The term hake refers to fish in the:

The Merlucciidae, commonly called merluccid hakes, are a family of cod-like fish, including most hakes. They are native to cold water in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, and typically are found at depths greater than 50 m (160 ft) in subtropical, temperate, sub-Arctic or sub-Antarctic regions.

The haddock is a saltwater ray-finned fish from the family Gadidae, the true cods. It is the only species in the monotypic genus Melanogrammus. It is found in the North Atlantic Ocean and associated seas, where it is an important species for fisheries, especially in northern Europe, where it is marketed fresh, frozen and smoked; smoked varieties include the Finnan haddie and the Arbroath smokie.
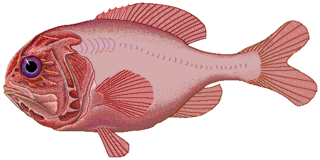
The orange roughy, also known as the red roughy, slimehead and deep sea perch, is a relatively large deep-sea fish belonging to the slimehead family (Trachichthyidae). The UK Marine Conservation Society has categorized orange roughy as "vulnerable to exploitation". It is found in 3 to 9 °C, deep waters of the Western Pacific Ocean, eastern Atlantic Ocean, Indo-Pacific, and in the eastern Pacific off Chile. The orange roughy is notable for its extraordinary lifespan, attaining over 200 years. It is important to commercial deep-trawl fisheries. The fish is a bright, brick-red color, fading to a yellowish-orange after death.
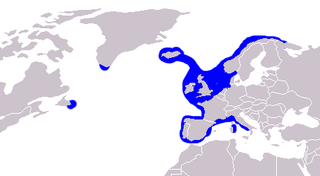
The common ling, also known as the white ling or simply the ling, is a large member of the family Lotidae, a group of cod-like fishes. It resembles the related rocklings, but it is much larger and has a single barbel. This species is unrelated to the pink ling, Genypterus blacodes, from the Southern Hemisphere. The common ling is found in the northern Atlantic, mainly off Europe, and into the Mediterranean Basin. It is an important quarry species for fisheries, especially in the northeastern Atlantic, although some doubts exist as to the sustainability of the fisheries. As an edible species, it is eaten fresh, frozen, or dried, but also preserved in lye, while the roe is a delicacy in Spain.

The North Pacific hake, Pacific hake, Pacific whiting, or jack salmon is a ray-finned fish in the genus Merluccius, found in the northeast Pacific Ocean from northern Vancouver Island to the northern part of the Gulf of California. It is a silver-gray fish with black speckling, growing to a length of 90 cm (3 ft). It is a migratory offshore fish and undergoes a daily vertical migration from the surface to the seabed at depths down to about 1,000 m (3,300 ft). It is the object of an important commercial fishery off the West Coast of the United States, and annual quotas are used to prevent overfishing.

The southern blue whiting is a codfish of the genus Micromesistius, found in the southern oceans with temperatures between 3 and 7 °C, at depths of 50 to 900 m. Its length is commonly between 30 and 60 cm, with a maximum length of 90 cm. Maximum weight is at least 1350 g.

The silver hake, Atlantic hake, or New England hake is a merluccid hake of the genus Merluccius, found in the northwest Atlantic Ocean. It is highly predatory and typically feeds on fish and crustaceans.

Merluccius is a genus of merluccid hakes from the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, where mainly found relatively deep.

Merluccius merluccius, the European hake, is a merluccid hake of the genus Merluccius. Other vernacular names include Cornish salmon and herring hake. It is a predatory species which was often netted alongside one of its favoured prey, the Atlantic herring, thus the latter common name. It is found in the eastern Atlantic from the Norway and Iceland south to Mauritania and into the Mediterranean Sea. It is an important species in European fisheries and is heavily exploited with some populations thought to be being fished unsustainably.

Merluccius capensis is a ray-finned fish in the genus Merluccius, found in the south-eastern Atlantic Ocean, along the coast of South Africa. It is a long, lean fish with a large head, similar in appearance to the European hake and the deep-water Cape hake. By day, it lives close to the bottom on the continental shelf and upper slope at depths not usually exceeding 400 m (1,300 ft); it makes a large, daily vertical migration rising at night to feed in the nectonic zone, and it also migrates southwards in spring and northwards in autumn. It is an important commercial fish species in southern Africa.
Merluccius paradoxus, the deep-water Cape hake, is a merluccid hake of the genus Merluccius, found in the south-eastern Atlantic Ocean, along the coast of Southern Africa, south of Angola. Its range extends in decreasing abundance around the southern coast of Africa and into the Indian Ocean, but it is at its most plentiful in the cold, nutrient-rich fishing grounds of the Benguela Current.
The Panama hake, also known as the dwarf hake, is a merluccid hake found off the west coast of the Americas from Del Mar, California, to Ensenada de Tumaco, Colombia.

Trachyrincus scabrus, the roughsnout grenadier or Mediterranean longsnout grenadier, is a species of bathydemersal marine fish from the subfamily Trachyrincinae, part of the family Macrouridae. It is found in the eastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean.
Merluccius hernandezi, the Cortez hake, is a species of fish from the family Merlucciidae, the true hakes. It is endemic to the Gulf of California where it can be found in the epipelagic and mesopelagic zones over the continental shelf, open sea, and sea mounts, to a depth of around 300m. It is a small species which has been referred to as a "dwarf hake" and is of little interest to fisheries, other than small scale local fisheries. It was described in 1985 and small hake in the Gulf of California were previously considered to be Panama hakes. This species differs from the Panama hake in that in juveniles the caudal fin has a central lobe and is truncate in adults, whereas the caudal fin is emarginate in the Panama hake, its pectoral fin projects well beyond the anus in but does not do so in the Panama hake.
Merluccius patagonicus, the Patagonian hake, is a species of fish from the family Merlucciidae from the western South Atlantic which was described in 2003. However some authorities consider the distinguishing features of M. patagonicus to be within the range of variability for M. hubbsi and that M. patagonicus is therefore a synonym of M. hubbsi.
Merluccius polli, the Benguela hake, is a species of fish from the family Merlucciidae, the true hakes. It is found in the tropical waters of the eastern Atlantic Ocean off the west coast of Africa.
Merluccius senegalensis, the Senegalese hake, is a species of fish from the family Merlucciidae, the true hakes. It is found in the sub tropical waters of the eastern Atlantic Ocean off the north western coast of Africa.
Merluccius tasmanicus is a species of fish from the family Merlucciidae from the western Pacific and south-eastern Pacific and south-western Atlantic which was described in 2006. It is however considered to be synonymous with Merluccius australis by some authorities.
Lyconus brachycolus is a species of hake fish in the family Merlucciidae.









