Related Research Articles
The Caddo people comprise the Caddo Nation of Oklahoma, a federally recognized tribe headquartered in Binger, Oklahoma. They speak the Caddo language.

Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands, Southeastern cultures, or Southeast Indians are an ethnographic classification for Native Americans who have traditionally inhabited the area now part of the Southeastern United States and the northeastern border of Mexico, that share common cultural traits. This classification is a part of the Eastern Woodlands. The concept of a southeastern cultural region was developed by anthropologists, beginning with Otis Mason and Franz Boas in 1887. The boundaries of the region are defined more by shared cultural traits than by geographic distinctions. Because the cultures gradually instead of abruptly shift into Plains, Prairie, or Northeastern Woodlands cultures, scholars do not always agree on the exact limits of the Southeastern Woodland culture region. Shawnee, Powhatan, Waco, Tawakoni, Tonkawa, Karankawa, Quapaw, and Mosopelea are usually seen as marginally southeastern and their traditional lands represent the borders of the cultural region.

The Kichai tribe was a Native American Southern Plains tribe that lived in Texas, Louisiana, and Oklahoma. Their name for themselves was K'itaish.
The Nasoni are a Native American tribe from eastern Texas and southwestern Arkansas.
The Kadohadacho are a Native American tribe within the Caddo Confederacy. Today they are enrolled in the Caddo Nation of Oklahoma.
The Yatasi are Native American peoples from northwestern Louisiana that are part of the Natchitoches Confederacy of the Caddo Nation. Today they are enrolled in the Caddo Nation of Oklahoma.
The Nacono were a Native American tribe from eastern Texas. Today they are part of the Caddo Nation of Oklahoma, a federally recognized tribe in Oklahoma.
The Eyeish were a Native American tribe from present-day eastern Texas.
The Nadaco, also commonly known as the Anadarko, are a Native American tribe from eastern Texas. Their name, Nadá-kuh, means "bumblebee place."
The Nabiti are a Native American tribe from eastern Texas. Their name means "Cedar Place" in the Caddo language.
The Nechaui were a Native American tribe from eastern Texas. Their name is thought to be derived from Nachawi, the Caddo language word for Osage orange.
The Ouachita are a Native American tribe who lived in northeastern Louisiana along the Ouachita River. Their name has also been pronounced as Washita by English speakers. The spelling "Ouachita" and pronunciation "Wah-sha-taw" came about as a result of French settlers and their influence. Many landscape features and places have been named for them since colonization of the region by Europeans and Americans.
The Nabedache were a Native American tribe from eastern Texas. Their name, Nabáydácu, means "blackberry place" in the Caddo language. An alternate theory says their original name was Wawadishe from the Caddo word, witish, meaning "salt."

The Nacogdoche are a Native American tribe from eastern Texas.
The Nanatsoho were a Native American tribe that lived at the border of Arkansas, Oklahoma, and Texas.
The Cahinnio were a Native American tribe that lived in Arkansas.
The Tula were a Native American group that lived in what is now western Arkansas. The Tula are known to history only from the chronicles of Spanish conquistador Hernando de Soto's exploits in the interior of North America.
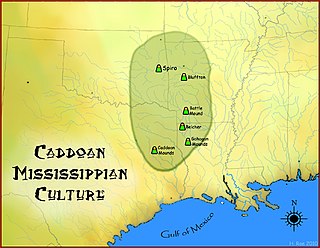
The Caddoan Mississippian culture was a prehistoric Native American culture considered by archaeologists as a variant of the Mississippian culture. The Caddoan Mississippians covered a large territory, including what is now Eastern Oklahoma, Western Arkansas, Northeast Texas, Southwest Missouri and Northwest Louisiana of the United States.
The Bidai were a tribe of Atakapa Indians from eastern Texas.

Caddo Mounds State Historic Site (41CE19) is an archaeological site in Weeping Mary, Texas. This Caddoan Mississippian culture site is composed of a village and ceremonial center that features two earthwork platform mounds and one burial mound. Located on an ancient Native American trail later named by the Spanish as El Camino Real de los Tejas, the settlement developed hundreds of years before the arrival of Europeans to the region. Archaeologists believe the site was created in approximately 800 CE, with most major construction taking place between 1100 and 1300 CE.
References
- Bolton, Herbet E. The Hasinais: Southern Caddoans As Seen by the Earliest Europeans. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press, 2002. ISBN 978-0-8061-3441-3.
- Sturtevant, William C., general editor and Raymond D. Fogelson, volume editor. Handbook of North American Indians: Southeast. Volume 14. Washington DC: Smithsonian Institution, 2004. ISBN 0-16-072300-0.
- Swanton, John Reed. Source material on the history and ethnology of the Caddo Indians. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press, 1996. ISBN 978-0-8061-2856-6.
