
The treble-bar or St. John's wort inchworm is a moth of the family Geometridae. the species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae. It is found throughout the Palearctic region and the Near East.

The garden dart is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is distributed throughout much of the Palearctic. Temperate regions of Europe, Central Asia and North Asia, as well as the mountains of North Africa. Absent from polar regions, on Iceland and some Mediterranean islands, as well as in Macaronesia.

The lesser broad-bordered yellow underwing or Langmaid's yellow underwing is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is distributed throughout southern and central Europe, and southern Sweden.

The ingrailed clay is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Johan Christian Fabricius in 1775. It is distributed through most of Europe and the Palearctic.

The small square-spot is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Karl Friedrich Vieweg in 1790. It is found in Europe apart from the far south-east then east through the Caucasus, Transcaucasia, Central Asia, Siberia, the Russian Far East and Kamchatka.

Mythimna impura, the smoky wainscot, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Jacob Hübner in 1808. It is distributed throughout most of the Palearctic realm from Ireland in the west of Europe east to the Caucasus, Turkey, Syria, Kazakhstan, Russia, Siberia, Mongolia, then Japan. In Europe it is found from the Arctic Circle to Spain and Italy in the south, as well as in the northern regions of Greece.

Mythimna pallens, the common wainscot, is a moth of the family Noctuidae distributed throughout the Palearctic realm from Ireland in the west, through Europe to Central Asia and Amur to the Kuriles in the east. The species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae.

Agrochola circellaris, or The Brick, is a species of moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Johann Siegfried Hufnagel in 1766. It is distributed throughout most of Europe, Asia Minor and Armenia.

The copper underwing, humped green fruitworm or pyramidal green fruitworm is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae.

The straw underwing is a species of moth in the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Johann Siegfried Hufnagel in 1766. It is found from North Africa west through South Europe and Central Europe. In the north it is in parts of Ireland, Scotland, Sweden, Norway, Finland and Estonia. Further east the range stretches from southern Russia and Asia minor to the Caucasus.

Apamea remissa, the dusky brocade, is a species of moth of the family Noctuidae. It is distributed throughout Europe and Turkey, ranging across the Palearctic realm to Siberia, Manchuria and Japan. It has also been reported from Alaska.

The marbled minor is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae. It is distributed throughout Europe, east through the Palearctic to central Asia and the Altai Mountains. It rises to heights of over 1500 meters in the Alps.

Oligia latruncula, the tawny marbled minor, is a species of moth belonging to the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Michael Denis and Ignaz Schiffermüller in 1775. It is distributed throughout Europe from northern Scotland and middle Fennoscandia in the north and then south to central Spain, Sicily and Greece. In the east, the species ranges to Western Asia. In the Alps it rises to an altitude of 2000 meters.

The mullein moth is a noctuid moth with a Palearctic distribution. The species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his landmark 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae.

Mesoligia furuncula, the cloaked minor, is a moth of the family Noctuoidea. It is found in the Palearctic realm (Europe, northwest Africa, Russia, Siberia, Japan, north Iran, Afghanistan, and China.

Mythimna straminea, the southern wainscot, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Georg Friedrich Treitschke in 1825. It is found in the western parts of the Palearctic realm, including Morocco, Europe, Turkey, the Caucasus, Israel, and Lebanon.
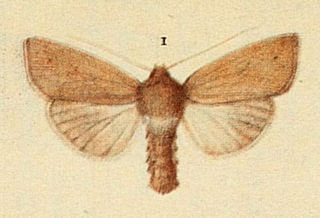
Mythimna favicolor, or Mathew's wainscot, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Charles Golding Barrett in 1896. It is found in Europe. The species is sometimes treated as a subspecies of Mythimna pallens, the common wainscot.

Shargacucullia lychnitis, the striped lychnis is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found throughout most parts of Europe the Near East and Middle East.

Mesoligia literosa, the rosy minor, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Adrian Hardy Haworth in 1809. It is found throughout Europe, North Africa and western Asia. and east across the Palearctic to Siberia.

Oligia dubia is a species of moth belonging to the family Noctuidae.





















