
Mentha is a genus of plants in the family Lamiaceae. The exact distinction between species is unclear; it is estimated that 13 to 24 species exist. Hybridization occurs naturally where some species' ranges overlap. Many hybrids and cultivars are known.

Peppermint is a hybrid species of mint, a cross between watermint and spearmint. Indigenous to Europe and the Middle East, the plant is now widely spread and cultivated in many regions of the world. It is occasionally found in the wild with its parent species.

Menthol is an organic compound, more specifically a monoterpenoid, made synthetically or obtained from the oils of corn mint, peppermint, or other mints. It is a waxy, clear or white crystalline substance, which is solid at room temperature and melts slightly above.
In chemistry, acetylation is an organic esterification reaction with acetic acid. It introduces an acetyl group into a chemical compound. Such compounds are termed acetate esters or simply acetates. Deacetylation is the opposite reaction, the removal of an acetyl group from a chemical compound.

Pulegone is a naturally occurring organic compound obtained from the essential oils of a variety of plants such as Nepeta cataria (catnip), Mentha piperita, and pennyroyal. It is classified as a monoterpene.
Acetyl-CoA synthetase (ACS) or Acetate—CoA ligase is an enzyme involved in metabolism of acetate. It is in the ligase class of enzymes, meaning that it catalyzes the formation of a new chemical bond between two large molecules.
In enzymology, an isopiperitenol dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.223) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
A (−)-menthol dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.207) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a (+)-neomenthol dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.208) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a (S)-limonene 3-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.47) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a (S)-limonene 6-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.48) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a (S)-limonene 7-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.49) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an isopiperitenone Delta-isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme (R)-limonene synthase (EC 4.2.3.20) catalyzes the reversible chemical reaction

In enzymology, a serine O-acetyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a taxadien-5alpha-ol O-acetyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
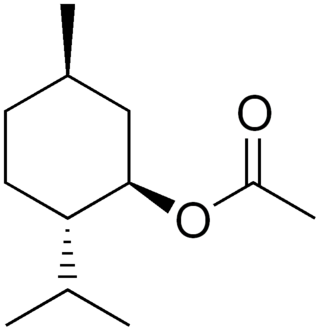
Menthyl acetate is a natural monoterpene which contributes to the smell and flavor of peppermint. It is the acetate ester of menthol. Menthyl acetate constitutes 3–5% of the volatile oil of mentha piperita, contributing to its smell and flavour.
(-)-Isopiperitenone reductase (EC 1.3.1.82) is an enzyme with systematic name (+)-cis-isopulegone:NADP+ oxidoreductase. It catalyses the following chemical reaction:
(Z)-3-hexen-1-ol acetyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name acetyl-CoA:(3Z)-hex-3-en-1-ol acetyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
(–)-α-Pinene synthase is an enzyme with systematic name geranyl-diphosphate diphosphate-lyase [cyclizing, (–)-α-pinene-forming]. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction






