
The Pinson Mounds comprise a prehistoric Native American complex located in Madison County, Tennessee, in the region that is known as the Eastern Woodlands. The complex, which includes 17 mounds, an earthen geometric enclosure, and numerous habitation areas, was most likely built during the Middle Woodland period. The complex is the largest group of Middle Woodland mounds in the United States. Sauls' Mound, at 72 feet (22 m), is the second-highest surviving mound in the United States.

The Great Serpent Mound is a 1,348-feet-long (411 m), three-feet-high prehistoric effigy mound located in Peebles, Ohio. It was built on what is known as the Serpent Mound crater plateau, running along the Ohio Brush Creek in Adams County, Ohio. The mound is the largest serpent effigy known in the world.

Angel Mounds State Historic Site, an expression of the Mississippian culture, is an archaeological site managed by the Indiana State Museum and Historic Sites that includes more than 600 acres of land about 8 miles (13 km) southeast of present-day Evansville, in Vanderburgh and Warrick counties in Indiana. The large residential and agricultural community was constructed and inhabited from AD 1100 to AD 1450, and served as the political, cultural, and economic center of the Angel chiefdom. It extended within 120 miles (190 km) of the Ohio River valley to the Green River in present-day Kentucky. The town had as many as 1,000 inhabitants inside the walls at its peak, and included a complex of thirteen earthen mounds, hundreds of home sites, a palisade (stockade), and other structures.

Wickliffe Mounds is a prehistoric, Mississippian culture archaeological site located in Ballard County, Kentucky, just outside the town of Wickliffe, about 3 miles (4.8 km) from the confluence of the Ohio and Mississippi rivers. Archaeological investigations have linked the site with others along the Ohio River in Illinois and Kentucky as part of the Angel phase of Mississippian culture. Wickliffe Mounds is controlled by the State Parks Service, which operates a museum at the site for interpretation of the ancient community. Listed on the National Register of Historic Places, it is also a Kentucky Archeological Landmark and State Historic Site.

Lake Jackson Mounds Archaeological State Park (8LE1) is one of the most important archaeological sites in Florida, the capital of chiefdom and ceremonial center of the Fort Walton Culture inhabited from 1050–1500. The complex originally included seven earthwork mounds, a public plaza and numerous individual village residences.

Watson Brake is an archaeological site in present-day Ouachita Parish, Louisiana, from the Archaic period. Dated to about 5400 years ago, Watson Brake is considered the oldest earthwork mound complex in North America. It is older than the Ancient Egyptian pyramids or Britain’s Stonehenge. Its discovery and dating in a paper published in 1997 changed the ideas of American archaeologists about ancient cultures in the Southeastern United States and their ability to manage large, complex projects over centuries. The archeologists revised their date of the oldest earthwork construction by nearly 2000 years, as well as having to recognize that it was developed over centuries by a hunter-gatherer society, rather than by what was known to be more common of other, later mound sites: a more sedentary society dependent on maize cultivation and with a hierarchical, centralized polity.

The Turpin site (33Ha19) is an archaeological site in the southwestern portion of the U.S. state of Ohio. Located near Newtown in Hamilton County, the site includes the remains of a village of the Fort Ancient culture and of multiple burial mounds. Numerous bodies have been found in and around the mounds as a result of thorough site investigations. The archaeological value of the site has resulted in its use in the study of similar locations and in its designation as a historic site.

This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in McCracken County, Kentucky.

This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Logan County, Kentucky.
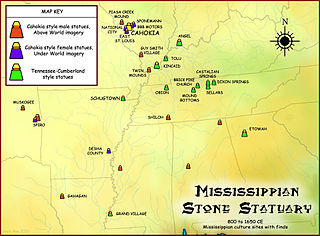
The Mississippian stone statuary are artifacts of polished stone in the shape of human figurines made by members of the Mississippian culture and found in archaeological sites in the American Midwest and Southeast. Two distinct styles exist; the first is a style of carved flint clay found over a wide geographical area but believed to be from the American Bottom area and manufactured at the Cahokia site specifically; the second is a variety of carved and polished locally available stone primarily found in the Tennessee-Cumberland region and northern Georgia. Early European explorers reported seeing stone and wooden statues in native temples, but the first documented modern discovery was made in 1790 in Kentucky, and given as a gift to Thomas Jefferson.
The Zaleski Mound Group is a collection of three burial mounds in the village of Zaleski, Ohio, United States. Built by people of the prehistoric Adena culture, these earthworks are valuable archaeological sites.

