
Migraine is a common neurological disorder characterized by recurrent headaches. Typically, the associated headache affects one side of the head, is pulsating in nature, may be moderate to severe in intensity, and could last from a few hours to three days. Non-headache symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light, sound, or smell. The pain is generally made worse by physical activity during an attack, although regular physical exercise may prevent future attacks. Up to one-third of people affected have aura: typically, it is a short period of visual disturbance that signals that the headache will soon occur. Occasionally, aura can occur with little or no headache following, but not everyone has this symptom.
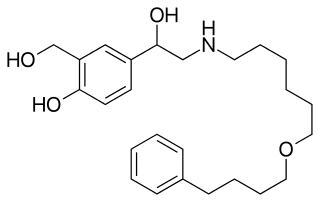
Long-acting β adrenoceptor agonists are usually prescribed for moderate-to-severe persistent asthma patients or patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). They are designed to reduce the need for shorter-acting β2 agonists such as salbutamol (albuterol), as they have a duration of action of approximately 12 hours in comparison with the 4-to-6-hour duration of salbutamol, making them candidates for sparing high doses of corticosteroids or treating nocturnal asthma and providing symptomatic improvement in patients with COPD. With the exception of formoterol, long-acting β2 agonists are not recommended for the treatment of acute asthma exacerbations because of their slower onset of action compared to salbutamol. Their long duration of action is due to the addition of a long, lipophilic side-chain that binds to an exosite on adrenergic receptors. This allows the active portion of the molecule to continuously bind and unbind at β2 receptors in the smooth muscle in the lungs.
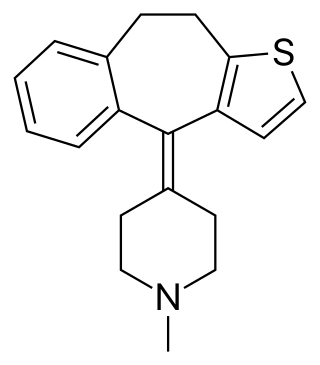
Pizotifen (INN) or pizotyline (USAN), trade name Sandomigran, is a benzocycloheptene-based drug used as a medicine, primarily as a preventive to reduce the frequency of recurrent migraine headaches.

Antimigraine drugs are medications intended to reduce the effects or intensity of migraine headache. They include drugs for the treatment of acute migraine symptoms as well as drugs for the prevention of migraine attacks.

Nelivaptan (INN) is a selective, orally active, non-peptide vasopressin receptor antagonist selective for the V1B subtype. The drug had entered clinical trials for treatment of anxiety and depression. In July 2008, Sanofi-Aventis announced that further development of this drug had been halted.

Vedaclidine (INN, codenamed LY-297,802, NNC 11-1053) is an experimental analgesic drug which acts as a mixed agonist–antagonist at muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, being a potent and selective agonist for the M1 and M4 subtypes, yet an antagonist at the M2, M3 and M5 subtypes. It is orally active and an effective analgesic over 3× the potency of morphine, with side effects such as salivation and tremor only occurring at many times the effective analgesic dose. Human trials showed little potential for development of dependence or abuse, and research is continuing into possible clinical application in the treatment of neuropathic pain and cancer pain relief.

Oxetorone (INN), as oxetorone fumarate (USAN), is a serotonin antagonist, antihistamine, and alpha blocker used as an antimigraine drug. Association with hyperprolactinemia has been described and antidopaminergic actions are also suspected.
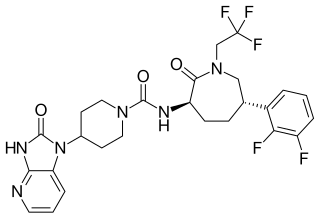
Telcagepant (INN) is a calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor antagonist which was an investigational drug for the acute treatment and prevention of migraine, developed by Merck & Co.
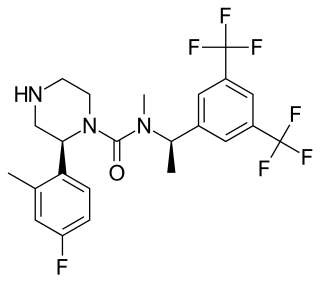
Vestipitant (INN) is a drug developed by GlaxoSmithKline which acts as a selective antagonist for the NK1 receptor. It is under development as a potential antiemetic and anxiolytic drug, and as a treatment for tinnitus and insomnia.
Preventive treatment of migraine can be an important component of migraine management. Such treatments can take many forms, including everything from surgery, taking certain drugs or nutritional supplements, to lifestyle alterations such as increased exercise and avoidance of migraine triggers.

Ezlopitant (INN, code name CJ-11,974) is an NK1 receptor antagonist. It has antiemetic and antinociceptive effects. Pfizer was developing ezlopitant for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome but it appears to have been discontinued.

Terbogrel (INN) is an experimental drug that has been studied for its potential to prevent the vasoconstricting and platelet-aggregating action of thromboxanes. Terbogrel is an orally available thromboxane A2 receptor antagonist and a thromboxane A synthase inhibitor. The drug was developed by Boehringer Ingelheim.

Elinogrel (INN, USAN) was an experimental antiplatelet drug acting as a P2Y12 inhibitor. Similarly to ticagrelor and in contrast to clopidogrel, elinogrel was a reversible inhibitor that acted fast and short (for about 12 hours), and it was not a prodrug but pharmacologically active itself. The substance was used in form of its potassium salt, intravenously for acute treatment and orally for long-term treatment. Development was terminated in 2012.
An orexin receptor antagonist, or orexin antagonist, is a drug that inhibits the effect of orexin by acting as a receptor antagonist of one or both of the orexin receptors, OX1 and OX2. Medical applications include treatment of sleep disorders such as insomnia.

Abediterol is a once-daily experimental drug candidate for the treatment of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It is currently under development by the Spanish pharmaceutical company Almirall and is in Phase II clinical trials.
Inclacumab (LC1004-002) (INN) is a human monoclonal antibody designed for the treatment of cardiovascular disease.
Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor antagonists are a class of drugs that act as antagonists of the calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor (CGRPR).

Serlopitant (INN, codenamed VPD-737) is a drug which acts as an NK1 receptor antagonist. It was assessed in clinical trials for the treatment of urinary incontinence and overactive bladder, but while it was superior to placebo it provided no advantage over existing approved drugs, and was not approved for further development for this indication. Serlopitant is now undergoing clinical trials for the treatment of chronic pruritus (itch)

Erenumab, sold under the brand name Aimovig, is a medication which targets the calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor (CGRPR) for the prevention of migraine. It is administered by subcutaneous injection.

Lanepitant (INN, code name LY303870) is a drug developed by Eli Lilly which acts as a selective antagonist for the NK1 receptor, and was one of the first compounds developed that act at this target. It was under development as a potential analgesic drug, but despite promising results in initial animal studies, human clinical trials against migraine, arthritis and diabetic neuropathy all failed to show sufficient efficacy to support further development, with the drug being only marginally more effective than placebo and inferior to older comparison drugs such as naproxen. Failure of analgesic action was thought to be due to poor penetration of the blood–brain barrier in humans, but research has continued into potential applications in the treatment of other disorders with a peripheral site of action, such as corneal neovascularization.
















