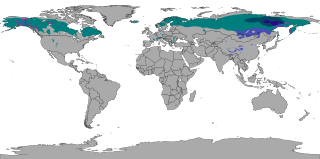
The subarctic climate is a continental climate with long, cold winters, and short, warm to cool summers. It is found on large landmasses, often away from the moderating effects of an ocean, generally at latitudes from 50°N to 70°N, poleward of the humid continental climates. Subarctic or boreal climates are the source regions for the cold air that affects temperate latitudes to the south in winter. These climates represent Köppen climate classification Dfc, Dwc, Dsc, Dfd, Dwd and Dsd.
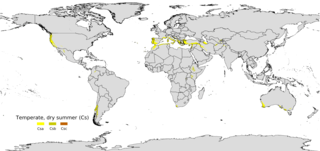
A Mediterranean climate, also called a dry summer climate, described by Köppen as Cs, is a temperate climate type that occurs in the lower mid-latitudes. Such climates typically have dry summers and wet winters, with summer conditions ranging from warm to hot and winter conditions typically being mild. These weather conditions are typically experienced in the majority of Mediterranean-climate regions and countries, but remain highly dependent on proximity to the ocean, altitude and geographical location.

An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification represented as Cfb, typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters, with a relatively narrow annual temperature range and few extremes of temperature. Oceanic climates can be found in both hemispheres generally between 45 and 63 latitude, most notably in northwestern Europe, northwestern America, as well as New Zealand. Other varieties of climates usually classified together with these include subtropical highland climates, represented as Cwb or Cfb, and subpolar oceanic climates, represented as Cfc or Cwc. Subtropical highland climates occur in some mountainous parts of the subtropics or tropics, some of which have monsoon influence, while subpolar oceanic climates occur near polar regions.

Coos Bay is an estuary where the Coos River enters the Pacific Ocean, the estuary is approximately 12 miles long and up to two miles wide. It is the largest estuary completely within Oregon state lines. The Coos Bay watershed covers an area of about 600 square miles and is located in northern Coos County, Oregon in the United States. The Coos River, which begins in the Oregon Coast Range, enters the bay from the east. From Coos River, the bay forms a sharp loop northward before arching back to the south and out to the Pacific Ocean. Haynes Inlet enters the top of this loop. South Slough branches off from the bay directly before its entrance into the Pacific Ocean. The bay was formed when sea levels rose over 20,000 years ago at the end of the Last Glacial Maximum, flooding the mouth of the Coos River. Coos Bay is Oregon's most important coastal industrial center and international shipping port, with close ties to San Francisco, the Columbia River, Puget Sound and other major ports of the Pacific rim.

A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot summers and cold winters. Precipitation is usually distributed throughout the year but often does have dry seasons. The definition of this climate regarding temperature is as follows: the mean temperature of the coldest month must be below 0 °C (32.0 °F) or −3 °C (26.6 °F) depending on the isotherm, and there must be at least four months whose mean temperatures are at or above 10 °C (50 °F). In addition, the location in question must not be semi-arid or arid. The cooler Dfb, Dwb, and Dsb subtypes are also known as hemiboreal climates.

The Southern California Bight is a 692-kilometer-long stretch of curved coastline that runs along the west coast of the United States and Mexico, from Point Conception in California to Punta Colonet in Baja California, plus the area of the Pacific Ocean defined by that curve. This includes the Channel Islands of California and the Coronado Islands and Islas de Todo Santos of Baja California.

Neshaminy State Park is a 330-acre (134 ha) Pennsylvania state park in Bensalem Township, Bucks County, Pennsylvania in the United States. Visitors to the park can catch a glimpse of the Philadelphia skyline from a hiking trail on Logan Point. The park is located at the confluence of Neshaminy Creek and the Delaware River. Neshaminy State Park is just off Interstate 95 on Pennsylvania Route 132.

The Oregon Coast Range, often called simply the Coast Range and sometimes the Pacific Coast Range, is a mountain range, in the Pacific Coast Ranges physiographic region, in the U.S. state of Oregon along the Pacific Ocean. This north-south running range extends over 200 miles (320 km) from the Columbia River in the north on the border of Oregon and Washington, south to the middle fork of the Coquille River. It is 30 to 60 miles wide and averages around 1,500 feet (460 m) in elevation above sea level. The coast range has three main sections, a Northern, Central, and Southern.

Alaska occupies the northwestern portion of the North American continent and is bordered only by Canada on the east. It is one of two U.S. states not bordered by another state; Hawaii is the other. Alaska has more ocean coastline than all of the other U.S. states combined. About 500 miles (800 km) of Canadian territory separate Alaska from Washington state. Alaska is thus an exclave of the United States that is part of the continental U.S. and the U.S. West Coast, but is not part of the contiguous U.S.

