulatory rather than depressant effects. At high doses, it causes convulsions similar to strychnine poisoning. The synthetic enantiomer (+)-thebaine does show analgesic effects apparently mediated through opioid receptors, unlike the inactive natural enantiomer (−)-thebaine. While thebaine is not used therapeutically, it is the main alkaloid extracted from Papaver bracteatum and can be converted industrially into a variety of compounds, including hydrocodone, hydromorphone, oxycodone, oxymorphone, nalbuphine, naloxone, naltrexone, buprenorphine, butorphanol and etorphine.

The term narcotic originally referred medically to any psychoactive compound with numbing or paralyzing properties. In the United States, it has since become associated with opiates and opioids, commonly morphine and heroin, as well as derivatives of many of the compounds found within raw opium latex. The primary three are morphine, codeine, and thebaine.

A poppy is a flowering plant in the subfamily Papaveroideae of the family Papaveraceae. Poppies are herbaceous plants, often grown for their colourful flowers. One species of poppy, Papaver somniferum, is the source of the narcotic drug mixture opium which contains powerful medicinal alkaloids such as morphine and has been used since ancient times as an analgesic and narcotic medicinal and recreational drug. It also produces edible seeds. Following the trench warfare in the poppy fields of Flanders, Belgium during World War I, poppies have become a symbol of remembrance of soldiers who have died during wartime, especially in the UK, Canada, Australia, New Zealand and other Commonwealth realms.

Papaver rhoeas, with common names including common poppy, corn poppy, corn rose, field poppy, Flanders poppy, and red poppy, is an annual herbaceous species of flowering plant in the poppy family Papaveraceae. It is a temperate native with a very wide distribution area, from Africa to temperate and tropical Asia and Europe.

Papaver is a genus of 70–100 species of frost-tolerant annuals, biennials, and perennials native to temperate and cold regions of Eurasia, Africa and North America. It is the type genus of the poppy family, Papaveraceae.

The Papaveraceae are an economically important family of about 42 genera and approximately 775 known species of flowering plants in the order Ranunculales, informally known as the poppy family. The family is cosmopolitan, occurring in temperate and subtropical climates, but almost unknown in the tropics. Most are herbaceous plants, but a few are shrubs and small trees. The family currently includes two groups that have been considered to be separate families: Fumariaceae and Pteridophyllaceae.

Papaver somniferum, commonly known as the opium poppy or breadseed poppy, is a species of flowering plant in the family Papaveraceae. It is the species of plant from which both opium and poppy seeds are derived and is also a valuable ornamental plant, grown in gardens. Its native range is probably the eastern Mediterranean, but is now obscured by ancient introductions and cultivation, being naturalized across much of Europe and Asia.

Papaverine is an opium alkaloid antispasmodic drug, used primarily in the treatment of visceral spasms and vasospasms, occasionally in the treatment of erectile dysfunction and acute mesenteric ischemia. While it is found in the opium poppy, papaverine differs in both structure and pharmacological action from the analgesic morphine and its derivatives.

Friedrich Wilhelm Adam Sertürner was a German pharmacist and a pioneer of alkaloid chemistry. He is best known for his discovery of morphine in 1804.

Poppy tea is an herbal tea infusion brewed from poppy straw or seeds of several species of poppy. The species most commonly used for this purpose is Papaver somniferum, which produces opium as a natural defense against predators. In the live flower, opium is released when the surface of the bulb, called the seed pod, is pierced or scraped. For the purpose of the tea, dried pods are more commonly used than the pods of the live flower. The walls of the dried pods contain opiate alkaloids, primarily consisting of morphine.

Drug injection is a method of introducing a drug into the bloodstream via a hollow hypodermic needle, which is pierced through the skin into the body. Intravenous therapy, a form of drug injection, is universally practiced in modernized medical care. As of 2004, there were 13.2 million people worldwide who self-administered injection drugs outside of medical supervision, of which 22% are from developed countries.

Berberine is a quaternary ammonium salt from the protoberberine group of benzylisoquinoline alkaloids found in such plants as Berberis vulgaris (barberry), Berberis aristata, Mahonia aquifolium, Hydrastis canadensis (goldenseal), Xanthorhiza simplicissima (yellowroot), Phellodendron amurense, Coptis chinensis, Tinospora cordifolia, Argemone mexicana, and Eschscholzia californica. Berberine is usually found in the roots, rhizomes, stems, and bark.

Poppy seed is an oilseed obtained from the opium poppy. The tiny, kidney-shaped seeds have been harvested from dried seed pods by various civilizations for thousands of years. It is still widely used in many countries, especially in Central Europe and South Asia, where it is legally grown and sold in shops. The seeds are used whole or ground into meal as an ingredient in many foods – especially in pastry and bread – and they are pressed to yield poppyseed oil.
"Polish" heroin is a crude preparation of heroin made from poppy straw. It is an opiate, used recreationally as a psychoactive drug. Poppy straw, like opium, is harvested from the opium poppy. Polish heroin was used mainly in Central and Eastern Europe prior to the dissolution of the Soviet Union and the end of communist control of the countries of the Warsaw Pact or Eastern Bloc.
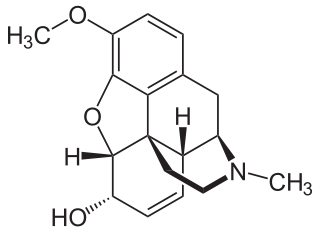
Codeine is an opiate and prodrug of morphine mainly used to treat pain, coughing, and diarrhea. It is also commonly used as a recreational drug. It is found naturally in the sap of the opium poppy, Papaver somniferum. It is typically used to treat mild to moderate degrees of pain. Greater benefit may occur when combined with paracetamol (acetaminophen) or a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) such as aspirin or ibuprofen. Evidence does not support its use for acute cough suppression in children or adults. In Europe, it is not recommended as a cough medicine in those under 12 years of age. It is generally taken by mouth. It typically starts working after half an hour, with maximum effect at two hours. Its effects last for about four to six hours. Codeine exhibits abuse potential similar to other opioid medications.
Legal cultivation of opium for medicinal purposes is carried out in India, only in selected areas, under free licensing conditions. India is the world's largest manufacturer of legal opium for the pharmaceutical industry according to the CIA World Factbook. India is one among 12 countries in world where legal cultivation for medical use is permissible within the ambit of United Nations, Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs 1961. In India legal cultivation is done primarily in Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh. Despite producing poppy for opium production India depends heavily on imports to meet need of Poppy seed for edible purposes and domestic Codeine demand for medical purposes . Opium is heavily imported from its top producing nations like Afghanistan. There is also an account of Opium black marketing in India.

Poppy straw is derived from opium poppies that are harvested when fully mature and dried by mechanical means, minus the ripe poppy seeds. Opium poppy straw today can be one of several different things. It is what remains after the poppy seed harvest, that is, the dried stalks, stem and leaves of poppies grown for their seeds. The dried leaves and stalks are harvested after the seed pods have been used for traditional opium extraction. The field dried leaves, stalk and seed pod are used in commercial manufacture of morphine or other poppy alkaloid derived drugs, by first processing the material to make poppy straw separating the seeds then making concentrate of poppy straw, where no extraction using traditional methods of latex extraction has been made. The straw was originally considered an agricultural by-product of the mechanised poppy seed harvest, which was primarily grown for its edible and oil-producing seed. This changed in 1927 when János Kabay developed a chemical process to extract morphine from the crushed capsule. Concentrated poppy straw consisting mainly of the crushed capsule without the seeds soon became a valuable source of morphine. Today, concentrate of poppy straw is a major source of many opiates and other alkaloids. It is the source of 90% of the world supply of legal morphine and in some countries it also is a source of illegal morphine, which could be processed into illegal heroin.

















