
Horseshoe bats are bats in the family Rhinolophidae. In addition to the single living genus, Rhinolophus, which has about 106 species, the extinct genus Palaeonycteris has been recognized. Horseshoe bats are closely related to the Old World leaf-nosed bats, family Hipposideridae, which have sometimes been included in Rhinolophidae. The horseshoe bats are divided into six subgenera and many species groups. The most recent common ancestor of all horseshoe bats lived 34–40 million years ago, though it is unclear where the geographic roots of the family are, and attempts to determine its biogeography have been indecisive. Their taxonomy is complex, as genetic evidence shows the likely existence of many cryptic species, as well as species recognized as distinct that may have little genetic divergence from previously recognized taxa. They are found in the Old World, mostly in tropical or subtropical areas, including Africa, Asia, Europe, and Oceania.

Natterer's bat is a European vespertilionid bat with pale wings. It has brown fur tending to greyish-white on its underside. It is found across most of the continent of Europe, parts of the Near East and North Africa. It feeds on insects and other invertebrates which it catches on the wing or pursues on the ground.

The greater horseshoe bat is an insectivorous bat of the genus Rhinolophus. Its distribution covers Europe, Northern Africa, Central Asia and Eastern Asia. It is the largest of the horseshoe bats in Europe and is thus easily distinguished from other species. The species is sedentary, typically travelling up to 30 kilometres (19 mi) between the winter and summer roosts, with the longest recorded movement being 180 km (110 mi). The frequencies used by this bat species for echolocation lie between 69–83 kHz, have most energy at 81 kHz and have an average duration of 37.4 ms.

The lesser horseshoe bat is a type of small European and North African insectivorous bat, related to its larger cousin, the greater horseshoe bat. As with all horseshoe bats, the species gets its name from its distinctive horseshoe-shaped noseleaf.

The greater mouse-eared bat is a European species of bat in the family Vespertilionidae.

Sundevall's roundleaf bat, also called Sundevall's leaf-nosed bat, is a species of bat in the family Hipposideridae.

The lesser woolly horseshoe bat, also called Beddome's horseshoe bat, is a species of bat in the family Rhinolophidae. It is found in India and Sri Lanka. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests, caves, and urban areas.

The Cape horseshoe bat is a species of bat in the family Rhinolophidae. It is endemic to South Africa, and is potentially threatened by habitat loss and disturbance of its roosting sites, although it is present in large enough numbers to be considered of least concern by the IUCN.

The Andaman horseshoe bat is a species of bat in the family Rhinolophidae. It is endemic to the Andaman Islands. During the day, it roosts in caves, but may also choose tree hollows.

The Mediterranean horseshoe bat is a species of insectivorous bat in the family Rhinolophidae. It is found in the Mediterranean region and Balkan peninsula, as well as parts of Italy.
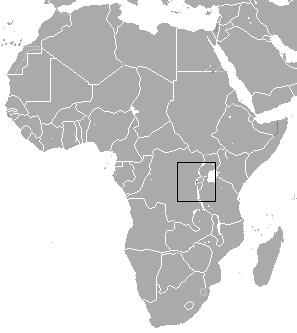
Rhinolophus hilli, Hill's horseshoe bat, is a species of bat in the family Rhinolophidae. It is endemic to Rwanda. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist montane forests, caves, and subterranean habitats. In 2013, Bat Conservation International listed this species as one of the 35 species of its worldwide priority list of conservation. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Blyth's horseshoe bat is a species of bat in the family Rhinolophidae. It is found across southern Asia from Afghanistan to Vietnam. The species can be identified from its pointed, bifid sella.
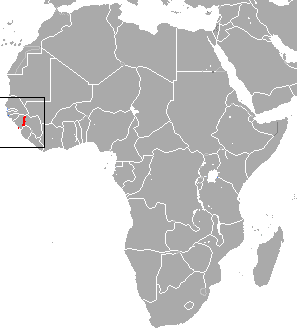
Maclaud's horseshoe bat is a species of bat in the family Rhinolophidae. It is endemic to Guinea. Its natural habitats are moist savanna, caves and other subterranean habitats. It is one of five African microbat species to be listed as endangered by the IUCN. In 2013, Bat Conservation International listed this species as one of the 35 species of its worldwide priority list of conservation. It is threatened by habitat loss.

The smaller horseshoe bat is a species of bat in the family Rhinolophidae. It is found in Australia and Papua New Guinea.
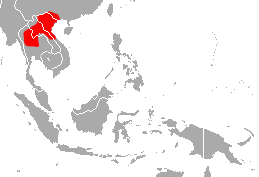
Bourret's horseshoe bat is a species of horseshoe bat native to Southeast Asia. The name "paradoxolophus" is derived from the Greek words paradoxos, meaning "contrary to expectation", and lophos, meaning "crest". This name refers to the bat's difference in nose-leaf morphology compared to other Rhinolophus species. There are no recognised subspecies.
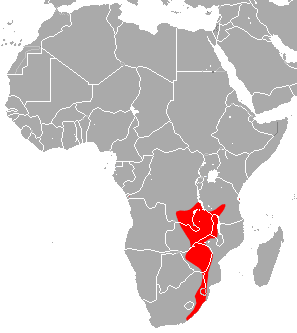
Swinny's horseshoe bat is a species of bat in the family Rhinolophidae. In English, R. swinnyi is commonly referred to as Swinny's horseshoe bat. In Afrikaans, it is commonly referred to as Swinny se saalneusvlermuis. This species belongs to the African clade. R. swinnyi was discovered by an African collector H. H. Swinny. They have been recorded in Angola, Republic of the Congo, Mozambique, South Africa, Tanzania, Zambia, Zimbabwe, and Malawi.

Orlova Chuka is a cave situated in the Danubian Plain, north-eastern Bulgaria. With a total length of 13,437 m, Orlova Chuka is the second longest cave in the country after Duhlata. The cave was discovered in 1941 and opened for tourists in 1957. Orlova Chuka is home to 14 species of bats.

A maternity colony refers to a temporary association of reproductive female bats for giving birth to, nursing, and weaning their pups. The colonies are initiated by pregnant bats. After giving birth, the colony consists of the lactating females and their offspring. After weaning, juveniles will leave the maternity colony, and the colony itself will break apart. The size of a maternity colony is highly variable by species, with some species forming colonies consisting of ten or fewer individuals, while the largest maternity colony in the world in Bracken Cave is estimated to have over 15 million bats.
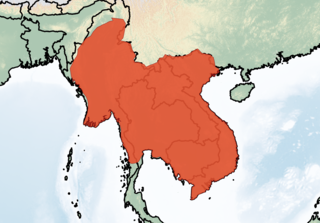
Rhinolophus microglobosus is a species of horseshoe bat found in Southeast Asia.
The Yaeyama little horseshoe bat is a species of bat in the family Rhinolophidae that is endemic to the Yaeyama Islands of Japan.




















