Aplastic anemia (AA) is a severe hematologic condition in which the body fails to make blood cells in sufficient numbers. Blood cells are produced in the bone marrow by stem cells that reside there. Aplastic anemia causes a deficiency of all blood cell types: red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.

Bone marrow is a semi-solid tissue found within the spongy portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production. It is composed of hematopoietic cells, marrow adipose tissue, and supportive stromal cells. In adult humans, bone marrow is primarily located in the ribs, vertebrae, sternum, and bones of the pelvis. Bone marrow comprises approximately 5% of total body mass in healthy adult humans, such that a man weighing 73 kg (161 lbs) will have around 3.7 kg (8 lbs) of bone marrow.
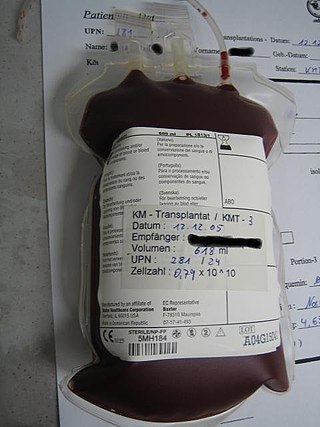
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood, in order to replicate inside a patient and produce additional normal blood cells. HSCT may be autologous, syngeneic, or allogeneic.

Graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) is a syndrome, characterized by inflammation in different organs. GvHD is commonly associated with bone marrow transplants and stem cell transplants.
A cord blood bank is a facility which stores umbilical cord blood for future use. Both private and public cord blood banks have developed in response to the potential for cord blood in treating diseases of the blood and immune systems. Public cord blood banks accept donations to be used for anyone in need, and as such function like public blood banks. Traditionally, public cord blood banking has been more widely accepted by the medical community. Private cord blood banks store cord blood solely for potential use by the donor or donor's family. Private banks typically charge around $2,000 for the collection and around $200 a year for storage.

Anthony Nolan is a UK charity that works in the areas of leukaemia and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. It manages and recruits donors to the Anthony Nolan Register, which is part of an aligned registry that also includes the Welsh Bone Marrow Donor Registry, NHS Blood and Transplant's British Bone Marrow Registry and Deutsche KnochenMarkSpenderdatei (DKMS) UK. This aligned register is known as the Anthony Nolan & NHS Stem Cell Registry. It also carries out research to help make bone marrow transplants more effective.
Cord blood is blood that remains in the placenta and in the attached umbilical cord after childbirth. Cord blood is collected because it contains stem cells, which can be used to treat hematopoietic and genetic disorders such as cancer.
The Singapore Cord Blood Bank is Singapore's only public cord blood bank that collects, processes and stores donated umbilical cord blood for use in stem cell transplants. Its cord blood units may be searched for use by qualifying transplant centers around the world.
Stem-cell therapy uses stem cells to treat or prevent a disease or condition. As of 2024, the only FDA-approved therapy using stem cells is hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. This usually takes the form of a bone marrow or peripheral blood stem cell transplantation, but the cells can also be derived from umbilical cord blood. Research is underway to develop various sources for stem cells as well as to apply stem-cell treatments for neurodegenerative diseases and conditions such as diabetes and heart disease.

World Marrow Donor Association (WMDA) is an organization based in Leiden, Netherlands, that coordinates the collection of the HLA phenotypes and other relevant data of volunteer hematopoietic cell donors and cord blood units across the globe.
Pablo Rubinstein is a pioneer in freezing of umbilical cord blood or placental blood cells for the use for unrelated donors to treat diseases like leukemia and genetic diseases such as Tay–Sachs disease and sickle cell anemia. He pioneered and established an international cord blood banking system and has played a leading role in international cord blood transplantation.
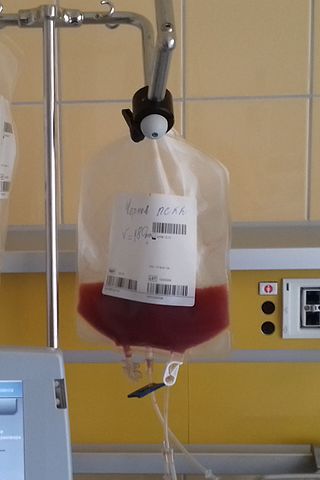
Peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (PBSCT), also called "Peripheral stem cell support", is a method of replacing blood-forming stem cells. Stem cells can be destroyed through cancer treatments such as chemotherapy or radiation, as well as any blood-related diseases, such as leukemia, lymphoma, neuroblastoma and multiple myeloma. PBSCT is now a much more common procedure than its bone marrow harvest equivalent due to the ease and less invasive nature of the procedure. Studies suggest that PBSCT has a better outcome in terms of the number of hematopoietic stem cell yield.

The Gift of Life Marrow Registry is a non-profit organization founded in 1991 and headquartered in Boca Raton, Florida that operates a public blood stem cell and bone marrow registry while facilitating transplants for children and adults battling life-threatening illnesses, including leukemia, lymphoma, other cancers and genetic diseases.

Reticular dysgenesis (RD) is a rare, inherited autosomal recessive disease that results in immunodeficiency. Individuals with RD have mutations in both copies of the AK2 gene. Mutations in this gene lead to absence of AK2 protein. AK2 protein allows hematopoietic stem cells to differentiate and proliferate. Hematopoietic stem cells give rise to blood cells.
Microtransplantation (MST) is an advanced technology to treat malignant hematological diseases and tumors by infusing patients with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) mobilized human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-mismatched allogeneic peripheral blood stem cells following a reduced-intensity chemotherapy or targeted therapy. The term "microtransplantation" comes from its mechanism of reaching donor cell microchimerism.
Guo Mei is a hematologist and associate director of 307th Hospital of Chinese People’s Liberation Army and deputy director of Radiation Research Institute.

LifeSouth Community Blood Centers is a not-for-profit blood bank incorporated in Florida. LifeSouth is headquartered in Gainesville, Florida, and serves over 125 hospitals in Florida, Georgia and Alabama. It has formerly been known as Civitan Regional Blood Centers.
Deutsche Knochenmarkspenderdatei, abbreviated as DKMS, is an international nonprofit bone marrow donor center based in Tübingen, Germany, with entities in Chile, India, Poland, South Africa, the United Kingdom and the United States. DKMS works in the areas of blood cancer and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and raises awareness of the need for donors for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation which people with blood cancers need for treatment as well as helping people sign up to their national bone marrow registries. Over the years, DKMS has expanded beyond Germany.
Amal Bishara is an Israeli Arab doctor, and the director of Bone Marrow Registry Outreach, Hadassah Medical Center, which is associated with the Hebrew University of Jerusalem in Israel. There she runs the only bone marrow transplant registry in the world for unrelated Arab donors. Dr. Amal has published and presented internationally on her research into immunogenetics. She serves on the Accreditation Committee of the European Federation for Immunogenetics.

DATRI is a not-for-profit organization registered in 2009 as a Section 8 company under Government of India. DATRI is one of the largest unrelated blood stem cell donors registry in India, that helps patients with blood cancer and other fatal blood disorders to find a HLA matched Blood Stem Cell donor. Blood stem cell transplant is a chance of cure for patients with blood cancer and other severe blood disorders. As of January 2023, DATRI has more than 5 lakhs voluntary donors registered and it has facilitated 1074 plus transplants worldwide. DATRI operates across India.











