Related Research Articles
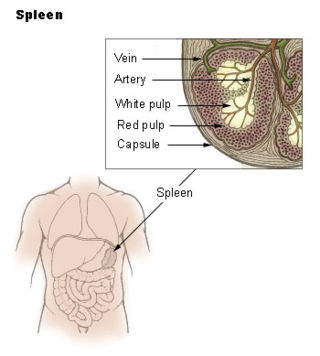
The spleen is an organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter. The word spleen comes from Ancient Greek σπλήν (splḗn).

A pancreas transplant is an organ transplant that involves implanting a healthy pancreas into a person who usually has diabetes.
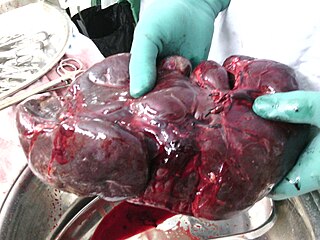
A splenectomy is the surgical procedure that partially or completely removes the spleen. The spleen is an important organ in regard to immunological function due to its ability to efficiently destroy encapsulated bacteria. Therefore, removal of the spleen runs the risk of overwhelming post-splenectomy infection, a medical emergency and rapidly fatal disease caused by the inability of the body's immune system to properly fight infection following splenectomy or asplenia.

Hereditary spherocytosis (HS) is a congenital hemolytic disorder, wherein a genetic mutation coding for a structural membrane protein phenotype leads to a spherical shaping of erythrocytic cellular morphology. As erythrocytes are sphere-shaped (spherocytosis), rather than the normal biconcave disk-shaped, their morphology interferes with these cells' abilities to be flexible during circulation throughout the entirety of the body - arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, veins, and organs. This difference in shape also makes the red blood cells more prone to rupture under osmotic and/or mechanical stress. Cells with these dysfunctional proteins are degraded in the spleen, which leads to a shortage of erythrocytes resulting in hemolytic anemia.
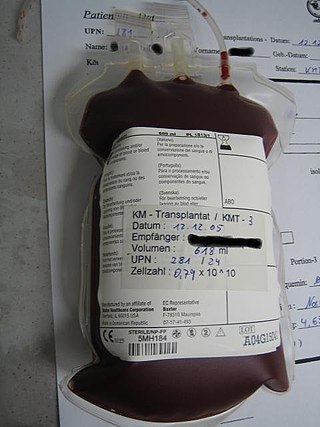
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood in order to replicate inside of a patient and to produce additional normal blood cells. It may be autologous, allogeneic or syngeneic.

Graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) is a syndrome, characterized by inflammation in different organs. GvHD is commonly associated with bone marrow transplants and stem cell transplants.
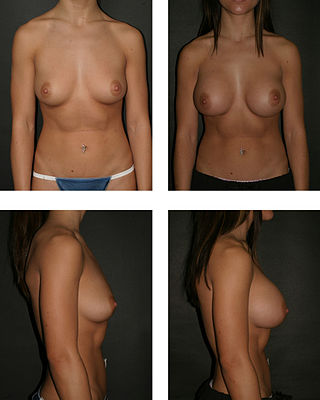
Breast augmentation and augmentation mammoplasty is a cosmetic surgery technique using breast-implants and fat-graft mammoplasty techniques to increase the size, change the shape, and alter the texture of the breasts. Augmentation mammoplasty is applied to correct congenital defects of the breasts and the chest wall. As an elective cosmetic surgery, primary augmentation changes the aesthetics – of size, shape, and texture – of healthy breasts.
Asplenia refers to the absence of normal spleen function and is associated with some serious infection risks. Hyposplenism is used to describe reduced ('hypo-') splenic functioning, but not as severely affected as with asplenism.
An overwhelming post-splenectomy infection (OPSI) is a rare but rapidly fatal infection occurring in individuals following removal of the spleen. The infections are typically characterized by either meningitis or sepsis, and are caused by encapsulated organisms including Streptococcus pneumoniae. It is a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment. Death has been reported to occur within 12 hours.
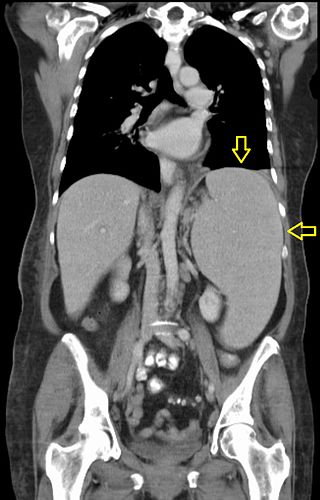
Splenomegaly is an enlargement of the spleen. The spleen usually lies in the left upper quadrant (LUQ) of the human abdomen. Splenomegaly is one of the four cardinal signs of hypersplenism which include: some reduction in number of circulating blood cells affecting granulocytes, erythrocytes or platelets in any combination; a compensatory proliferative response in the bone marrow; and the potential for correction of these abnormalities by splenectomy. Splenomegaly is usually associated with increased workload, which suggests that it is a response to hyperfunction. It is therefore not surprising that splenomegaly is associated with any disease process that involves abnormal red blood cells being destroyed in the spleen. Other common causes include congestion due to portal hypertension and infiltration by leukemias and lymphomas. Thus, the finding of an enlarged spleen, along with caput medusae, is an important sign of portal hypertension.
An autosplenectomy is a negative outcome of disease and occurs when a disease damages the spleen to such an extent that it becomes shrunken and non-functional. The spleen is an important immunological organ that acts as a filter for red blood cells, triggers phagocytosis of invaders, and mounts an immunological response when necessary. Lack of a spleen, called asplenia, can occur by autosplenectomy or the surgical counterpart, splenectomy. Asplenia can increase susceptibility to infection. Autosplenectomy can occur in cases of sickle-cell disease where the misshapen cells block blood flow to the spleen, causing scarring and eventual atrophy of the organ. Autosplenectomy is a rare condition that is linked to certain diseases but is not a common occurrence. It is also seen in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).

