The derivative is a fundamental tool of calculus that quantifies the sensitivity of change of a function's output with respect to its input. The derivative of a function of a single variable at a chosen input value, when it exists, is the slope of the tangent line to the graph of the function at that point. The tangent line is the best linear approximation of the function near that input value. For this reason, the derivative is often described as the instantaneous rate of change, the ratio of the instantaneous change in the dependent variable to that of the independent variable. The process of finding a derivative is called differentiation.
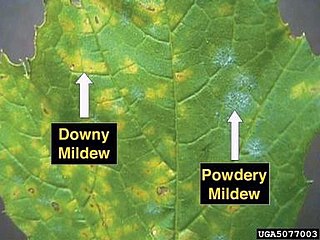
Powdery mildew is a fungal disease that affects a wide range of plants. Powdery mildew diseases are caused by many different species of ascomycete fungi in the order Erysiphales. Powdery mildew is one of the easier plant diseases to identify, as its symptoms are quite distinctive. Infected plants display white powdery spots on the leaves and stems. The lower leaves are the most affected, but the mildew can appear on any above-ground part of the plant. As the disease progresses, the spots get larger and denser as large numbers of asexual spores are formed, and the mildew may spread up and down the length of the plant.

Oidium is a genus of Deuteromycetes, where traditionally most anamorphs of the order Erysiphales are included. Most of them are plant pathogens causing different forms of powdery mildew, for example:

Erysiphales are an order of ascomycete fungi. The order contains one family, Erysiphaceae. Many of them cause plant diseases called powdery mildew.
Microsphaera coryli is a plant pathogen.
Microsphaera ellisii is a plant pathogen.
Microsphaera euphorbiae is a plant pathogen.
Microsphaera hommae is a plant pathogen.

Microsphaera penicillata is a plant pathogen that causes powdery mildew on sycamore.
Microsphaera vaccinii is a plant pathogen.
Microsphaera verruculosa is a plant pathogen.
Microsphaera diffusa is a plant pathogen. M. diffusa infections on soybeans are referred to as powdery mildew.

Erysiphe is a genus of fungi in the family Erysiphaceae. Many of the species in this genus are plant pathogens which cause powdery mildew.

Blueberry is a widely distributed and widespread group of perennial flowering plant with blue or purple berries. They are classified in the section Cyanococcus within the genus Vaccinium. Vaccinium also includes cranberries, bilberries, huckleberries and Madeira blueberries. Commercial blueberries—both wild (lowbush) and cultivated (highbush)—are all native to North America. The highbush varieties were introduced into Europe during the 1930s.

Erysiphe alphitoides is a species of fungus which causes powdery mildew on oak trees.
The Nakamurella is a genus of bacteria.
Elliot Calvin Howe was an American botanist and a member of the Torrey Botanical Club. Most notably, he discovered several species of fungi throughout his life, including Tricholoma Peckii, Hygrophorus Peckianus, Puccinia curtipes, P. Peckianus, Microsphaera menispermi, M. platani and M. symphoricarpi, and two were named after him to commemorate his contributions to the field, Stropharia Howeanum Pk. and Hypoxylon Howeanum Pk.
Powdery mildew of lilac, or Erysiphe syringae is a fungal pathogen of lilacs.
Erysiphe azerbaijanica is a species of powdery mildew in the family Erysiphaceae. It is found in Azerbaijan, where it grows on the leaves of sweet chestnut trees.