A dehydrogenase is an enzyme belonging to the group of oxidoreductases that oxidizes a substrate by reducing an electron acceptor, usually NAD+/NADP+ or a flavin coenzyme such as FAD or FMN. Like all catalysts, they catalyze reverse as well as forward reactions, and in some cases this has physiological significance: for example, alcohol dehydrogenase catalyzes the oxidation of ethanol to acetaldehyde in animals, but in yeast it catalyzes the production of ethanol from acetaldehyde.

Glutathione peroxidase (GPx) is the general name of an enzyme family with peroxidase activity whose main biological role is to protect the organism from oxidative damage. The biochemical function of glutathione peroxidase is to reduce lipid hydroperoxides to their corresponding alcohols and to reduce free hydrogen peroxide to water.
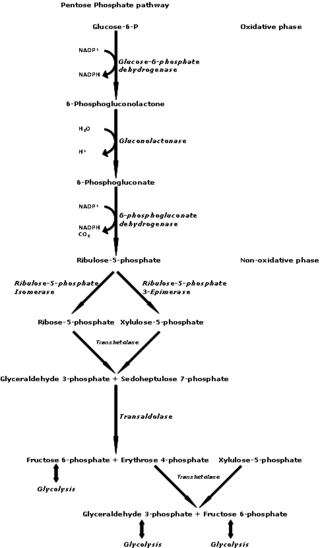
The pentose phosphate pathway is a metabolic pathway parallel to glycolysis. It generates NADPH and pentoses as well as ribose 5-phosphate, a precursor for the synthesis of nucleotides. While the pentose phosphate pathway does involve oxidation of glucose, its primary role is anabolic rather than catabolic. The pathway is especially important in red blood cells (erythrocytes).
Nitrate reductase (NADPH) (EC 1.7.1.3, assimilatory nitrate reductase, assimilatory reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-nitrate reductase, NADPH-nitrate reductase, assimilatory NADPH-nitrate reductase, triphosphopyridine nucleotide-nitrate reductase, NADPH:nitrate reductase, nitrate reductase (NADPH2), NADPH2:nitrate oxidoreductase) is an enzyme with systematic name nitrite:NADP+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalises the following chemical reaction

In enzymology, an acetoacetyl-CoA reductase (EC 1.1.1.36) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an allyl-alcohol dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.54) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a dTDP-galactose 6-dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.186) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Testosterone 17beta-dehydrogenase (NADP+) (EC 1.1.1.64, 17-ketoreductase, NADP-dependent testosterone-17beta-oxidoreductase, testosterone 17beta-dehydrogenase (NADP)) is an enzyme with systematic name 17beta-hydroxysteroid:NADP+ 17-oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
In enzymology, a ribose 1-dehydrogenase (NADP+) (EC 1.1.1.115) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a testosterone 17beta-dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction between testosterone and androst-4-ene-3,17-dione. This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on the CH-OH group of donor with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor.
In enzymology, an orotate reductase (NADPH) (EC 1.3.1.15) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2-oxoaldehyde dehydrogenase (NADP+) (EC 1.2.1.49) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an aldehyde dehydrogenase (NADP+) (EC 1.2.1.4) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (NADP+) (phosphorylating) (EC 1.2.1.13) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a fatty-acid peroxidase (EC 1.11.1.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a lignin peroxidase (EC 1.11.1.14) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a NADH peroxidase (EC 1.11.1.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a NADPH dehydrogenase (EC 1.6.99.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a NADPH—hemoprotein reductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a nitrite reductase [NAD(P)H] (EC 1.7.1.4) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction






