West Bridgewater is a town in Plymouth County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 7,707 at the 2020 census.

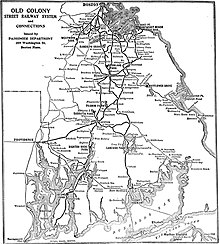
The Old Colony Railroad (OC) was a major railroad system, mainly covering southeastern Massachusetts and parts of Rhode Island, which operated from 1845 to 1893. Old Colony trains ran from Boston to points such as Plymouth, Fall River, New Bedford, Newport, Providence, Fitchburg, Lowell and Cape Cod. For many years the Old Colony Railroad Company also operated steamboat and ferry lines, including those of the Fall River Line with express train service from Boston to its wharf in Fall River where passengers boarded luxury liners to New York City. The company also briefly operated a railroad line on Martha's Vineyard, as well as the freight-only Union Freight Railroad in Boston. The OC was named after the "Old Colony", the nickname for the Plymouth Colony.

The West End Street Railway was a streetcar company that operated in Boston, Massachusetts and several surrounding communities in the late nineteenth century.

The Boston and Providence Railroad was a railroad company in the states of Massachusetts and Rhode Island which connected its namesake cities. It opened in two sections in 1834 and 1835 - one of the first rail lines in the United States - with a more direct route into Providence built in 1847. Branches were built to Dedham in 1834, Stoughton in 1845, and North Attleboro in 1871. It was acquired by the Old Colony Railroad in 1888, which in turn was leased by the New Haven Railroad in 1893. The line became the New Haven's primary mainline to Boston; it was realigned in Boston in 1899 during the construction of South Station, and in Pawtucket and Central Falls in 1916 for grade crossing elimination.
The Central Massachusetts Railroad was a railroad in Massachusetts. The eastern terminus of the line was at North Cambridge Junction where it split off from the Middlesex Central Branch of the Boston and Lowell Railroad in North Cambridge and through which it had access to North Station in Boston. From there, the route ran 98.77 miles west through the modern-day towns of Belmont, Waltham, Weston, Wayland, Sudbury, Hudson, Bolton, Berlin, Clinton, West Boylston, Holden, Rutland, Oakham, Barre, New Braintree, Hardwick, Ware, Palmer, Belchertown, Amherst, and Hadley to its western terminal junction at N. O. Tower in Northampton with the Connecticut River Railroad.

The Fall River Branch Railroad was incorporated in Massachusetts in 1844, to provide a rail link from the emerging textile town of Fall River to the New Bedford and Taunton Railroad at Myricks Junction. It began operating in 1845 with 12 miles of track. A year later, in 1846 it merged with the Middleborough Railroad Corporation and the Randolph & Bridgewater Railroad Corporation to become the Fall River Railroad Company, with a new connection to Bridgewater. It operated as the Fall River Railroad until 1854 when it merged into the Old Colony Railroad to become the Old Colony and Fall River Railroad Company.

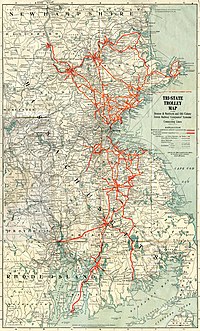
The Connecticut Company was the primary electric street railway company in the U.S. state of Connecticut, operating both city and rural trolleys and freight service. It was controlled by the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad, which also controlled most steam railroads in the state. After 1936, when one of its major leases was dissolved, it continued operating streetcars and, increasingly, buses in certain Connecticut cities until 1976, when its assets were purchased by the state government.
Memorial Press Group, based in Plymouth, Massachusetts, United States, was a chain of weekly newspapers along the South Shore near Boston, Massachusetts. Long owned by The Patriot Ledger in nearby Quincy, MPG and its daily parent were sold to GateHouse Media in 2006.