Corneal transplantation, also known as corneal grafting, is a surgical procedure where a damaged or diseased cornea is replaced by donated corneal tissue. When the entire cornea is replaced it is known as penetrating keratoplasty and when only part of the cornea is replaced it is known as lamellar keratoplasty. Keratoplasty simply means surgery to the cornea. The graft is taken from a recently deceased individual with no known diseases or other factors that may affect the chance of survival of the donated tissue or the health of the recipient.

Splenic infarction is a condition in which blood flow supply to the spleen is compromised, leading to partial or complete infarction in the organ. Splenic infarction occurs when the splenic artery or one of its branches are occluded, for example by a blood clot.
Transfusion-associated graft-versus-host disease (TA-GvHD) is a rare complication of blood transfusion, in which the immunologically competent donor T lymphocytes mount an immune response against the recipient's lymphoid tissue. These donor lymphocytes engraft, recognize recipient cells as foreign and mount an immune response against recipient tissues. Donor lymphocytes are usually identified as foreign and destroyed by the recipient's immune system. However, in situations where the recipient is severely immunocompromised, or when the donor and recipient HLA type is similar, the recipient's immune system is not able to destroy the donor lymphocytes. This can result in transfusion associated graft-versus-host disease. This is in contrast with organ/tissue transplant associated GvHD, where matching HLA reduces the incident of the complication.
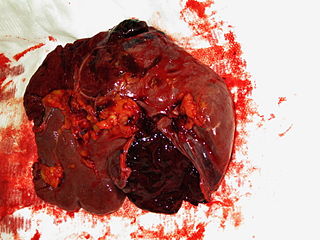
Blunt splenic trauma occurs when a significant impact to the spleen from some outside source damages or ruptures the spleen. Treatment varies depending on severity, but often consists of embolism or splenectomy.
Juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia (JMML) is a rare form of chronic leukemia that affects children, commonly those aged four and younger. The name JMML now encompasses all diagnoses formerly referred to as juvenile chronic myeloid leukemia (JCML), chronic myelomonocytic leukemia of infancy, and infantile monosomy 7 syndrome. The average age of patients at diagnosis is two (2) years old. The World Health Organization has included JMML as a subcategory of myelodysplastic and myeloproliferative disorders.
Transplantable organs and tissues may refer to both organs and tissues that are relatively often transplanted, as well as organs and tissues which are relatively seldom transplanted. In addition to this it may also refer to possible-transplants which are still in the experimental stage.
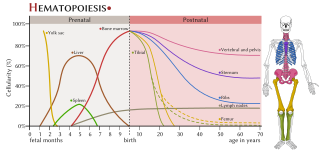
The haematopoietic system is the system in the body involved in the creation of the cells of blood.

Intestine transplantation is the surgical replacement of the small intestine for chronic and acute cases of intestinal failure. While intestinal failure can oftentimes be treated with alternative therapies such as parenteral nutrition (PN), complications such as PN-associated liver disease and short bowel syndrome may make transplantation the only viable option. One of the rarest type of organ transplantation performed, intestine transplantation is becoming increasingly prevalent as a therapeutic option due to improvements in immunosuppressive regimens, surgical technique, PN, and the clinical management of pre and post-transplant patients.
Splenosis is the result of spleen tissue breaking off the main organ and implanting at another site inside the body. This is called heterotopic autotransplantation of the spleen. It most commonly occurs as a result of traumatic splenic rupture or abdominal surgery. Depending on the location of the spleen, the new piece usually implants in another part of the abdominal cavity. Single case reports also describe splenosis in the thoracic cavity, in subcutaneous tissue, in the liver or in the cranial cavity. Splenosis must be distinguished from the presence of additional spleens, which are innate and are the result of differences in embryological development. Additionally, splenosis must be differentiated from malignant tumors which may look similar when imaged.
References
- ↑ Wu; et al. (January 2011). "Graft-versus-host disease after intestinal and multivisceral transplantation". Transplantation. 91 (2): 219–224. doi: 10.1097/tp.0b013e3181ff86ec . PMID 21076376. S2CID 35828611.
- ↑ Deierhoi; et al. (April 1986). "Lethal graft-versus-host disease in a recipient of a pancreas-spleen transplant". Transplantation. 41 (4): 544–546. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198604000-00028 . PMID 3515658.
- 1 2 Surendran, A; Smith, M; Houli, N; Usatoff, V; Spelman, D; Choi, J (April 2020). "Splenic autotransplantation: a systematic review". ANZ Journal of Surgery. 90 (4): 460–466. doi:10.1111/ans.15383. hdl: 11343/286471 . PMID 31576640. S2CID 203639290.