Related Research Articles

Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) is a blood disorder that results in blood clots forming in small blood vessels throughout the body. This results in a low platelet count, low red blood cells due to their breakdown, and often kidney, heart, and brain dysfunction. Symptoms may include large bruises, fever, weakness, shortness of breath, confusion, and headache. Repeated episodes may occur.
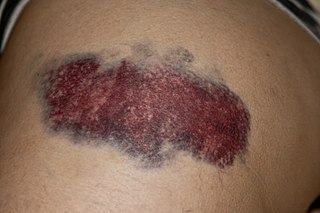
A bruise, also known as a contusion, is a type of hematoma of tissue, the most common cause being capillaries damaged by trauma, causing localized bleeding that extravasates into the surrounding interstitial tissues. Most bruises occur close enough to the epidermis such that the bleeding causes a visible discoloration. The bruise then remains visible until the blood is either absorbed by tissues or cleared by immune system action. Bruises which do not blanch under pressure can involve capillaries at the level of skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscle, or bone.

Henoch–Schönlein purpura (HSP), also known as IgA vasculitis, is a disease of the skin, mucous membranes, and sometimes other organs that most commonly affects children. In the skin, the disease causes palpable purpura, often with joint pain and abdominal pain. With kidney involvement, there may be a loss of small amounts of blood and protein in the urine, but this usually goes unnoticed; in a small proportion of cases, the kidney involvement proceeds to chronic kidney disease. HSP is often preceded by an infection, such as a throat infection.

Purpura is a condition of red or purple discolored spots on the skin that do not blanch on applying pressure. The spots are caused by bleeding underneath the skin secondary to platelet disorders, vascular disorders, coagulation disorders, or other causes. They measure 3–10 mm, whereas petechiae measure less than 3 mm, and ecchymoses greater than 1 cm.

A petechia is a small red or purple spot that can appear on the skin, conjunctiva, retina, and mucous membranes which is caused by haemorrhage of capillaries. The word is derived from Italian petecchia, 'freckle,' of obscure origin. It refers to one of the three descriptive types of hematoma differentiated by size, the other two being ecchymosis and purpura. The term is typically used in the plural (petechiae), since a single petechia is seldom noticed or significant.
Purpura fulminans is an acute, often fatal, thrombotic disorder which manifests as blood spots, bruising and discolouration of the skin resulting from coagulation in small blood vessels within the skin and rapidly leads to skin necrosis and disseminated intravascular coagulation.

Schamberg's disease, is a chronic discoloration of the skin found in people of all ages, usually only affecting the feet, legs or thighs or a combination. It may occur as a single event or subsequent bouts may cause further spread. It is most common in males. It is named after Jay Frank Schamberg, who described it in 1901. There is no known cure for this disease but it is not a life-threatening condition and is mainly of cosmetic concern, although, because it can appear so suddenly, so extensively and because it usually leaves permanent discoloration of the skin, it can cause understandable psychological concern. The skin lesions sometimes cause itching, which can be treated by applying cortisone cream. The cortisone cream will only help with the itching and does not improve the discoloration of the skin. Schamberg's disease causes no other symptoms beside skin discoloration and itching. The condition is caused by inflammation of capillaries near the surface of skin and subsequent leaking of red blood cells into surrounding tissues. As the red blood cells break down and get mostly resorbed, some of the iron released by the red blood cells remains in the skin and causes the characteristic rust-colored appearance. The cause of the capillary inflammation is usually unknown.

Amyloid purpura is a condition marked by bleeding under the skin (purpura) in some individuals with amyloidosis. Its cause is unknown, but coagulation defects caused by amyloid are thought to contribute.
Nonthrombocytopenic purpura is a type of purpura not associated with thrombocytopenia.
Waldenström hyperglobulinemic purpura is a skin condition that presents with episodic showers of petechiae occurring on all parts of the body, most profusely on the lower extremities.

Solar purpura is a skin condition characterized by large, sharply outlined, 1- to 5-cm, dark purplish-red ecchymoses appearing on the dorsa of the forearms and less often the hands.
Obstructive purpura is a skin condition that may result from mechanical obstruction to circulation, with resulting stress on the small vessels leading to purpura.
Traumatic purpura is a skin condition resulting from trauma which produces ecchymoses of bizarre shapes suggestive of abuse.
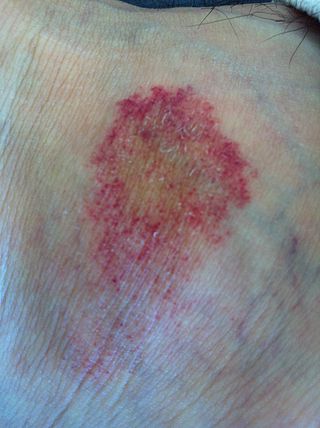
Pigmented purpuric dermatosis refers to one of the three major classes of skin conditions characterized by purpuric skin eruptions.

Majocchi's disease, also known as Purpura annularis telangiectodes of Majocchi is a not-well-recognized and uncommon skin condition characterized by purple/bluish-red 1- to 3-cm annular patches composed of dark red telangiectases with petechiae. It is one of a group of disorders referred to as pigmented purpuric dermatosis that all occur as a result of vascular inflammation and pigment deposition.
Doucas and Kapetanakis pigmented purpura, also known as eczematoid purpura, or eczematoid-like purpura, is a skin condition characterized by scaly and eczematous patches, which also have petechiae and hemosiderin staining.

Cutaneous small-vessel vasculitis (CSVV), is inflammation of small blood vessels, usually accompanied by small lumps beneath the skin. The condition is also known as hypersensitivity vasculitis, cutaneous leukocytoclastic vasculitis, hypersensitivity angiitis, cutaneous leukocytoclastic angiitis, cutaneous necrotizing vasculitis and cutaneous necrotizing venulitis,

Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy (AHEI) is a type of leukocytoclastic vasculitis that is not fatal. Although it causes fever, large palpable purpuric skin lesions, and edema, it is a harmless condition. AHEI's appearance is frequently similar to that of Henoch-Schönlein purpura. Because AHEI is a self-limiting disease, conservative treatment is common.

Palpable purpura is characterized by firm, elevated hemorrhagic plaques or papules that can measure several centimeters in diameter. These are typically found on dependent surfaces, like the back of a recumbent patient or the lower legs. The center of a lesion may become ulcerative, pustular, vesicular, necrotic, or nodular. They tend to be asymptomatic, but when nodular or ulcerative, they can become tender. Palpable purpura is the most common cutaneous lesion among individuals with inflammatory vascular injury, whereas nonpalpable purpura typically indicates bleeding caused by a platelet or coagulation disorder.
Cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19 are characteristic signs or symptoms of the Coronavirus disease 2019 that occur in the skin. The American Academy of Dermatology reports that skin lesions such as morbilliform, pernio, urticaria, macular erythema, vesicular purpura, papulosquamous purpura and retiform purpura are seen in people with COVID-19. Pernio-like lesions were more common in mild disease while retiform purpura was seen only in critically ill patients. The major dermatologic patterns identified in individuals with COVID-19 are urticarial rash, confluent erythematous/morbilliform rash, papulovesicular exanthem, chilbain-like acral pattern, livedo reticularis and purpuric "vasculitic" pattern. Chilblains and Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children are also cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19.
References
- ↑ James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-7216-2921-6.