Brockton station is an MBTA Commuter Rail station in Brockton, Massachusetts. It serves the MBTA Middleborough/Lakeville Line and is a stop on the CapeFLYER seasonal line. The station consists of a single full-length high-level platform which is fully handicapped accessible. It is located adjacent to the BAT Centre, the primary hub for Brockton Area Transit Authority local bus service.

Brockton Area Transit Authority, branded as Brockton Area Transit (BAT), is a public, non-profit organization in Massachusetts, charged with providing public transportation to the Brockton area, consisting of the city of Brockton and the adjoining towns of Abington, Avon, Bridgewater, East Bridgewater, Easton, Hanson, Rockland, Stoughton, West Bridgewater and Whitman.

The Fall River Railroad was incorporated in 1846 as a merger between the Fall River Branch Railroad, the Middleborough Railroad Corporation and the Randolph & Bridgewater Railroad Corporation. The railroad ran from Fall River through Middleborough and Bridgewater to South Braintree where it connected to the Old Colony Railroad line.
The New Bedford and Taunton Railroad was originally incorporated at the Old Colony Railroad Corporation in 1836 as an extension of the Taunton Branch Railroad between Taunton and New Bedford, Massachusetts, United States. The name was changed to "New Bedford and Taunton Railroad" in 1839 before service began in 1840. The line ran 20 miles between Taunton and New Bedford.
The Dighton and Somerset Railroad, currently referred to as the Dean Street Industrial Track, is a railroad that ran between Fall River and Braintree, Massachusetts. It opened in 1866; from the 1890s to the 1930s and again in the late 1950s, it was the primary rail route from Boston to the South Coast. Passenger service ended in stages with the final regular service in 1958, though freight service on two short segments continues into the 21st century. MBTA Commuter Rail service is proposed to be extended onto the northern part of the line around 2030 as part of the South Coast Rail project.
The New Bedford Railroad was a railroad in Massachusetts. It was incorporated on July 1, 1873, as a merger between the New Bedford and Taunton Railroad, the Taunton Branch Railroad, and the Middleborough and Taunton Railroad. The main line ran from a junction with the Boston and Providence Railroad in Mansfield through the towns of Norton, Taunton, Berkley, Lakeville, and Freetown to the deep-water whaling port of New Bedford. The railroad also had several branches, including the former Middleborough and Taunton Railroad, which ran from Weir Village, Taunton into Middleborough through Raynham, and a shortcut to Providence via the Boston and Providence Railroad which ran from Taunton to Attleborough through Norton.
The Lynn and Boston Railroad was a streetcar railway chartered for operations between Boston and Lynn, Massachusetts in 1859. Following a number of acquisitions, the railway was a part of a 1901 street railway merger that formed the Boston and Northern Street Railway.

The Bay State Street Railway Company was a horse-drawn and electric streetcar railroad operated on the streets of Boston, Massachusetts and communities directly north and south of the city. Its immediate successor was the Eastern Massachusetts Street Railway, and its modern successor is the state-run Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA).

Middleborough station is an under-construction MBTA Commuter Rail station in Middleborough, Massachusetts. It is expected to open in late 2023 as part of the South Coast Rail project, replacing Middleborough/Lakeville station for regular service. The station will have a single side platform located inside the wye between the Middleborough Main Line and the Middleboro Secondary.

The South Boston Railroad was a street railway company that operated in Boston, Massachusetts in the mid-nineteenth century. It provided horsecar service for passengers traveling between South Boston and the city downtown.

The Middlesex Railroad was an early street railway company that operated in the Boston, Massachusetts area in the mid-nineteenth century. It provided horsecar service for passengers traveling between Charlestown/lower Middlesex County and downtown Boston.

The Boston & Northern Street Railway Company (B&N) was a horse-drawn and electric streetcar railroad operated on the streets of Boston, Massachusetts, and communities to the north. Founded in 1859 as the Lynn and Boston Railroad (L&B), via lease and merger it became a primary mass transit provider for northeastern Massachusetts and New Hampshire. Its immediate successor was the Bay State Street Railway , and its modern successor is the state-run Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA).