
N-Acetylmannosamine is a hexosamine monosaccharide. It is a neutral, stable naturally occurring compound. N-Acetylmannosamine is also known as N-Acetyl-D-mannosamine monohydrate,, N-Acetyl-D-mannosamine which can be abbreviated to ManNAc or, less commonly, NAM). ManNAc is the first committed biological precursor of N-acetylneuraminic acid. Sialic acids are the negatively charged, terminal monosaccharides of carbohydrate chains that are attached to glycoproteins and glycolipids (glycans).

Phosphopentose epimerase encoded by the RPE gene is a metalloprotein that catalyzes the interconversion between D-ribulose 5-phosphate and D-xylulose 5-phosphate.
In enzymology, a N-acylmannosamine 1-dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.233) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a N-acylglucosamine 2-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a phosphoacetylglucosamine mutase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
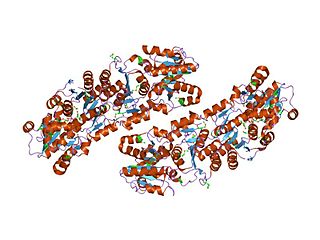
In enzymology, an UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
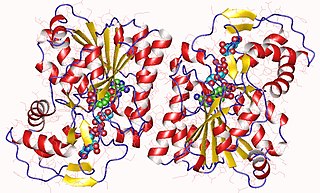
In enzymology, an UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 4-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
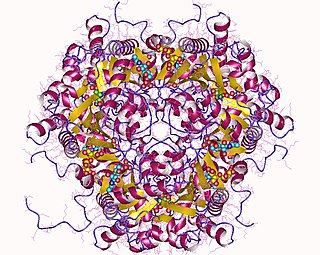
In enzymology, a glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase (EC 3.5.99.6) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, glucosamine-phosphate N-acetyltransferase (GNA) is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of an acetyl group from acetyl-CoA to the primary amine in glucosamide-6-phosphate, generating a free CoA and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine-6-phosphate.
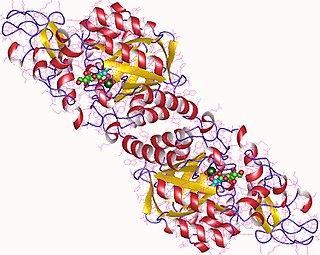
In enzymology, a N-acetylneuraminate synthase (EC 2.5.1.56) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-acylneuraminate-9-phosphate synthase (EC 2.5.1.57) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase (isomerizing) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 1,3-beta-galactosyl-N-acetylhexosamine phosphorylase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-acylmannosamine kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

N-acylglucosamine 2-epimerase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RENBP gene.
UDP-3-O-(3-hydroxymyristoyl)glucosamine N-acyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name (3R)-3-hydroxymyristoyl-(acyl-carrier protein):UDP-3-O-( -3-hydroxymyristoyl)-alpha-D-glucosamine N-acetyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase (hydrolysing) (EC 3.2.1.183, UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase, GNE (gene), siaA (gene), neuC (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine hydrolase (2-epimerising). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Epimerox is an experimental broad-spectrum antibiotic compound being developed by scientists at the Rockefeller University and Astex Pharmaceuticals. It is a small molecule inhibitor compound that blocks the activity of the enzyme UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase, an epimerase enzyme that is called 2-epimerase for short.
2-Epimerase can refer one of to several enzymes:













