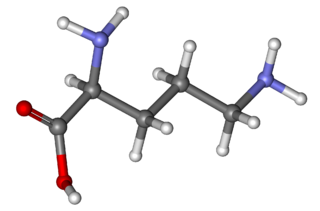
Ornithine is a non-proteinogenic amino acid that plays a role in the urea cycle. Ornithine is abnormally accumulated in the body in ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. The radical is ornithyl.
The enzyme ornithine decarboxylase catalyzes the decarboxylation of ornithine to form putrescine. This reaction is the committed step in polyamine synthesis. In humans, this protein has 461 amino acids and forms a homodimer.

Ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC) is an enzyme that catalyzes the reaction between carbamoyl phosphate (CP) and ornithine (Orn) to form citrulline (Cit) and phosphate (Pi). There are two classes of OTC: anabolic and catabolic. This article focuses on anabolic OTC. Anabolic OTC facilitates the sixth step in the biosynthesis of the amino acid arginine in prokaryotes. In contrast, mammalian OTC plays an essential role in the urea cycle, the purpose of which is to capture toxic ammonia and transform it into urea, a less toxic nitrogen source, for excretion.

Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP, pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, P5P), the active form of vitamin B6, is a coenzyme in a variety of enzymatic reactions. The International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology has catalogued more than 140 PLP-dependent activities, corresponding to ~4% of all classified activities. The versatility of PLP arises from its ability to covalently bind the substrate, and then to act as an electrophilic catalyst, thereby stabilizing different types of carbanionic reaction intermediates.

The enzyme phenylalanine racemase is the enzyme that acts on amino acids and derivatives. It activates both the L & D stereo isomers of phenylalanine to form L-phenylalanyl adenylate and D-phenylalanyl adenylate, which are bound to the enzyme. These bound compounds are then transferred to the thiol group of the enzyme followed by conversion of its configuration, the D-isomer being the more favorable configuration of the two, with a 7 to 3 ratio between the two isomers. The racemisation reaction of phenylalanine is coupled with the highly favorable hydrolysis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and pyrophosphate (PP), thermodynamically allowing it to proceed. This reaction is then drawn forward by further hydrolyzing PP to inorganic phosphate (Pi), via Le Chatelier's principle.
Serine racemase is the first racemase enzyme in human biology to be identified. This enzyme converts L-serine to its enantiomer form, D-serine. D-serine acts as a neuronal signaling molecule by activating NMDA receptors in the brain.
In enzymology, a 2-aminohexano-6-lactam racemase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, an alanine racemase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

α-Methylacyl-CoA racemase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AMACR gene. AMACR catalyzes the following chemical reaction:
In enzymology, an amino-acid racemase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an arginine racemase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, glutamate racemase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a methionine racemase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a proline racemase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme ornithine cyclodeaminase catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a lysine carbamoyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-acetylornithine carbamoyltransferase (EC 2.1.3.9) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme diaminopimelate decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.20) catalyzes the cleavage of carbon-carbon bonds in meso 2,6 diaminoheptanedioate to produce CO2 and L-lysine, the essential amino acid. It employs the cofactor pyridoxal phosphate, also known as PLP, which participates in numerous enzymatic transamination, decarboxylation and deamination reactions.
Hydantoin racemase is an enzyme with systematic name D-5-monosubstituted-hydantoin racemase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction










