
Quincy is a city in Norfolk County, Massachusetts, United States. It is the largest city in the county. Quincy is part of the Greater Boston area as one of Boston's immediate southern suburbs. Its population in 2020 was 101,636, making it the seventh-largest city in the state. Known as the “City of Presidents,” Quincy is the birthplace of two U.S. presidents — John Adams and his son John Quincy Adams — as well as John Hancock, the first signer of the Declaration of Independence and the first and third governor of Massachusetts.

The Wampanoag, also rendered Wôpanâak, are a Native American people of the Northeastern Woodlands currently based in southeastern Massachusetts and formerly parts of eastern Rhode Island. Their historical territory includes the islands of Martha's Vineyard and Nantucket.

The Pokanoket are a group of Wampanoag people and the village governed by Massasoit, chief sachem of the Wampanoag people.
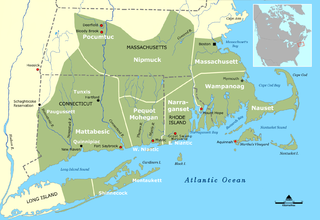
The Massachusett language is an Algonquian language of the Algic language family that was formerly spoken by several peoples of eastern coastal and southeastern Massachusetts. In its revived form, it is spoken in four Wampanoag communities. The language is also known as Natick or Wôpanâak (Wampanoag), and historically as Pokanoket, Indian or Nonantum.

The Massachusett were a Native American tribe from the region in and around present-day Greater Boston in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. The name comes from the Massachusett language term for "At the Great Hill," referring to the Blue Hills overlooking Boston Harbor from the south.

Mattapan is a neighborhood in Boston, Massachusetts, United States. Mattapan is the original Native American name for the Dorchester area, possibly meaning "a place to sit." At the 2010 census, it had a population of 36,480, with the majority of its population immigrants.
Praying Indian is a 17th-century term referring to Native Americans of New England, New York, Ontario, and Quebec who converted to Christianity either voluntarily or involuntarily. Many groups are referred to by the term, but it is more commonly used for tribes that were organized into villages. The villages were known as praying towns and were established by missionaries such as the Puritan leader John Eliot and Jesuit missionaries who established the St. Regis and Kahnawake and the missions among the Huron in western Ontario.

Wollaston Beach is the largest public beach in the Boston Harbor. The beach is located parallel to Quincy Shore Drive in North Quincy, Massachusetts, which was constructed to provide access to the bay beach for Greater Boston. Wollaston beach expands Quincy Bay forming part of Boston Harbor. The northern end of the beach is the Native American historical site, Moswetuset Hummock which is where the original Moswetuset Sac'hem (Chief) had a tribal council.
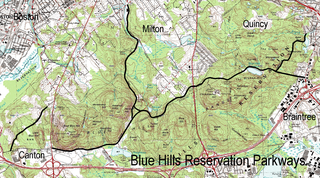
The Blue Hills Reservation Parkways are a network of historic parkways in and around the Blue Hills Reservation, a Massachusetts state park south of Boston, Massachusetts. It consists of six roadways that provide circulation within the park, and that join the park to two connecting parkways, the Blue Hills Parkway and the Furnace Brook Parkway. The roadway network was designed by Charles Eliot in the 1890s, except for Green Street, which was added to the network in the 1940s. The parkways were added to the National Register of Historic Places in 2003.

The Chickatawbut Observation Tower is a historic tower on Chickatawbut Road in Quincy, Massachusetts, in the Blue Hill Reservation, a Massachusetts state park.

Squantum is a neighborhood of Quincy, Massachusetts, connected to the mainland by a causeway that crosses over a wetland area of the bay. Often thought of as a peninsula, Squantum proper is technically a barrier island as it is surrounded on all four sides by water and is only connected to the mainland and Moon Island via causeways. Located in the northernmost portion of the city, Squantum is bordered on the north by Dorchester Bay and Boston Harbor, on the east by Moon Island and Quincy Bay, on the south by Quincy Bay and North Quincy, and on the west by the Marina Bay development. The population of the neighborhood in 2010 according to the United States Census Bureau was 2,365. Squantum has scenic, waterfront views of Boston Harbor and the Boston skyline and has many of Quincy’s most expensive homes. Squantum residents are the wealthiest of any neighborhood in Quincy, according to the 2010 United States Census Bureau, and the home ownership rate is approximately 92%. The neighborhood is further characterized by its tree-lined streets, its "island getaway" feel, close-knit community, and its annual Squantum Fourth of July Parade. As described in a 2020 book, "One road leads in and out of a square mile of land that is a playground for children and a haven for adults." Squantum also has one of the largest Irish populations, on a per capita basis, of any neighborhood in the United States.

Chickatawbut was the sachem, or leader, of a large group of indigenous people known as the Massachusett tribe in what is now eastern Massachusetts, United States, during the initial period of English settlement in the region in the early seventeenth century.

Quincy Shore Reservation is a public recreation area and protected shoreline on Quincy Bay, Boston Harbor, in Quincy, Massachusetts. Its primary attraction is a 2.3-mile-long (3.7 km) beach, accessible along its entire length by Quincy Shore Drive. The largest beach on Boston Harbor, it is known locally as Wollaston Beach, named for the adjacent Wollaston neighborhood.

Ayer is a town in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. Originally part of Groton, it was incorporated February 14, 1871, and became a major commercial railroad junction. The town was home to Camp Stevens, a training camp for Massachusetts volunteers during the American Civil War. Later, Fort Devens was established by the federal government to train New England soldiers for World War I. Fort Devens is a major influence on the area, although it is considerably smaller than when it was first closed in the mid-1990s. The town's population was 8,479 at the 2020 census.

Ponkapoag, also Punkapaug, Punkapoag, Ponkhapoag or Punkapog, is the name of a Native American "praying town" settled in the late 17th century western Blue Hills area of eastern Massachusetts by persons who had accepted Christianity. It was established in 1657, during the colonization of the Atlantic seaboard of the United States by settlers from Britain. This was the name given to the winter residence of the group of Massachusett who lived at the mouth of the Neponset River near Dorchester in the summer, in what colonists called Neponset Mill.

Cutshamekin was a Native American leader, who was a sachem of the Massachusett tribe based along the Neponset River and Great Blue Hill in what is now Dorchester, Massachusetts and Milton, Massachusetts before becoming one of the first leaders of the praying Indian town of Natick, Massachusetts. He is the possible namesake of Jamaica Plain.

Quashaamit was a bilingual Praying Indian sachem or sub-sachem, and teaching minister. His tribal affiliation may have Nipmuc, Massachusett, and/or Wampanoag.
The Massachusett Tribe at Ponkapoag is a cultural heritage group that claims descendancy from the Massachusett people, an Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands.

The Praying Indians of Natick and Ponkapoag is a cultural heritage group that claims descendancy from Praying Indians in Massachusetts, including the Massachusett people, an Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands.
The Praying Indians of Natick were a community of Indigenous Christian converts, known as Praying Indians, in the town of Natick, Massachusetts, one of many Praying Towns. They were also known as Natick Indians.
























