| Part of a series on |
| Puzzles |
|---|
 |
A metapuzzle, also known as a meta-puzzle or meta, is a puzzle that uses the solutions to a set of puzzles to create or provide data for a final puzzle. [1]
| Part of a series on |
| Puzzles |
|---|
 |
A metapuzzle, also known as a meta-puzzle or meta, is a puzzle that uses the solutions to a set of puzzles to create or provide data for a final puzzle. [1]
This section needs additional citations for verification .(July 2022) |
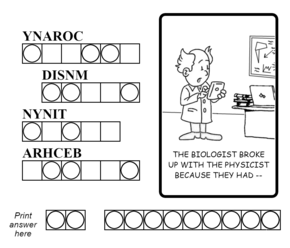
Game designer Cliff Johnson defines a meta-puzzle as "a collection of puzzles that, when solved, each give a piece of a master puzzle." [2] A metapuzzle is a puzzle that unites several puzzles that feed into it. For example, five puzzles that had the answers BLACK, HAMMER, FROST, KNIFE, and UNION would lead to the metapuzzle answer JACK, which combines with all of those words to make new words and phrases.
A "meta-meta" can exist in larger sets of puzzles, uniting several metapuzzles. So if that metapuzzle answer JACK was alongside three metapuzzles with the answers TEN, QUEEN, and ACE, the meta-meta answer would be KING, the remaining card in an ace high straight.
Metapuzzles are frequently found in puzzle hunts.
The structure of a metapuzzle often makes it possible to guess, with a greater or lesser degree of certainty, the solutions to the puzzles that feed into it without solving them. This technique is called backsolving. For instance, in the above example, after solving the puzzles whose answers were BLACK, HAMMER, FROST, and KNIFE, and the metapuzzle answer JACK, a backsolver might, instead of solving the fifth puzzle, correctly guess UNION as its answer simply based on the knowledge that it must form a word or phrase with JACK. Backsolving is not infallible; the same backsolver might incorrectly guess SPRING-HEELED as the answer just as easily as correctly guessing UNION.
In a rally metapuzzle, individual puzzles are checkpoints in a race or maze; solving the puzzle unlocks the location of the next puzzle. [1]
In a compilation metapuzzle, the answers to puzzles unite as components used to solve a final puzzle. This form of puzzle is particularly inclined towards backsolving, where some of the component puzzle answers are used to solve the final metapuzzle, and the metapuzzle's solution is used to solve the remaining component puzzles. [1]
A cascade is a metapuzzle where the solution to one puzzle becomes the basis for the next puzzle. For instance, a cryptogram might produce clues for a crossword puzzle, and the crossword's solution might form a word search. [1]
Crossword metapuzzles are crosswords that, when correctly solved, provide the basis for a second puzzle. Crosswords with metapuzzle components started to grow in popularity in the 2010s, after Matt Gaffney began making crossword metapuzzles in 2008. [3]

A crossword is a word game consisting of a grid of black and white squares, into which solvers enter words or phrases ("entries") crossing each other horizontally ("across") and vertically ("down") according to a set of clues. Each white square is typically filled with one letter, while the black squares are used to separate entries. The first white square in each entry is typically numbered to correspond to its clue.

A cryptic crossword is a crossword puzzle in which each clue is a word puzzle. Cryptic crosswords are particularly popular in the United Kingdom, where they originated, as well as Ireland, Israel, the Netherlands, and in several Commonwealth nations, including Australia, Canada, India, Kenya, Malta, New Zealand, and South Africa. Compilers of cryptic crosswords are commonly called "setters" in the UK and "constructors" in the US. Particularly in the UK, a distinction may be made between cryptics and "quick" crosswords, and sometimes two sets of clues are given for a single puzzle grid.
A puzzle is a game, problem, or toy that tests a person's ingenuity or knowledge. In a puzzle, the solver is expected to put pieces together in a logical way, in order to arrive at the correct or fun solution of the puzzle. There are different genres of puzzles, such as crossword puzzles, word-search puzzles, number puzzles, relational puzzles, and logic puzzles. The academic study of puzzles is called enigmatology.
The MIT Mystery Hunt is an annual puzzlehunt competition at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge, Massachusetts. It is one of the oldest and most complex puzzlehunts in the world and attracts roughly 120 teams and 3,000 contestants annually in teams of 5 to 150 people. It has inspired similar competitions at Microsoft, Stanford University, Melbourne University, University of South Carolina, University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign and University of Aveiro (Portugal) as well as in the Seattle, San Francisco, Miami, Washington, D.C., Indianapolis and Columbus, Ohio metropolitan areas. Because the puzzle solutions often require knowledge of esoteric and eclectic topics, the hunt is sometimes used to exemplify popular stereotypes of MIT students.

William F. Shortz is an American puzzle creator and editor who is the crossword puzzle editor for The New York Times. He graduated from Indiana University with a degree in the invented field of enigmatology. After starting his career at Penny Press and Games magazine, he was hired by The New York Times in 1993. Shortz's American Crossword Puzzle Tournament is the country's oldest and largest crossword tournament.

Kakuro or Kakkuro or Kakoro is a kind of logic puzzle that is often referred to as a mathematical transliteration of the crossword. Kakuro puzzles are regular features in many math-and-logic puzzle publications across the world. In 1966, Canadian Jacob E. Funk, an employee of Dell Magazines, came up with the original English name Cross Sums and other names such as Cross Addition have also been used, but the Japanese name Kakuro, abbreviation of Japanese kasan kurosu, seems to have gained general acceptance and the puzzles appear to be titled this way now in most publications. The popularity of Kakuro in Japan is immense, second only to Sudoku among Nikoli's famed logic-puzzle offerings.

The Cross-Wits is an American syndicated game show which premiered on December 15, 1975, and lasted for five seasons until its cancellation on September 12, 1980. The show was hosted by Jack Clark, with Jerri Fiala as hostess. Announcing duties were handled by John Harlan, Jay Stewart, and Jerry Bishop. The show was produced by Ralph Edwards Productions and distributed by Metromedia Producers Corporation.

Masquerade is a picture book, written and illustrated by Kit Williams and published in August 1979, that sparked a treasure hunt by including concealed clues to the location of a jewelled golden hare that had been created and hidden somewhere in Britain by Williams. The book became the inspiration for a genre of books known today as armchair treasure hunts.

At The Carnival is a puzzle video game by Cliff Johnson published in 1989 by Miles Computing.
Games World of Puzzles is an American games and puzzle magazine. Originally the merger of two other puzzle magazines spun off from its parent publication Games magazine in the early 1990s, Games World of Puzzles was reunited with Games in October 2014.

A puzzle hunt is an event where teams compete to solve a series of puzzles, many of which are tied together via metapuzzles. Puzzlehunt puzzles are usually not accompanied by direct instructions for how to solve them; figuring out the necessary approach is part of the puzzle. These hunts may be hosted at a particular location, in multiple locations, or via the internet.
The Microsoft Puzzlehunt is a quasi-annual Microsoft tradition started in 1999. It is a puzzlehunt in the same vein as the MIT Mystery Hunt and has some similarity to The Game. The hunt is a team puzzle competition which challenges each team to solve a large number of original puzzles of all different kinds. The answers, when used in conjunction with the metapuzzle, lead to a hidden treasure concealed somewhere on the Microsoft campus. Teams spend the weekend solving original and unique puzzles, usually created by the team that won the last hunt. Puzzles may be anything from traditional puzzles like crosswords, word searches, cryptograms, jigsaw puzzles, word play and logic problems to wandering around campus to find landmarks or puzzles that have to be solved on location. Microsoft Puzzlehunt was founded by Bruce Leban, along with Roy Leban and Gordon Dow.
The Maze of Games is a puzzlehunt and interactive multimedia novel. It started in 1995 as one of America's largest annual puzzlehunts and an offshoot of LIVE/WIRE, held at the Gen Con and Origins gaming conventions before later being adapted into a novel. The Maze of Games has been the largest event at one or both of those conventions every year since. It was created by game designers Mark Gottlieb, Mike Selinker, and Teeuwynn Woodruff. The event uses puzzle placards to lead attendees in a maze throughout the convention, and uses meta-puzzles to unite the puzzles into a final answer. The event is designed so that the thousands of attendees can all play at once. $2500 worth of electrical tape was used to create the titular "Maze" on the convention show floor.

An acrostic is a type of word puzzle, related somewhat to crossword puzzles, that uses an acrostic form. It typically consists of two parts. The first part is a set of lettered clues, each of which has numbered blanks representing the letters of the answer. The second part is a long series of numbered blanks and spaces, representing a quotation or other text, into which the answers for the clues fit. In some forms of the puzzle, the first letters of each correct clue answer, read in order from clue A on down the list, will spell out the author of the quote and the title of the work it is taken from; this can be used as an additional solving aid.

All Clued Up is a British game show based on the American version entitled The $1,000,000 Chance of a Lifetime. It aired on ITV from 16 April 1988 to 30 August 1991 and was hosted by David Hamilton.
The New York Times Crossword is a daily American-style crossword puzzle published in The New York Times as part of The New York Times Games, online on the newspaper's website, syndicated to more than 300 other newspapers and journals, and on mobile apps.

Merv Griffin's Crosswords is an American game show based on crossword puzzles. The show was created by its namesake, Merv Griffin, who died shortly after beginning production on the series. Ty Treadway was the host, and Edd Hall was the announcer.

Club Bing was a group of online word games by Microsoft that lasted from April 2007 to May 2012. Players who completed or partially completed a game earned "tickets" that could be exchanged for Microsoft or other products. The site was credited with a significant increase in market share for the search engine Bing.

A Printer's Devilry is a form of cryptic crossword puzzle, first invented by Afrit in 1937. A Printer's Devilry puzzle does not follow the standard Ximenean rules of crossword setting, since the clues do not define the answers. Instead, each clue consists of a sentence from which a string of letters has been removed and, where necessary, the punctuation and word breaks in the clue rearranged to form a new more-or-less grammatical sentence. The challenge to the solver is to find the missing letters, which will spell out a word or phrase that should be entered into the grid.
Wordle is a web-based word game created and developed by Welsh software engineer Josh Wardle. Players have six attempts to guess a five-letter word, with feedback given for each guess in the form of colored tiles indicating when letters match or occupy the correct position. The mechanics are similar to the 1955 pen-and-paper game Jotto and the television game show franchise Lingo. Wordle has a single daily solution, with all players attempting to guess the same word.