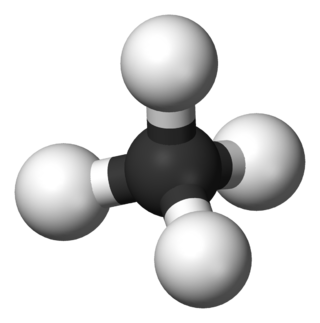
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic; their odor is usually faint, and may be similar to that of gasoline or lighter fluid. They occur in a diverse range of molecular structures and phases: they can be gases, liquids, low melting solids or polymers.

A mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association between a fungus and a plant. The term mycorrhiza refers to the role of the fungus in the plant's rhizosphere, its root system. Mycorrhizae play important roles in plant nutrition, soil biology, and soil chemistry.

Bioremediation broadly refers to any process wherein a biological system, living or dead, is employed for removing environmental pollutants from air, water, soil, flue gasses, industrial effluents etc., in natural or artificial settings. The natural ability of organisms to adsorb, accumulate, and degrade common and emerging pollutants has attracted the use of biological resources in treatment of contaminated environment. In comparison to conventional physicochemical treatment methods bioremediation may offer advantages as it aims to be sustainable, eco-friendly, cheap, and scalable.

A polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) is a class of organic compounds that is composed of multiple aromatic rings. The simplest representative is naphthalene, having two aromatic rings, and the three-ring compounds anthracene and phenanthrene. PAHs are uncharged, non-polar and planar. Many are colorless. Many of them are found in coal and in oil deposits, and are also produced by the incomplete combustion of organic matter—for example, in engines and incinerators or when biomass burns in forest fires.

Phytoremediation technologies use living plants to clean up soil, air and water contaminated with hazardous contaminants. It is defined as "the use of green plants and the associated microorganisms, along with proper soil amendments and agronomic techniques to either contain, remove or render toxic environmental contaminants harmless". The term is an amalgam of the Greek phyto (plant) and Latin remedium. Although attractive for its cost, phytoremediation has not been demonstrated to redress any significant environmental challenge to the extent that contaminated space has been reclaimed.
Biological augmentation is the addition of archaea or bacterial cultures required to speed up the rate of degradation of a contaminant. Organisms that originate from contaminated areas may already be able to break down waste, but perhaps inefficiently and slowly.

An arbuscular mycorrhiza (AM) is a type of mycorrhiza in which the symbiont fungus penetrates the cortical cells of the roots of a vascular plant forming arbuscules. Arbuscular mycorrhiza is a type of endomycorrhiza along with ericoid mycorrhiza and orchid mycorrhiza. They are characterized by the formation of unique tree-like structures, the arbuscules. In addition, globular storage structures called vesicles are often encountered.
Glomeromycota are one of eight currently recognized divisions within the kingdom Fungi, with approximately 230 described species. Members of the Glomeromycota form arbuscular mycorrhizas (AMs) with the thalli of bryophytes and the roots of vascular land plants. Not all species have been shown to form AMs, and one, Geosiphon pyriformis, is known not to do so. Instead, it forms an endocytobiotic association with Nostoc cyanobacteria. The majority of evidence shows that the Glomeromycota are dependent on land plants for carbon and energy, but there is recent circumstantial evidence that some species may be able to lead an independent existence. The arbuscular mycorrhizal species are terrestrial and widely distributed in soils worldwide where they form symbioses with the roots of the majority of plant species (>80%). They can also be found in wetlands, including salt-marshes, and associated with epiphytic plants.
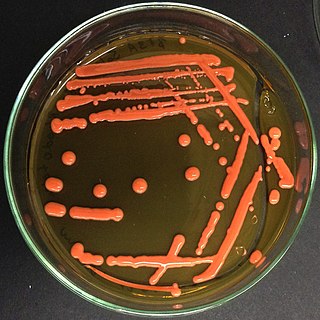
Rhodotorula is a genus of fungi in the class Microbotryomycetes. Most species are known in their yeast states which produce orange to red colonies when grown on Sabouraud's dextrose agar (SDA). The colour is the result of pigments that the yeast creates to block out certain wavelengths of light (620–750 nm) that would otherwise be damaging to the cell. Hyphal states, formerly placed in the genus Rhodosporidium, give rise to teliospores from which laterally septate basidia emerge, producing sessile basidiospores. Species occur worldwide and can be isolated from air, water, soil, and other substrates.

Phospholipid-derived fatty acids (PLFAs) are widely used in microbial ecology as chemotaxonomic markers of bacteria and other organisms. Phospholipids are the primary lipids composing cellular membranes. Phospholipids can be saponified, which releases the fatty acids contained in their diglyceride tail. Once the phospholipids of an unknown sample are saponified, the composition of the resulting PLFA can be compared to the PLFA of known organisms to determine the identity of the sample organism. PLFA analysis may be combined with other techniques, such as stable isotope probing to determine which microbes are metabolically active in a sample. PLFA analysis was pioneered by D.C. White at the University of Tennessee, in the early to mid 1980s.
Petroleum microbiology is a branch of microbiology that deals with the study of microorganisms that can metabolize or alter crude or refined petroleum products. These microorganisms, also called hydrocarbonoclastic microorganisms, can degrade hydrocarbons and, include a wide distribution of bacteria, methanogenic archaea, and some fungi. Not all hydrocarbonoclasic microbes depend on hydrocarbons to survive, but instead may use petroleum products as alternative carbon and energy sources. Interest in this field is growing due to the increasing use of bioremediation of oil spills.
Bioremediation of petroleum contaminated environments is a process in which the biological pathways within microorganisms or plants are used to degrade or sequester toxic hydrocarbons, heavy metals, and other volatile organic compounds found within fossil fuels. Oil spills happen frequently at varying degrees along with all aspects of the petroleum supply chain, presenting a complex array of issues for both environmental and public health. While traditional cleanup methods such as chemical or manual containment and removal often result in rapid results, bioremediation is less labor-intensive, expensive, and averts chemical or mechanical damage. The efficiency and effectiveness of bioremediation efforts are based on maintaining ideal conditions, such as pH, RED-OX potential, temperature, moisture, oxygen abundance, nutrient availability, soil composition, and pollutant structure, for the desired organism or biological pathway to facilitate reactions. Three main types of bioremediation used for petroleum spills include microbial remediation, phytoremediation, and mycoremediation. Bioremediation has been implemented in various notable oil spills including the 1989 Exxon Valdez incident where the application of fertilizer on affected shoreline increased rates of biodegradation.

