
Messier 100 is a grand design intermediate spiral galaxy in the southern part of the mildly northern Coma Berenices. It is one of the brightest and largest galaxies in the Virgo Cluster and is approximately 55 million light-years from our galaxy, its diameter being 107,000 light years, and being about 60% as large. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1781 and 29 days later seen again and entered by Charles Messier in his catalogue "of nebulae and star clusters". It was one of the first spiral galaxies to be discovered, and was listed as one of fourteen spiral nebulae by Lord William Parsons of Rosse in 1850. NGC 4323 and NGC 4328 are satellite galaxies of M100; the former is connected with it by a bridge of luminous matter.
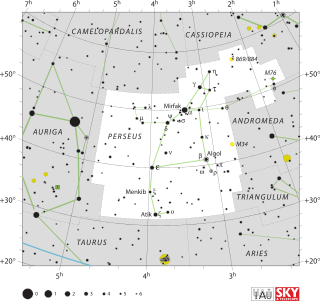
Perseus is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus. It is one of the 48 ancient constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located near several other constellations named after ancient Greek legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west. Some star atlases during the early 19th century also depicted Perseus holding the disembodied head of Medusa, whose asterism was named together as Perseus et Caput Medusae; however, this never came into popular usage.

NGC 3553 is a lenticular galaxy in the constellation Ursa Major. It was discovered in March 1885 by Guillaume Bigourdan. It is a member of the galaxy cluster Abell 1185.

NGC 3539 is a lenticular galaxy in the constellation Ursa Major. It was discovered in April 1831 by John Herschel. It is a member of the galaxy cluster Abell 1185.

NGC 3258 is an elliptical galaxy in the constellation Antlia. It is a member of the Antlia Cluster, which lies about 40.7 megaparsecs away. It was discovered on May 2, 1834 by John Herschel.

NGC 922 is a peculiar galaxy in the southern constellation of Fornax, located at a distance of 142 Mly from the Milky Way. It is one of the nearest known collisional galaxies. This object was described by the Herschels as "considerably faint, pretty large, round, gradually pretty much brighter middle." The general form is described by the morphological classification of SB(s)cd pec, which indicates a peculiar (pec) barred spiral galaxy (SB) with no inner ring system around the bar (s) and loosely-wound spiral arms (cd).

NGC 838 is an unbarred lenticular galaxy located at approximately 170 million light-years away in the constellation of Cetus. It is part of the Hickson Compact Group 16.

NGC 5917 is a spiral galaxy located in the constellation of Libra. It was discovered by English astronomer John Herschel on 16 July 1835. This galaxy is located at a distance of 90.4 ± 6.2 million light-years (27.73 ± 1.90 Mpc) from the Milky Way, and is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 1,934.1 km/s. It is interacting with the neighboring galaxy, PGC 54817, at an angular separation of 4.2′. Tidal tails extend from PGC 54817 to the halo of NGC 5917.

NGC 5559 is a barred spiral galaxy, located 240 million light-years away in the constellation of Boötes. It was discovered on April 10, 1785, by the astronomer William Herschel.

NGC 1310 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the southern constellation of Fornax. It was discovered by English astronomer John Herschel on 22 October 1835.

NGC 940 is a lenticular galaxy in the constellation Triangulum. It is estimated to be 222 million light-years from the Milky Way and has a diameter of approximately 80,000 ly. NGC 940 was discovered by Heinrich d'Arrest.

NGC 980 is a lenticular galaxy located in the constellation Andromeda about 256 million light years from the Milky Way. It was discovered by the German - British astronomer William Herschel in 1786.

NGC 790 is a lenticular galaxy in the constellation Cetus. It is estimated to be 233 million light-years from the Milky Way and has a diameter of approximately 90,000 light years. NGC 790 was discovered on September 10, 1785 by the German-British astronomer William Herschel.

NGC 996 is an elliptical galaxy of the Hubble type E0 in the constellation Andromeda. It is estimated to be 210 million light years from the Milky Way and has a diameter of approximately 75,000 ly. The supernova SN 1996bq occurred in this galaxy. NGC 996 was discovered on December 7, 1871 by astronomer Édouard Stephan.

NGC 938 is an elliptical galaxy located in the constellation Aries, approximately 184 million light years from the Milky Way. It was discovered by the Prussian astronomer Heinrich d'Arrest in 1863.

NGC 823, also known as IC 1782, is an unbarred lenticular galaxy in the constellation Fornax. It is estimated to be 194 million light-years from the Milky Way and has a diameter of approximately 100,000 light years. NGC 823 was discovered on October 14, 1830, by astronomer John Herschel.

NGC 824 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the constellation Fornax about 260 million light-years from the Milky Way. It was discovered by British astronomer John Herschel in 1837.

NGC 2803, also known as PCG 26181, is an elliptical or lenticular galaxy in the zodiac constellation Cancer. It was discovered March 21, 1784, by William Herschel. It is interacting with NGC 2802.

NGC 4614 is a barred lenticular galaxy in the New General Catalog. It is located in the constellation of Coma Berenices. It was discovered in 1864 by the German astronomer Heinrich d'Arrest with a 11.9 inch diameter lens type telescope.

NGC 4589 is an elliptical galaxy located in the Draco constellation. It was discovered by German-British astronomer William Herschel on November 22, 1797. This galaxy lies at a distance of 73.0 million light-years (22.39 Mpc) from the Milky Way, and is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 2,002 km/s. It is known by its designations PGC 42139 or UGC 7797.




















