A dehydrogenase is an enzyme belonging to the group of oxidoreductases that oxidizes a substrate by reducing an electron acceptor, usually NAD+/NADP+ or a flavin coenzyme such as FAD or FMN. Like all catalysts, they catalyze reverse as well as forward reactions, and in some cases this has physiological significance: for example, alcohol dehydrogenase catalyzes the oxidation of ethanol to acetaldehyde in animals, but in yeast it catalyzes the production of ethanol from acetaldehyde.
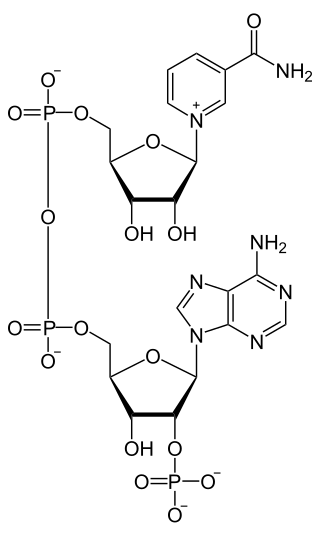
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or, in older notation, TPN (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid syntheses, which require NADPH as a reducing agent ('hydrogen source'). NADPH is the reduced form, whereas NADP+ is the oxidized form. NADP+ is used by all forms of cellular life.

In biochemistry, flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) is a redox-active coenzyme associated with various proteins, which is involved with several enzymatic reactions in metabolism. A flavoprotein is a protein that contains a flavin group, which may be in the form of FAD or flavin mononucleotide (FMN). Many flavoproteins are known: components of the succinate dehydrogenase complex, α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, and a component of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.
Pyruvate dehydrogenase (NADP+) EC 1.2.1.51 is an enzyme that should not be confused with Pyruvate dehydrogenase (acetyltransferase) EC 1.2.4.1.
NAD+ kinase (EC 2.7.1.23, NADK) is an enzyme that converts nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) into NADP+ through phosphorylating the NAD+ coenzyme. NADP+ is an essential coenzyme that is reduced to NADPH primarily by the pentose phosphate pathway to provide reducing power in biosynthetic processes such as fatty acid biosynthesis and nucleotide synthesis. The structure of the NADK from the archaean Archaeoglobus fulgidus has been determined.

In enzymology, a hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase (NADPH) (EC 1.1.1.34) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a malate dehydrogenase (NADP+) (EC 1.1.1.82) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase (NADPH, A-specific) (EC 1.3.1.39) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (NADP+) (phosphorylating) (EC 1.2.1.13) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase (EC 1.18.1.2) abbreviated FNR, is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a rubredoxin—NAD(P)+ reductase (EC 1.18.1.4) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a NADPH peroxidase (EC 1.11.1.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Azobenzene reductase also known as azoreductase (EC 1.7.1.6) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
Bis-gamma-glutamylcystine reductase (EC 1.8.1.13) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an FMN reductase (EC 1.5.1.29) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (quinone) (EC 1.6.5.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a NADPH dehydrogenase (quinone) (EC 1.6.5.10) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a NADPH—hemoprotein reductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Sulfite reductase (NADPH) (EC 1.8.1.2, sulfite (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) reductase, NADPH-sulfite reductase, NADPH-dependent sulfite reductase, H2S-NADP oxidoreductase, sulfite reductase (NADPH2)) is an enzyme with systematic name hydrogen-sulfide:NADP+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalises the following chemical reaction
Adrenodoxin-NADP+ reductase (EC 1.18.1.6, adrenodoxin reductase, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-adrenodoxin reductase, ADR, NADPH:adrenal ferredoxin oxidoreductase) is an enzyme with systematic name adrendoxin:NADP+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction