
Ammonoids are a group of extinct marine mollusc animals in the subclass Ammonoidea of the class Cephalopoda. These molluscs, commonly referred to as ammonites, are more closely related to living coleoids than they are to shelled nautiloids such as the living Nautilus species. The earliest ammonites appeared during the Devonian, with the last species vanishing during the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event.

Hamites is a genus of heteromorph ammonite that evolved late in the Aptian stage of the Early Cretaceous and lasted into the Cenomanian stage of the Late Cretaceous. The genus is almost certainly paraphyletic but remains in wide use as a "catch all" for heteromorph ammonites of the superfamily Turrilitoidea that do not neatly fit into the more derived groupings. In an attempt to identify clades within the genus, it has been divided up into a series of new genera or subgenera by different palaeontologists, including Eohamites, Hamitella, Helicohamites, Lytohamites, Planohamites, Psilohamites, and Sziveshamites.

Nautiloids are a group of marine cephalopods (Mollusca) which originated in the Late Cambrian and are represented today by the living Nautilus and Allonautilus. Fossil nautiloids are diverse and speciose, with over 2,500 recorded species. They flourished during the early Paleozoic era, when they constituted the main predatory animals. Early in their evolution, nautiloids developed an extraordinary diversity of shell shapes, including coiled morphologies and giant straight-shelled forms (orthocones). Only a handful of rare coiled species, the nautiluses, survive to the present day.

Baculites is an extinct genus of cephalopods with a nearly straight shell, included in the heteromorph ammonites. The genus, which lived worldwide throughout most of the Late Cretaceous, and which briefly survived the K-Pg mass extinction event, was named by Lamarck in 1799.
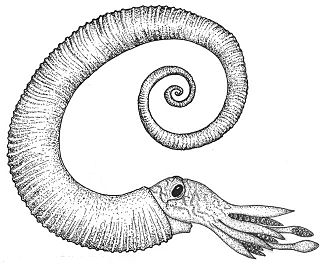
The Ancyloceratina were a diverse suborder of ammonite most closely related to the ammonites of order Lytoceratina. They evolved during the Late Jurassic but were not very common until the Cretaceous period, when they rapidly diversified and became one of the most distinctive components of Cretaceous marine faunas. They have been recorded from every continent and many are used as zonal or index fossils. The most distinctive feature of the majority of the Ancyloceratina is the tendency for most of them to have shells that are not regular spirals like most other ammonites. These irregularly-coiled ammonites are called heteromorph ammonites, in contrast to regularly coiled ammonites, which are called homomorph ammonites.

Scaphites is a genus of heteromorph ammonites belonging to the Scaphitidae family. They were a widespread genus that thrived during the Late Cretaceous period.

Didymoceras is an extinct genus of ammonite cephalopod from the Late Cretaceous epoch. It is one of the most bizarrely shaped genera, with a shell that spirals upwards into a loose, hooked tip. It is thought to have drifted in the water vertically, moving up and down. The generic name is Greek for "paired horns".

Ainoceras is a genus of extinct, aberrantly coiled ammonite cephalopod that live in the Pacific Ocean during the Campanian division of the Cretaceous, where Japan is today. Their shells were coiled very similarly to the related Anaklinoceras, in that, when young, the shell coiled helically, and then upon reaching adulthood, the shell then bent over the older coils. However, Ainoceras differed in this respect in that, whereas in Anaklinoceras, the youngest coil wrapped very closely around the older coils, while in Ainoceras, the youngest coil bent over the older coils in a wide loop or oxbow.

Allocrioceras is an ammonoid cephalopod from the Turonian to Santonian stages of the Late Cretaceous, included in the turrilitoid family Anisoceratidae. Its shell is strongly ribbed and is in the form of a widely open spiral.

Ancyloceras is an extinct genus of heteromorph ammonites found throughout the world during the Lower Cretaceous, from the Lower Barremian epoch until the genus extinction during the Lower Aptian.
Fresvillia is an extinct cephalopod genus belonging to baculitid family of the ammonoid order Ancyloceratida that lived during the Late Cretaceous, found in France. Baculitids are a kind of heteromorph ammonite characterized by a straight adult shaft, often preceded by a small coiled juvenile portion.

Baculitidae is a family of extinct ammonoid cephalopods that lived mostly during the Late Cretaceous, and often included in the suborder Ancyloceratina.

Exiteloceras is an ammonite genus from the Late Cretaceous.

Nostoceras is an extinct genus of ammonites. The etymology of the name Nostoceras comes from "nostos" meaning return and "ceros" meaning horn, named as such by Alpheus Hyatt because it bends back on itself.
Heteroceras is a Lower Cretaceous heteromorph ammonite belonging to the ancyloceratoidean family, Heteroceratidae.

Eubostrychoceras is a genus of helically wound, corkscrew form, heteromorph ammonite which lived during the Upper Cretaceous. The genus is included in the ancycleratid family Nostoceratidae.

Didymoceras nebrascense was an extinct species of heteromorph ammonite from the upper Campanian age. It was sexually dimorphic, with two adult sizes averaging at 270 mm (11
Acrioceratidae is a family of heteromorph ammonites included in the Ancyloceratoidea comprising ancyloceratid-like forms that start off with a coiled juvenile section, followed by a straight or curved shaft ending in a hook. Two described genera are included, Acrioceras and Dissimilites.
Antarcticoceras is a genus of crioconic ammonites in the family Shasticrioceratidae. It lived during the Early Cretaceous Period. Antarcticioceras fossils can be found in the Cretaceous rocks of Antarctica and South America.

Macroscaphitidae is an extinct family of ptychoceratoid cephalopods from the subclass Ammonoidea that lived from the Lower Barremian to the Lower Cenomanian stages of the Cretaceous. Fossils of Macroscaphitidae were found all around the world although the abundance of found fossils is rather limited. Known fossils from collections were found largely in Europe, South America and Africa. It is known for some species of which complete specimens were found that these animals developed a hetermorphic shell, i.e. the coiling of the shell was not regular, such that the first whirls formed a planispirally coiled evolute section as seen in homomorphic ammonites, but had an additional straight middle part and a presumably upwards facing aperture. Due to their odd morphology the taxonomic classification of Macroscaphitidae changed often over time since their discovery and may not be finally settled even now.
