The climate of Alaska is determined by average temperatures and precipitation received statewide over many years. The extratropical storm track runs along the Aleutian Island chain, across the Alaska Peninsula, and along the coastal area of the Gulf of Alaska which exposes these parts of the state to a large majority of the storms crossing the North Pacific. The climate in Juneau and the southeast panhandle is a mid-latitude oceanic climate, in the southern sections and a subarctic oceanic climate in the northern parts. The climate in Southcentral Alaska is a subarctic climate due to its short, cool summers. The climate of the interior of Alaska is best described as extreme and is the best example of a true subarctic climate, as the highest and lowest recorded temperatures in Alaska have both occurred in the interior. The climate in the extreme north of Alaska is an Arctic climate with long, cold winters, and cool summers where snow is possible year-round.

North Carolina's climate varies from the Atlantic coast in the east to the Appalachian Mountain range in the west. The mountains often act as a "shield", blocking low temperatures and storms from the Midwest from entering the Piedmont of North Carolina.

The Geography of Oklahoma encompasses terrain and ecosystems ranging from arid plains to subtropical forests and mountains. Oklahoma contains 10 distinct ecological regions, more per square mile than in any other state by a wide margin. It is situated in the Great Plains and U.S. Interior Highlands region near the geographical center of the 48 contiguous states. Usually considered part of the South Central United States, Oklahoma is bounded on the east by Arkansas and Missouri, on the north by Kansas, on the northwest by Colorado, on the far west by New Mexico, and on the south and near-west by Texas.

Devils Punch Bowl State Natural Area is a state day use park on the central Oregon Coast in the United States. It is centered on a large bowl naturally carved in a rock headland which is partially open to the Pacific Ocean. Waves enter the bowl and often violently churn, swirl, and foam. Outside the bowl, ocean conditions are attractive to surfers near a large offshore rock pinnacle named Gull Rock, located about 1⁄2 mile (800 m) west-northwest of Devils Punch Bowl, which funnels and concentrates waves easily seen from the park. There are at least seventeen large rocks, part of Oregon Islands National Wildlife Refuge, which provide interesting wave viewing, and attract and provide a home for wildlife.
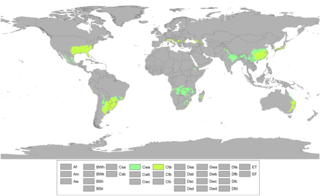
A humid subtropical climate is a temperate climate type characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents, generally between latitudes 25° and 40° and are located poleward from adjacent tropical climates. It is also known as warm temperate climate in some climate classifications.

The climate of Los Angeles is mild to hot year-round, and mostly dry. It is classified as a Mediterranean climate, which is a type of dry subtropical climate. It is characterized by seasonal changes in rainfall—with a dry summer and a winter rainy season. Under the modified Köppen climate classification, the coastal areas are classified as Csb, and the inland areas as Csa.
Mu'minobod, previously known as Muminabad, Leningradskiy or Leningrad is a settlement in south Tajikistan. It is the administrative capital of the Muminobod District in the eastern part of Khatlon Province, located north-east of the city of Kulob, not far from the Panj River and the international border with Afghanistan. The population of the town is 14,100.
Little Rock has a humid subtropical climate, with hot, usually humid summers, but subject to drought, primarily in late summer. According to the Trewartha climate classification system, Little Rock is subtropical because nine of its months exceed 50 °F (10 °C) in average temperature. Summers are usually hot, occasionally extremely hot; winters are short and cool, but with marked temperature variations, as the area is subject to alternating incursions of warm, moist air from the Gulf of Mexico and cold, dry air from Canada.

Dalnevostochny Morskoy Nature Reserve is Russia's first marine reserve, covering large portions of the sea and 30 islands in Peter the Great Gulf, on the west side of the Sea of Japan. It has the highest class of environmental protection as a federal 'zapovednik'. There are four distinct areas with different biological and protection regimes, covering 63,000 ha (240 sq mi) of sea area, additional land on included islands, a 500-meter conservation strip of coastline along the marine area, and a conservation buffer zone inland to a width of 3 miles. The reserve is situated on the continental coast south of Vladivostok in the Russian Far East. The administrative district is Khasansky District of Primorsky Krai. It was formally established in 1978. The reserve is part of the UNESCO "Far East Reserve" MAB Biosphere Reserve, noted for its protection of marine biodiversity, and as a re-population area for open seas fisheries.

Karadag Nature Reserve is a protected nature reserve that covers a portion of the southeast coast of the Crimean peninsula. Encompassing mountains, forest-steppe, shoreline and marine areas, Karadag is an area of high biodiversity and the subject of much scientific study throughout the past 100 years. It supports a high number of Crimea's endemic species, and important bird colonies. The reserve is 36 km southwest of the city of Feodosia, and is currently administered by the Russian Academy of Sciences.

The Petenes mangroves ecoregion covers mangrove habitat along the Gulf of Mexico coast of southern Mexico, where Campeche state and Yucatan state meet, centering on the Celestun Lagoon inland from the barrier-island town of Celestún. Because the region has relatively little rainfall and no rivers feeding the lagoons, the freshwater to support the mangrove ecosystem springs from underground aquifers. The area is important for migratory birds, and as a nesting area for sea turtles. The area around the Celestun Lagoon is protected by the Ría Celestún Biosphere Reserve, a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve.