
Nitrogen trichloride, also known as trichloramine, is the chemical compound with the formula NCl3. This yellow, oily, pungent-smelling and explosive liquid is most commonly encountered as a byproduct of chemical reactions between ammonia-derivatives and chlorine (for example, in swimming pools). Alongside monochloramine and dichloramine, trichloramine is responsible for the distinctive 'chlorine smell' associated with swimming pools, where the compound is readily formed as a product from hypochlorous acid reacting with ammonia and other nitrogenous substances in the water, such as urea from urine.

Phosphorus pentachloride is the chemical compound with the formula PCl5. It is one of the most important phosphorus chlorides, others being PCl3 and POCl3. PCl5 finds use as a chlorinating reagent. It is a colourless, water-sensitive and moisture-sensitive solid, although commercial samples can be yellowish and contaminated with hydrogen chloride.

Dichlorine monoxide is an inorganic compound with the molecular formula Cl2O. It was first synthesised in 1834 by Antoine Jérôme Balard, who along with Gay-Lussac also determined its composition. In older literature it is often referred to as chlorine monoxide, which can be a source of confusion as that name now refers to the neutral species ClO.

Niobium(V) chloride, also known as niobium pentachloride, is a yellow crystalline solid. It hydrolyzes in air, and samples are often contaminated with small amounts of NbOCl3. It is often used as a precursor to other compounds of niobium. NbCl5 may be purified by sublimation.

Tantalum(V) chloride, also known as tantalum pentachloride, is an inorganic compound with the formula TaCl5. It takes the form of a white powder and is commonly used as a starting material in tantalum chemistry. It readily hydrolyzes to form tantalum(V) oxychloride (TaOCl3) and eventually tantalum pentoxide (Ta2O5); this requires that it be synthesised and manipulated under anhydrous conditions, using air-free techniques.

Phosphoryl chloride is a colourless liquid with the formula POCl3. It hydrolyses in moist air releasing phosphoric acid and fumes of hydrogen chloride. It is manufactured industrially on a large scale from phosphorus trichloride and oxygen or phosphorus pentoxide. It is mainly used to make phosphate esters such as tricresyl phosphate.

Antimony oxychloride, known since the 15th century, has been known by a plethora of alchemical names. Since the compound functions as both an emetic and a laxative, it was originally used as a purgative.

Vanadium oxytrichloride is the inorganic compound with the formula VOCl3. This yellow distillable liquid hydrolyzes readily in air. It is an oxidizing agent. It is used as a reagent in organic synthesis. Samples often appear red or orange owing to an impurity of vanadium tetrachloride.
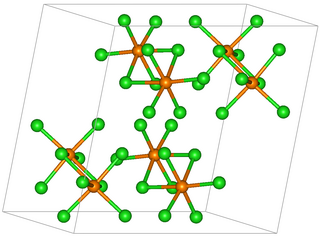
Rhenium pentachloride is an inorganic compound of chlorine and rhenium. The compound has the formula Re2Cl10 but it is usually referred to as rhenium pentachloride. It is a red-brown solid.

Niobium pentoxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Nb2O5. A colorless, insoluble, and fairly unreactive solid, it is the most widespread precursor for other compounds and materials containing niobium. It is predominantly used in alloying, with other specialized applications in capacitors, optical glasses, and the production of lithium niobate.

Arsenic pentachloride is a chemical compound of arsenic and chlorine. This compound was first prepared in 1976 through the UV irradiation of arsenic trichloride, AsCl3, in liquid chlorine at −105 °C. AsCl5 decomposes at around −50 °C. The structure of the solid was finally determined in 2001. AsCl5 is similar to phosphorus pentachloride, PCl5 in having a trigonal bipyramidal structure where the equatorial bonds are shorter than the axial bonds (As-Cleq = 210.6 pm, 211.9 pm; As-Clax= 220.7 pm).

Osmium(IV) chloride or osmium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound composed of osmium and chlorine with the empirical formula OsCl4. It exists in two polymorphs (crystalline forms). The compound is used to prepare other osmium complexes.
The nitridoborates are chemical compounds of boron and nitrogen with metals. These compounds are typically produced at high temperature by reacting hexagonal boron nitride with metal nitrides or by metathesis reactions involving nitridoborates. A wide range of these compounds have been made involving lithium, alkaline earth metals and lanthanides, and their structures determined using crystallographic techniques such as X-ray crystallography. Structurally one of their interesting features is the presence of polyatomic anions of boron and nitrogen where the geometry and the B–N bond length have been interpreted in terms of π-bonding.
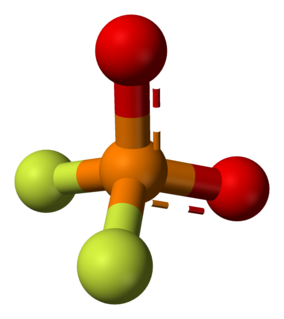
Difluorophosphate or difluorodioxophosphate or phosphorodifluoridate is an anion with formula PO
2F−
2. It has a single negative charge and resembles perchlorate (ClO−
4) and monofluorosulfonate (SO3F−) in shape and compounds. These ions are isoelectronic, along with tetrafluoroaluminate, phosphate, orthosilicate, and sulfate. It forms a series of compounds. The ion is toxic to mammals as it causes blockage to iodine uptake in the thyroid. However it is degraded in the body over several hours.
Georg Karl Brauer was a German chemist.
The telluride iodides are chemical compounds that contain both telluride ions (Te2−) and iodide ions (I−). They are in the class of mixed anion compounds or chalcogenide halides.
A selenite fluoride is a chemical compound or salt that contains fluoride and selenite anions. These are mixed anion compounds. Some have third anions, including nitrate, molybdate, oxalate, selenate, silicate and tellurate.

In chemistry, a transition metal chloride complex is a coordination complex that consists of a transition metal coordinated to one or more chloride ligand. The class of complexes is extensive.
Vanadium (V) chloride chlorimide is a chemical compound containing vanadium in a +5 oxidation state bound to three chlorine atoms and with a double bond to a chlorimide group (=NCl). It has formula VNCl4. This can be also considered as a chloroiminato complex.
Osmium tetrabromide is the inorganic compound with the formula OsBr4. A black solid, this compound can be produced by heating osmium tetrachloride and bromine under pressure.