The Jackson Mound is a Native American mound in the south-central portion of the U.S. state of Ohio. Located north of Pancoastburg in Fayette County, it measures approximately 75 feet (23 m) in diameter and 5.5 feet (1.7 m) in height. The mound has never been excavated, making the certain identification of its builders impossible; however, its location on a high terrace above a relatively small stream suggests that it was built by the Adena culture, which favored such sites for its many mounds. If true, it was originally more conical in shape, and it is likely to cover the remains of a wooden charnel house built by the Adena.

Poverty Point State Historic Site/Poverty Point National Monument is a prehistoric earthwork constructed by the Poverty Point culture, located in present-day northeastern Louisiana. Evidence of the Poverty Point culture extends throughout much of the Southeastern Woodlands of the Southern United States. The culture extended 100 miles (160 km) across the Mississippi Delta and south to the Gulf Coast.
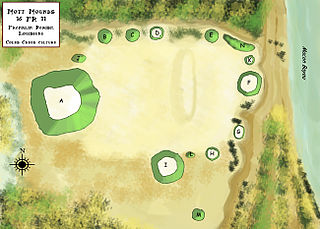
The Mott Archaeological Preserve or Mott Mounds Site is an archaeological site in Franklin Parish, Louisiana on the west bank of Bayou Macon. It originally had eleven mounds with components from the Marksville, Troyville, Coles Creek, and Plaquemine periods. It was at one time one of the largest mound centers in the Southeast and has one of the largest mounds in Louisiana with a base which cover more than two acres. It was purchased by the Archaeological Conservancy in 2002. and is now used for research and educational purposes.
The Spanish Fort Site (22-SH-500) is an archaeological site in the Delta region of the U.S. state of Mississippi. It is one of three major earthwork sites in the far southern portion of the Yazoo River valley, and it has been designated a historic site because of its archaeological value. Despite its name, the site was not built by the Spanish, and its original purpose is believed to have been ceremonial, not martial.
The Ramey Mound, designated 15BH1, is an archaeological site in Bath County in the northeastern part of the U.S. state of Kentucky. Built by people of the prehistoric Adena culture, the site has been known for more than two centuries; it was recorded in 1807 as consisting of an enclosure at least 3 feet (0.91 m) high. In 1871, another survey observed four mounds in association with the main earthwork: one was located just east of the enclosure, another directly to the west, a larger one to the southeast, and a small one to the southwest. The source of a nearby brook lies within the site and transverses the enclosure; the 1871 survey supposed that it had been dug to provide earth for the enclosure. By the time of this later survey, cultivation had reduced the earthwork to the point that it was nearly indistinguishable.

The Raleigh Mound (33KN32) is a Native American mound in the village of Fredericktown, Ohio, United States. Built thousands of years ago, the mound is an important archaeological site.

The Emerald Mound and Village Site is a pre-Columbian archaeological site located northwest of the junction of Emerald Mound Grange and Midgley Neiss Roads in St. Clair County, Illinois. The site includes five mounds, two of which have been destroyed by modern activity, and the remains of a village. Middle Mississippian peoples inhabited the village, which was a satellite village of Cahokia. The largest of the mounds is a two-tiered structure that stands 50 feet (15 m) high; its square base is 300 feet (91 m) across, while its upper tier is 150 feet (46 m) across. At the time of its discovery, the mound was the second-largest known in Illinois after Monks Mound at Cahokia.

The Hidden Valley Rockshelter (44-BA-31) is a significant archaeological site located near the community of Warm Springs in Bath County, Virginia, United States. A large rockshelter located near the Jackson River, it has been occupied by humans for thousands of years, and it has been named a historic site.

Spanish Hill is a hill located in the borough of South Waverly, Pennsylvania. Opinions regarding the origin of structures found on the site vary from embankments created by early farmers, to the remnants of a Native American village and battlements, due to the site's similarity to the description found in the account of Étienne Brûlé of a settlement called Carantouan. The area in the hill's vicinity was previously occupied by Susquehannock Native Americans. It was a common site for both amateur and professional archaeology, as well as relic hunting. The source of the name remains unknown, but various theories have been proposed as to its origin.


