Bioremediation is the process of decontaminating polluted sites through the usage of either endogenous or external microorganism. In situ is a term utilized within a variety of fields meaning "on site" and refers to the location of an event. Within the context of bioremediation, in situ indicates that the location of the bioremediation has occurred at the site of contamination without the translocation of the polluted materials. Bioremediation is used to neutralize pollutants including Hydrocarbons, chlorinated compounds, nitrates, toxic metals and other pollutants through a variety of chemical mechanisms. Microorganism used in the process of bioremediation can either be implanted or cultivated within the site through the application of fertilizers and other nutrients. Common polluted sites targeted by bioremediation are groundwater/aquifers and polluted soils. Aquatic ecosystems affected by oil spills have also shown improvement through the application of bioremediation. The most notable cases being the Deepwater Horizon oil spill in 2010 and the Exxon Valdez oil spill in 1989. Two variations of bioremediation exist defined by the location where the process occurs. Ex situ bioremediation occurs at a location separate from the contaminated site and involves the translocation of the contaminated material. In situ occurs within the site of contamination In situ bioremediation can further be categorized by the metabolism occurring, aerobic and anaerobic, and by the level of human involvement.

Mycorrhiza helper bacteria (MHB) are a group of organisms that form symbiotic associations with both ectomycorrhiza and arbuscular mycorrhiza. MHBs are diverse and belong to a wide variety of bacterial phyla including both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Some of the most common MHBs observed in studies belong to the phylas Pseudomonas and Streptomyces. MHBs have been seen to have extremely specific interactions with their fungal hosts at times, but this specificity is lost with plants. MHBs enhance mycorrhizal function, growth, nutrient uptake to the fungus and plant, improve soil conductance, aid against certain pathogens, and help promote defense mechanisms. These bacteria are naturally present in the soil, and form these complex interactions with fungi as plant root development starts to take shape. The mechanisms through which these interactions take shape are not well-understood and needs further study.
Gordonia sp. nov. Q8 is a bacterium in the phylum of Actinomycetota. It was discovered in 2017 as one of eighteen new species isolated from the Jiangsu Wei5 oilfield in East China with the potential for bioremediation. Strain Q8 is rod-shaped and gram-positive with dimensions 1.0–4.0 μm × 0.5–1.2 μm and an optimal growth temperature of 40 °C. Phylogenetically, it is most closely related to Gordonia paraffinivorans and Gordonia alkaliphila, both of which are known bioremediators. Q8 was assigned as a novel species based on a <70% ratio of DNA homology with other Gordonia bacteria.
Mycorrhizal amelioration of heavy metals or pollutants is a process by which mycorrhizal fungi in a mutualistic relationship with plants can sequester toxic compounds from the environment, as a form of bioremediation.
Dr. Mohamed Hijri is a biologist who studies arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF). He is a professor of biology and research at the Institut de recherche en biologie végétale at the University of Montreal.
Hydrocarbonoclastic bacteria are a heterogeneous group of prokaryotes which can degrade and utilize hydrocarbon compounds as source of carbon and energy. Despite being present in most of environments around the world, several of these specialized bacteria live in the sea and have been isolated from polluted seawater.
The International Collection of (Vesicular) Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi (INVAM) is the largest collection of living arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) and includes Glomeromycotan species from 6 continents. Curators of INVAM acquire, grow, identify, and elucidate the biology, taxonomy, and ecology of a diversity AMF with the mission to expand availability and knowledge of these symbiotic fungi. Culturing AMF presents difficulty as these fungi are obligate biotrophs that must complete their life cycle while in association with their plant hosts, while resting spores outside of the host are vulnerable to predation and degradation. Curators of INVAM have thus developed methods to overcome these challenges to increase the availability of AMF spores. The inception of this living collection of germplasm occurred in the 1980s and it takes the form of fungi growing in association with plant symbionts in the greenhouse, with spores preserved in cold storage within their associated rhizosphere. AMF spores acquired from INVAM have been used extensively in both basic and applied research projects in the fields of ecology, evolutionary biology, agroecology, and in restoration. INVAM is umbrellaed under the Kansas Biological Survey at The University of Kansas, an R1 Research Institution. The Kansas Biological Survey is also home to the well-known organization Monarch Watch. INVAM is currently located within the tallgrass prairie ecoregion, and many collaborators and researchers associated with INVAM study the role of AMF in the mediation of prairie biodiversity. James Bever and Peggy Schultz are the Curator and Director of Operation team, with Elizabeth Koziol and Terra Lubin as Associate Curators.














