
Phosphopentose epimerase encoded by the RPE gene is a metalloprotein that catalyzes the interconversion between D-ribulose 5-phosphate and D-xylulose 5-phosphate.

Methylmalonyl CoA epimerase is an enzyme involved in fatty acid catabolism that is encoded in human by the "MCEE" gene located on chromosome 2. It is routinely and incorrectly labeled as "methylmalonyl-CoA racemase". It is not a racemase because the CoA moiety has 5 other stereocenters.
Epimerases and racemases are isomerase enzymes that catalyze the inversion of stereochemistry in biological molecules. Racemases catalyze the stereochemical inversion around the asymmetric carbon atom in a substrate having only one center of asymmetry. Epimerases catalyze the stereochemical inversion of the configuration about an asymmetric carbon atom in a substrate having more than one center of asymmetry, thus interconverting epimers.
In enzymology, a 3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 4-hydroxyproline epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an ADP-L-glycero-D-manno-heptose 6-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a chondroitin-glucuronate 5-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a dTDP-4-dehydrorhamnose 3,5-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glucose-6-phosphate 1-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a N-acylglucosamine 2-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a threonine racemase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
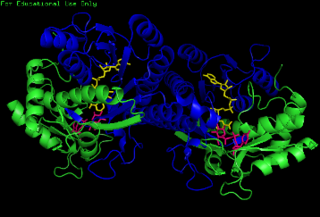
The enzyme UDP-glucose 4-epimerase, also known as UDP-galactose 4-epimerase or GALE, is a homodimeric epimerase found in bacterial, fungal, plant, and mammalian cells. This enzyme performs the final step in the Leloir pathway of galactose metabolism, catalyzing the reversible conversion of UDP-galactose to UDP-glucose. GALE tightly binds nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a co-factor required for catalytic activity.
In enzymology, an UDP-glucuronate 4-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an UDP-glucuronate 5'-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
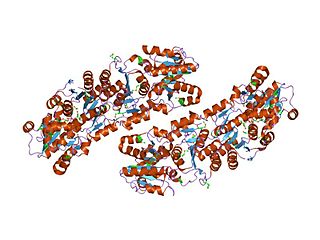
In enzymology, an UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an isonocardicin synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Bifunctional UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GNE gene.

Nocardicin A is a monocyclic β-lactam antibiotic included in the monobactam subclass. It is obtained from the fermentation broth of a strain of actinomycetes Nocardia uniformis subsp. tsuyamenensis as a metabolic product catalyzed by the enzyme nocardicin-A epimerase. It is stereochemically and biologically related to penicillin and cephalosporins.
NAD(P)H-hydrate epimerase is an enzyme with systematic name (6R)-6beta-hydroxy-1,4,5,6-tetrahydronicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide 6-epimerase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction








