
A byssus is a bundle of filaments secreted by many species of bivalve mollusc that function to attach the mollusc to a solid surface. Species from several families of clams have a byssus, including pen shells (Pinnidae), true mussels (Mytilidae), and Dreissenidae.
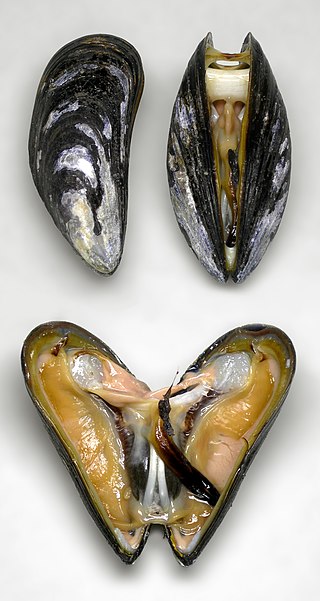
The blue mussel, also known as the common mussel, is a medium-sized edible marine bivalve mollusc in the family Mytilidae, the mussels. Blue mussels are subject to commercial use and intensive aquaculture. A species with a large range, empty shells are commonly found on beaches around the world.

Lithophaga, the date mussels, are a genus of medium-sized marine bivalve molluscs in the family Mytilidae. Some of the earliest fossil Lithophaga shells have been found in Mesozoic rocks from the Alps and from Vancouver Island.

Mytilidae are a family of small to large marine and brackish-water bivalve molluscs in the order Mytilida. One of the genera, Limnoperna, even inhabits freshwater environments. Mytilidae, which contains some 52 genera, is the only extant family within the order Mytilida.

Perna viridis, known as the Asian green mussel, is an economically important mussel, a bivalve belonging to the family Mytilidae. It is harvested for food but is also known to harbor toxins and cause damage to submerged structures such as drainage pipes. It is native in the Asia-Pacific region but has been introduced in the Caribbean, and in the waters around Japan, North America, and South America.

Perna perna, the brown mussel, is an economically important mussel, a bivalve mollusc belonging to the family Mytilidae. It is harvested as a food source but is also known to harbor toxins and cause damage to marine structures. It is native to the waters of Africa, Europe, and South America and was introduced in the waters of North America.

The Chilean mussel or Chilean blue mussel is a species of blue mussel native to the coasts of Chile from Biobío Region to Cape Horn. Today genomic evidence confirmed that the native Chilean blue mussel is genetically distinct from the Northern Hemisphere M. edulis, M. galloprovincialis and M. trossulus and also genetically different from Mytilus platensis,the other species of smooth shelled mussel from South America.

Choromytilus meridionalis, the black mussel, is a species of bivalve. It is a marine mollusc in the family Mytilidae. They are part of the Phylum Mollusca which is the second-largest phylum of invertebrates with around 85,000 species. In this article, we will be discussing the taxonomy, morphology, ecology, reproduction, and distribution of Choromytilus meridionalis.
Thalassonerita is a monotypic genus of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Neritidae. Its sole species is Thalassonerita naticoidea. T. naticoidea is endemic to underwater cold seeps in the northern Gulf of Mexico and in the Caribbean. Originally classified as Bathynerita, the genus was reassessed in 2019 after Thalassonerita was found to be a senior synonym of Bathynerita.

Bathymodiolus childressi is a species of deepwater mussel, a marine bivalve mollusk species in the family Mytilidae, the mussels.

Geukensia demissa is a species of mussel, a marine bivalve mollusk in the family Mytilidae, the true mussels. This species is native to the Atlantic coast of North America. The common names for this species include ribbed mussel, Atlantic ribbed marsh mussel and ribbed horsemussel. However, the common name ribbed mussel is also used for the Southern Hemisphere mussel Aulacomya atra. The appearance of the shell is grooved and oval in shape. The interior of this mussel is tinted purple.

Ischadium is a monotypic genus of mussels in the family Mytilidae. The sole species is Ischadium recurvum, known as the "Hooked mussel" or "Bent mussel". It can be found along the Atlantic coast of North America, ranging from Cape Cod to the West Indies. They are often found growing on Eastern oysters, either intertidal or subtidal. They also attach to other hard substrates, including artificial reefs and dead shells of brackish water clams, Rangia cuneata.

Limnoperna fortunei, the golden mussel, is a medium-sized freshwater bivalve mollusc of the family Mytilidae. The native range of the species is China, but it has accidentally been introduced to South America and several Asian countries where it has become an invasive species. It is considered to be an ecosystem engineer because it alters the nature of the water and the bottom habitats of lakes and rivers and modifies the associated invertebrate communities. It also has strong effects on the properties of the water column, modifying nutrient proportions and concentrations, increasing water transparency, decreasing phytoplankton and zooplankton densities, on which it feeds, and enhancing the growth of aquatic macrophytes. Because mussels attach to hard substrata, including the components of industrial, water-treatment and power plants, they have become a major biofouling problem in the areas invaded.

Trichomya is a monotypic genus of marine bivalve molluscs in the family Mytilidae, the mussels. The only species is Trichomya hirsuta which is endemic to southern and eastern Australia. Its common names include the hairy mussel, the greenling and the kelp greenling.

Bathymodiolus marisindicus is a species of deepwater hydrothermal vent mussel, a marine bivalve mollusk species in the family Mytilidae, the mussels. This species is found in the Indian Ocean.
Potamocorbula amurensis is a species of small saltwater clam, a marine bivalve mollusc in the order Myida. Common names include the overbite clam, the Asian clam, the Amur River clam and the brackish-water corbula. The species is native to marine and brackish waters in the northern Pacific Ocean, its range extending from Siberia to China, Korea and Japan. It has become naturalised in San Francisco Bay.

Mytella is a genus of saltwater clams, marine bivalve molluscs in the subfamily Arcuatulinae of the family Mytilidae, the mussels.

Mytella guyanensis is a species of tropical saltwater mussel, marine bivalve molluscs in the family Mytilidae. This species has been referred to colloquially as the “Trinidad Swamp Mussel” —although not formally confirmed as the common name. It was first described in detail by the French naturalist Jean Baptiste Lamarck in 1819.

Brachidontes pharaonis is a species of mussel from the family Mytilidae. It is native to the Indian Ocean and the Red Sea, and has colonised the Mediterranean Sea where it is regarded as an invasive species.

Arcuatula senhousia(= Musculista senhousia), commonly known as the Asian date mussel, Asian mussel or bag mussel, is a small saltwater mussel, a marine bivalve mollusk species in the family Mytilidae, the mussels. Other common names for this species include: the Japanese mussel, Senhouse's mussel, the green mussel, and the green bagmussel. It is harvested for human consumption in China.

















