
Nymphaeaceae is a family of flowering plants, commonly called water lilies. They live as rhizomatous aquatic herbs in temperate and tropical climates around the world. The family contains five genera with about 70 known species. Water lilies are rooted in soil in bodies of water, with leaves and flowers floating on or rising from the surface. Leaves are oval and heart-shaped in Barclaya. Leaves are round, with a radial notch in Nymphaea and Nuphar, but fully circular in Victoria and Euryale.

Nuphar is a genus of aquatic plants in the family Nymphaeaceae, with a temperate to subarctic Northern Hemisphere distribution. Common names include water-lily, pond-lily, alligator-bonnet or bonnet lily, and spatterdock.

Nymphaea lotus, the white Egyptian lotus, tiger lotus, white lotus, or Egyptian water-lily, is a flowering plant of the family Nymphaeaceae.

Nuphar lutea, the yellow water-lily, brandy-bottle, or spadderdock, is an aquatic plant of the family Nymphaeaceae, native to northern temperate and some subtropical regions of Europe, northwest Africa, and western Asia. This species was used as a food source and in medicinal practices from prehistoric times with potential research and medical applications going forward.

Nuphar advena is a species of Nuphar native throughout the eastern United States and in some parts of Canada, such as Nova Scotia, as well as Mexico and Cuba. It is locally naturalized in Britain.

Nymphaea macrosperma is an annual or perennial, aquatic, rhizomatous herb in the family Nymphaeaceae native to Australia and New Guinea.

Nuphar pumila, the least water-lily, is a perennial, rhizomatous, aquatic herb in the family Nymphaeaceae native to subarctic and temperate Eurasia.

Nuphar microphylla is a perennial, rhizomatous, aquatic herb found in North America. It is listed as a special concern and believed extirpated in Connecticut.

Nuphar subintegerrima is a species of rhizomatous aquatic plant endemic to Japan.

Nymphaea prolifera is a species of waterlily naturally found from Mexico to Brazil and northeastern Argentina. Additionally, it has been reported to occur in Uruguay.
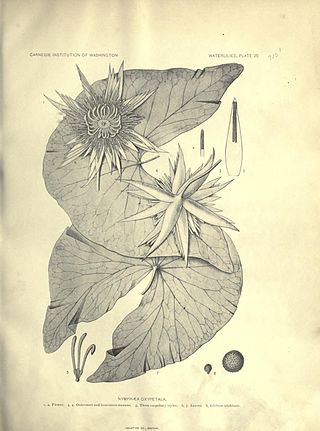
Nymphaea oxypetala is a species of waterlily native to Bolivia, Brazil, Cuba, Ecuador, Paraguay, and Venezuela. It is a remarkable species with excessively acuminate and acute sepals and petals.

Nymphaea rudgeana is a species of waterlily native to the region spanning from Mexico to tropical South America.

Nuphar submersa is a species of rhizomatous aquatic plant endemic to Japan.

Nuphar oguraensis is a species of rhizomatous aquatic plant endemic to Japan.

Nuphar × saijoensis is a species of rhizomatous aquatic plant endemic to Japan. It is a natural hybrid of Nuphar japonica and Nuphar pumila, or Nuphar japonica and Nuphar pumila subsp. oguraensis.

Nuphar × rubrodisca is a species of rhizomatous aquatic plant native to Canada and the USA. It is a natural hybrid of Nuphar variegata and Nuphar microphylla.
Cabomba palaeformis is a species of aquatic plant in the family Cabombaceae native to Mexico and Central America.

Nuphar pumila subsp. sinensis is a subspecies of Nuphar pumila native to China.

Nuphar sect. Astylus is a section within the genus Nuphar native to North America.

Nuphar sect. Nuphar is a section within the genus Nuphar native to Eurasia, in addition to a single North American species Nuphar microphylla.

















