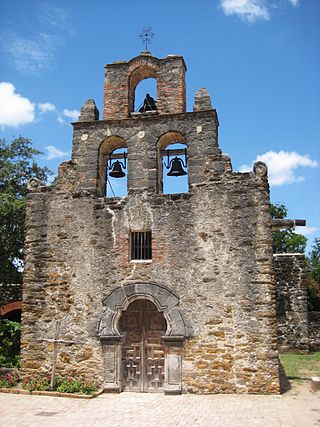The Adai were a Native American people of northwestern Louisiana and northeastern Texas. They were an Indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands and part of the Caddo Confederacy.

Los Adaes was the capital of Tejas (Texas) on the northeastern frontier of New Spain from 1721 to 1773. It included a Franciscan mission, San Miguel de Cuéllar de los Adaes, and a presidio, Nuestra Señora del Pilar de Los Adaes. The name Adaes derives from the indigenous Adai people, members of the Caddoan confederacy of Indians who were the people the missionaries aimed to convert to Christianity. The presidio and mission were established to counter French influence in Louisiana territory and defend New Spain from possible invasion or encroachment by the French. In 1763 Louisiana came under the control of Spain and the Los Adaes outpost was no longer necessary for defense. In 1773 the Spanish closed the mission and presidio and forced the population to move to San Antonio.

San Antonio Missions National Historical Park is a National Historical Park and part of a UNESCO World Heritage Site preserving four of the five Spanish frontier missions in San Antonio, Texas, USA. These outposts were established by Catholic religious orders to spread Christianity among the local natives. These missions formed part of a colonization system that stretched across the Spanish Southwest in the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries.

Spanish Texas was one of the interior provinces of the colonial Viceroyalty of New Spain from 1519 until 1821. Spain claimed ownership of the region in 1519. Slave raids by Spaniards into what became Texas began in the 16th century and created an atmosphere of antagonism with Native Americans (Indians) which would cause endless difficulties for the Spanish in the future. Spain did not attempt to establish a permanent presence until after France established the colony of Fort Saint Louis in 1685. In 1688, the French colony failed due to internal dissention and attacks by the Karankawa Indians. In 1690, responding to fear of French encroachment, Spanish explorer Alonso de León escorted several Catholic missionaries to east Texas, where they established the first mission in Texas. That attempt to establish a Spanish colony failed due to the hostility of the Caddo Indians.

The Spanish Missions in Texas comprise the many Catholic outposts established in New Spain by Dominican, Jesuit, and Franciscan orders to spread their doctrine among Native Americans and to give Spain a toehold in the frontier land. The missions introduced European livestock, fruits, vegetables, and industry into the Texas area. In addition to the presidio and pueblo (town), the misión was one of the three major agencies employed by the Spanish crown to extend its borders and consolidate its colonial territories. In all, twenty-six missions were maintained for different lengths of time within the future boundaries of the state of Texas.
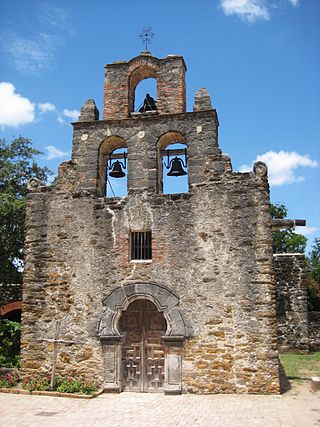
Mission San Francisco de la Espada is a Roman Rite Catholic mission established in 1690 by Spain and relocated in 1731 to present-day San Antonio, Texas, in what was then known as northern New Spain. The mission was built in order to convert local Native Americans to Christianity and solidify Spanish territorial claims in the New World against encroachment from France. Today, the structure is one of four missions that comprise San Antonio Missions National Historical Park.

The Akokisa were an Indigenous tribe who lived on Galveston Bay and the lower Trinity and Sabine rivers in Texas, primarily in the present-day Greater Houston area. They were a band of the Atakapa Indians, closely related to the Atakapa of Lake Charles, Louisiana.

The San Antonio River is a major waterway that originates in central Texas in a cluster of springs in midtown San Antonio, about 4 miles north of downtown, and follows a roughly southeastern path through the state. It eventually feeds into the Guadalupe River about 10 miles from San Antonio Bay on the Gulf of Mexico. The river is 240 miles long and crosses five counties: Bexar, Goliad, Karnes, Refugio, and Wilson.
Mission Valley is an area of El Paso, Texas, United States, which includes part of Eastside and all Lower Valley districts. It is the third largest area of the city, behind East El Paso and Central El Paso. Hawkins Road and Interstate 10 border the Mission Valley. This location is considered the oldest area of El Paso, dating back to the late 17th century when present-day Texas was under the rule of Nueva España.
The Forts of Texas include a number of historical and operational military installations. For over 200 years, various groups fought over access to or control over the region that is now Texas. Possession of the region was claimed and disputed by the European powers of Spain and France, and the continental countries of Mexico, the United States, the Republic of Texas, and the Confederate States of America. Ownership of specific lands was claimed and disputed by different ethnic groups, including numerous Native American tribes, Mexican residents, Anglo- and African-American settlers, and European immigrants. Access to and control of resources were claimed and disputed by various economic groups, including indigenous hunter/gatherers, farmers, herders, ranchers, colonists, settlers, buffalo hunters, traders, bandits, smugglers, pirates, and revolutionaries. Over the centuries, claims and disputes were enforced by Native American warriors, Spanish conquistadors, French cavaliers, Texas Rangers, local militias, and uniformed regular army regiments of Spain, Mexico, Texas, the United States, and the Confederacy.

Franciscan Friars established Mission Nuestra Señora de la Purísima Concepción de Acuña in 1711 as Nuestra Señora de la Purísima Concepción de los Hainais in East Texas. The mission was by the Domingo Ramón-St. Denis expedition and was originally meant to be a base for converting the Hasinai to Catholicism and teaching them what they needed to know to become Mexican citizens. The friars moved the mission in 1731 to San Antonio. After its relocation most of the people in the mission were Pajalats who spoke a Coahuiltecan language. Catholic Mass is still held at the mission every Sunday.
Melchor de Mediavilla y Azcona was the acting governor of Texas between 1727 and 1731.

The Aranama were an Indigenous people who lived along the San Antonio and Guadalupe rivers of present-day Texas, near the Gulf Coast.

The Toboso people were an Indigenous group of what is today northern Mexico, living in the modern states of Chihuahua and Coahuila and along the middle reaches of the Conchos River as well as in the Bolsón de Mapimí region. They were associated with the Jumano and are sometimes identified as having been part of the Jumano people.
The Mayeye were a Tonkawa language–speaking Native American people, who once lived in southeastern Texas. Coastal Mayeyes likely were absorbed into Karankawa communities. Inland Mayeyes likely joined larger Tonkawa communities.
The Xarames were an Indigenous people of the Americas of the San Antonio, Texas region. They were the dominant Native American group during the early history of Mission San Antonio de Valero. They were a Coahuiltecan people.

The Coahuiltecan were various small, autonomous bands of Native Americans who inhabited the Rio Grande valley in what is now northeastern Mexico and southern Texas. The various Coahuiltecan groups were hunter gatherers. First encountered by Europeans in the 16th century, their population declined due to European diseases, slavery, and numerous small-scale wars fought against the Spanish, criollo, Apache, and other Indigenous groups.
The Pastia people were a hunter-gatherer tribe of the Coahuiltecan. The Pastias inhabited the area south of San Antonio, largely between the Medina and San Antonio Rivers and the southward bend of the Nueces River running through modern day La Salle and McMullen counties. They were first contacted by Spanish explorers in the early eighteenth century, and were extinct as an ethnic group by the middle of the following century.
José Domingo Ramón was a Spanish military man and explorer who founded several missions and a presidio in East Texas to prevent French expansion in the area.
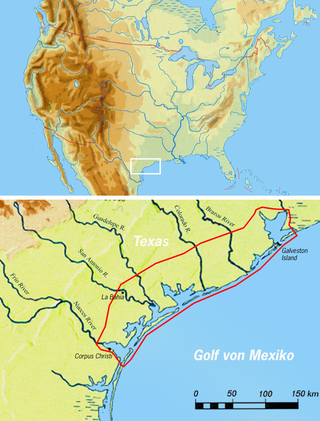
The Copano were a Native American sub-tribe of Karankawa peoples from Texas.