
The Eurotiales are an order of sac fungi, also known as the green and blue molds. It was circumscribed in 1980.

The Hypocreales are an order of fungi within the class Sordariomycetes. In 2008, it was estimated that it contained some 237 genera, and 2647 species in seven families. Since then, a considerable number of further taxa have been identified, including an additional family, the Stachybotryaceae. Wijayawardene et al. in 2020 added more families and genera to the order. According to the Catalog of Life, As of April 2021 the Hypocreales contains 6 families, 137 genera, and 1411 species. Hyde et al. (2020a) listed 14 families under Hypocreales, while, Wijayawardene et al. (2022) accepted 15 families in the order, where Cylindriaceae was additionally added. Earlier, Hyde et al. (2020a) had placed Cylindriaceae in class Xylariomycetidae. Samarakoon et al. (2022) agreed. Hence, Cylindriaceae should have been excluded from Hypocreales and placed in Xylariomycetidae. Xiao et al. (2022) recently introduced a new family Polycephalomycetaceae to Hypocreales.

The Hypocreaceae are a family within the class Sordariomycetes. Species are recognisable by their brightly coloured perithecial ascomata, typically yellow, orange or red. The family was proposed by Giuseppe De Notaris in 1844. According to the Dictionary of the Fungi, the family has 22 genera and 454 species. In 2020, it was re-analysed and determined to have only 17 genera and about 658 species.

The Nectriaceae comprise a family of fungi in the order Hypocreales. It was circumscribed by brothers Charles and Louis René Tulasne in 1865. In 2020, an Outline of fungi was produced and listed 70 genera and about 1,336 species.
Chrysosporium is a genus of hyaline hyphomycetes fungi in the family Onygenaceae.

Hypocreomycetidae is a subclass of sac fungi.

Phyllachoraceae is a family of sac fungi.

The Microascales are an order of fungi in the class Sordariomycetes, subclass Hypocreomycetidae. This is a relatively small order of mostly saprobic fungi that live in soil, rotting vegetation and dung. Some species are plant pathogens, such as Ceratocystis fimbriata, transmitted by beetles to living trees and causing cacao wilt and many other economically important diseases. Species in the genus Pseudallescheria are pathogenic to humans The order was circumscribed in 1980. Wijayawardene et al. in 2020 added more families and genera to the order.
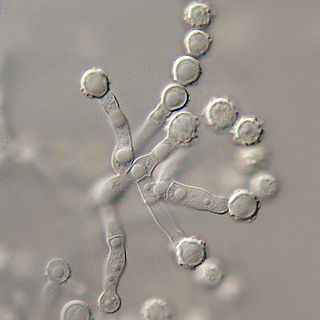
Microascus is a genus of fungi in the family Microascaceae.

The Bionectriaceae are a family of fungi in the order Hypocreales. A 2008 estimate places 35 genera and 281 species in the family. Species in the family tend to grow on plant material, including woody debris, while some species associate with algae, bryophytes, or other fungi.
The Cephalothecaceae are a family of fungi in the class Sordariomycetes. The family was circumscribed in 1917 by Austrian naturalist Franz Xaver Rudolf von Höhnel. Species in this family are saprobic, often growing on rotten wood or on other fungi. They are known to be distributed in northern temperate regions. The family was placed in a monotypic class CephalothecalesHubka & Réblová in Index Fungorum 424: 1 (2019).
Cryptodiscus is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Stictidaceae.

The Onygenaceae are a family of fungi in the Ascomycota, class Eurotiomycetes.
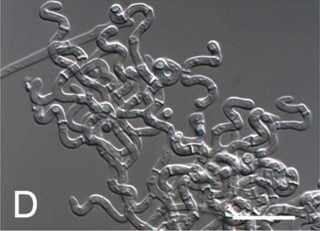
Arachnomyces is a genus of cleistothecial ascomycete fungi described in 1902, of which the anamorph (asexual) stage is the genus Onychocola. Although morphologically similar to members of other families, the fungus now belongs to its own monotypic family Arachnomycetaceae, which is the only family in the monotypic order Arachnomycetales.

The Apiosporaceae are a family of fungi in the Ascomycota. It was placed in the order Amphisphaeriales in 2020.
The Ceratostomataceae are a family of fungi in the phylum Ascomycota, class Sordariomycetes, subclass Hypocreomycetidae and order Coronophorales.
Scopinella is a genus of fungi in the Coronophorales order. The relationship of this taxon to other taxa within the order was unknown, It has been placed into the family of Ceratostomataceae.

Cordana is an ascomycete fungus genus. In 2020, it was placed within the monotypic family of Cordanaceae, and within the order Coniochaetales.

Coniochaetaceae is a fungal family in the order Coniochaetales. The family was updated in 2020.
Brachysporium is a genus of anamorphic fungi in the family Trichosphaeriaceae. It has 25 species. The genus was circumscribed in 1886 by Pier Andrea Saccardo, with Brachysporium obovatum assigned as the type species. The genus Cryptadelphia, circumscribed in 2004 to contain six presumed teleomorphs of Brachysporium, has since been placed in synonymy with Brachysporium.














