Messier 109 is a barred spiral galaxy exhibiting a weak inner ring structure around the central bar approximately 67.2 ± 23 million light-years away in the northern constellation Ursa Major. M109 can be seen south-east of the star Phecda.

NGC 3877 is a type Sc spiral galaxy that was discovered by William Herschel on February 5, 1788. It is located below the magnitude 3.7 star Chi Ursae Majoris in Ursa Major.

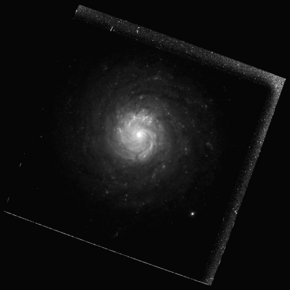
NGC 4088 is an intermediate spiral galaxy in the constellation Ursa Major. The galaxy forms a physical pair with NGC 4085, which is located 11′ away.

NGC 5164 is a barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Ursa Major. It was discovered by William Herschel on April 14, 1789.

NGC 5474 is a peculiar dwarf galaxy in the constellation Ursa Major. It is one of several companion galaxies of the Pinwheel Galaxy (M101), a grand-design spiral galaxy. Among the Pinwheel Galaxy's companions, this galaxy is the closest to the Pinwheel Galaxy itself. The gravitational interaction between NGC 5474 and the Pinwheel Galaxy has strongly distorted the former. As a result, the disk is offset relative to the nucleus. The star formation in this galaxy is also offset from the nucleus. NGC 5474 shows some signs of a spiral structure. As a result, this galaxy is often classified as a dwarf spiral galaxy, a relatively rare group of dwarf galaxies.

NGC 3191 is a barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Ursa Major. It was discovered on 5 February 1788 by William Herschel. It is located at a distance of about 400 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 3191 is about 115,000 light years across.

NGC 3642 is a spiral galaxy in the constellation Ursa Major. The galaxy has a low-ionization nuclear emission-line region. It is located at a distance of circa 30 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 3642 is about 50,000 light years across. The galaxy is characterised by an outer pseudoring, which was probably formed after the accretion of a gas rich dwarf galaxy.

NGC 7083 is an unbarred spiral galaxy located about 134 million light-years away in the constellation of Indus. It is also classified as a flocculent spiral galaxy. NGC 7083 was discovered by astronomer James Dunlop on August 28, 1826.

NGC 3675 is a spiral galaxy located in the constellation Ursa Major. It is located at a distance of circa 50 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 3675 is about 100,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel in 1788.

NGC 4907 is a barred spiral galaxy located about 270 million light-years away in the constellation of Coma Berenices. It is also classified as a LINER galaxy. NGC 4907 was discovered by astronomer Heinrich d'Arrest on May 5, 1864. The galaxy is a member of the Coma Cluster, located equidistant between NGC 4928 and NGC 4829.

NGC 3631 is a spiral galaxy located in the constellation Ursa Major. It is located at a distance of about 35 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 3631 is about 60,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel on April 14, 1789. It is a grand design spiral galaxy seen face on.

NGC 3726 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the constellation Ursa Major. It is located at a distance of circa 45 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 3726 is about 85,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel on February 5, 1788.

NGC 2998 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the constellation Ursa Major. It is 195 million light-years away from the Earth. It is an intermediate spiral galaxy. Its stellar mass is about that of the Milky Way.

NGC 3893 is a spiral galaxy located in the constellation Ursa Major. It is located at a distance of circa 50 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 3893 is about 70,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel on February 9, 1788. NGC 3893 interacts with its satellite, NGC 3896.

NGC 3729 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the constellation Ursa Major. It is located at a distance of circa 65 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 3729 is about 60,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel on April 12, 1789.

NGC 4100 is a spiral galaxy in the northern constellation of Ursa Major. It was discovered by William Herschel on Mar 9, 1788. This galaxy is a member of the NGC 3992 group in the Ursa Major Cluster.

NGC 4260 is a barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Virgo. It was discovered by William Herschel on April 13, 1784.

NGC 3741 is an irregular galaxy in the constellation Ursa Major. It was discovered by John Herschel on March 19, 1828. At a distance of about 10 million light-years, it is located in the M94 Group. It is relatively undisturbed by other galaxies.

NGC 3898 is a spiral galaxy in the constellation Ursa Major that was discovered by William Herschel on April 14, 1789. It is positioned 1.5° northwest of NGC 3998 and is barely visible in a small telescope. The galaxy has an apparent visual magnitude of 10.7 and an angular size of 3.3′ × 1.5′. It is located at a distance of 72 ± 6 million light-years (22.08 ± 1.79 Mpc) from the Milky Way, and is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 1,142.7±13.9 km/s.

NGC 3985 is a barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Ursa Major. It is located at a distance of about 45 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 3726 is about 18,000 light years across. NGC 3985 is situated north of the celestial equator and, as such, it is more easily visible from the Northern Hemisphere. The galaxy appears to have one spiral arm.