
Shearwaters are medium-sized long-winged seabirds in the petrel family Procellariidae. They have a global marine distribution, but are most common in temperate and cold waters, and are pelagic outside the breeding season.

The sooty shearwater is a medium-large shearwater in the seabird family Procellariidae. In New Zealand, it is also known by its Māori name tītī, and is harvested by Māori people for muttonbird, like its relatives the wedge-tailed shearwater and the Australian short-tailed shearwater.
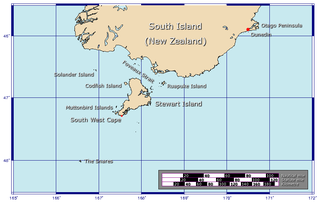
Foveaux Strait is a strait that separates Stewart Island from the South Island of New Zealand. The width of the strait ranges from about 23 to 53 km, and the depth varies between 18 and 46 m. The strait was first charted by an American sealer, Owen Folger Smith. He charted the strait from a whaleboat of the sealing brig Union in 1804.

The short-tailed shearwater or slender-billed shearwater, also called yolla or moonbird, and commonly known as the muttonbird in Australia, is the most abundant seabird species in Australian waters, and is one of the few Australian native birds in which the chicks are commercially harvested. It is a migratory species that breeds mainly on small islands in Bass Strait and Tasmania and migrates to the Northern Hemisphere for the boreal summer.
Muttonbird or mutton bird may refer to species of petrel, especially shearwaters, whose young are harvested for food and other uses before they fledge in Australia and New Zealand. The English term "muttonbird" originally emerged among settlers on Norfolk Island as the strong taste and fattiness of these birds' meat was likened to mutton. The Māori name for the birds, tītī, is also widely used in New Zealand.
The Tītī / Muttonbird Islands are an island group near Stewart Island in the far south of New Zealand. The islands are not permanently inhabited, and are named for the traditional seasonal harvesting ("muttonbirding") of the sooty shearwater by Māori. These birds are known as "muttonbirds" due to their supposedly mutton-like taste.

Steep Island, also known as Steep Head, is a 21.6 ha island in Bass Strait in south-eastern Australia. It is part of Tasmania’s Hunter Island Group and lies between north-west Tasmania and King Island. It was once used for grazing sheep but title has been transferred to the Tasmanian Aboriginal community; with an estimated 250,000 shearwater burrows present, it is principally used for muttonbirding.

The Twin Islets form a close pair of small, steep-sided, granite islands, with a combined area of 5.61 ha, in south-eastern Australia. They are part of Tasmania’s Hogan Group, lying in northern Bass Strait between the Furneaux Group and Wilsons Promontory in Victoria.

East Island is a granite island, with an area of 12.42 ha, in south-eastern Australia. It is part of Tasmania’s Hogan Group, lying in northern Bass Strait between the Furneaux Group and Wilsons Promontory in Victoria.
Cone Islet is a small granite island, with an area of 4.82 ha, in south-eastern Australia. It is part of Tasmania’s Curtis Group, lying in northern Bass Strait between the Furneaux Group and Wilsons Promontory in Victoria.

The Forsyth Island, part of the Passage Group within the Furneaux Group, is a 167-hectare (410-acre) granite island, located in Bass Strait south of Cape Barren Island, in Tasmania, in south-eastern Australia. With the Passage and Gull islands, the Forsyth Island forms part of the Forsyth, Passage and Gull Islands Important Bird Area (IBA), identified as such by BirdLife International because it supports over 1% of the world populations of little penguins and black-faced cormorants.

The Great Dog Island, also known as Big Dog Island, and part of the Great Dog Group within the Furneaux Group, is a 354-hectare (870-acre) granite island, located in Bass Strait, lying south of the Flinders Island and north of the Cape Barren Island, in Tasmania, in south-eastern Australia.

The Babel Island, part of the Babel Group within the Furneaux Group, is a 440-hectare (1,100-acre) granite island, located in Bass Strait, lying off the east coast of Flinders Island, Tasmania, south of Victoria, Australia. The privately owned island was named by Matthew Flinders from the noises made by the seabirds there.

Inner Sister Island, part of the Sister Islands Conservation Area, is a granite and dolerite island, with an area of 748 hectares (2.89 sq mi), located in Bass Strait, Tasmania, Australia.

Outer Sister Island, part of the Sister Islands Conservation Area, is a granite and dolerite island, with an area of 545 hectares (2.10 sq mi), located in Bass Strait, Tasmania, Australia.

Sentinel Island is a granite island, with an area of 10 ha, in south-eastern Australia. It is part of Tasmania’s Sentinel Island Group, lying in eastern Bass Strait off the north-west coast of Flinders Island in the Furneaux Group. Until 1985 it was used for grazing sheep.
Little Island is a granite island, with an area of 3 ha, in south-eastern Australia. It is part of Tasmania’s Sentinel Island Group, lying in eastern Bass Strait off the north-west coast of Flinders Island in the Furneaux Group.
South Pasco Island is an island, with an area of 21 ha, in south-eastern Australia. It is part of Tasmania’s Pasco Island Group, lying in eastern Bass Strait off the north-west coast of Flinders Island in the Furneaux Group. It is used for grazing sheep.
The Low Islets are two small, flat, adjacent, granite islands, with a combined area of about 2 ha, in south-eastern Australia. They are part of Tasmania’s Prime Seal Island Group, lying in eastern Bass Strait west of Flinders in the Furneaux Group. The larger of the two islets has been used for grazing sheep, cattle and horses.
Wybalenna Island comprises four round granite islands with a combined area of about 16 ha, in south-eastern Australia. It is part of Tasmania’s Prime Seal Island Group, lying in eastern Bass Strait west of Flinders in the Furneaux Group. The island is a conservation area.













