
A platform mound is any earthwork or mound intended to support a structure or activity. It typically refers to a flat-topped mound, whose sides may be pyramidal.

A platform mound is any earthwork or mound intended to support a structure or activity. It typically refers to a flat-topped mound, whose sides may be pyramidal.


The indigenous peoples of North America built substructure mounds for well over a thousand years, starting in the Archaic period and continuing through the Woodland period. Many different archaeological cultures (Poverty Point culture, Troyville culture, Coles Creek culture, Plaquemine culture and Mississippian culture) of North Americas Eastern Woodlands are specifically well known for using platform mounds as a central aspect of their overarching religious practices and beliefs.
These platform mounds are usually four-sided truncated pyramids, steeply sided, with steps built of wooden logs ascending one side of the earthworks. When Europeans first arrived in North America, the peoples of the Mississippian culture were still using and building platform mounds. Documented uses for Mississippian platform mounds include semi-public chief's house platforms, public temple platforms, mortuary platforms, charnel house platforms, earth lodge/town house platforms, residence platforms, square ground and rotunda platforms, and dance platforms. [1]
Many of the mounds were the result of multiple episodes of mound construction, with the mound becoming larger with each event. The site of a mound was usually a site with special significance, either a pre-existing mortuary site or civic structure. This site was covered with a layer of basket-transported soil and clay known as mound fill, and a new structure constructed on its summit. At periodic intervals, averaged about twenty years, these structures would be removed, possibly ritually destroyed as part of renewal ceremonies, [2] and a new layer of fill added, along with a new structure on the now higher summit. Sometimes the surface of the mounds would get a several inches thick coat of brightly colored clay. [2] [3] These layers also incorporated layers of different kinds of clay, soil and sod, an elaborate engineering technique to forestall slumping of the mounds and to ensure their steep sides did not collapse. This pattern could be repeated many times during the life of a site. [4] The large amounts of fill needed for the mounds left large holes in the landscape now known by archaeologists as "borrow pits". These pits were sometimes left to fill with water and stocked with fish. [5]
Some mounds were developed with separate levels (or terraces) and aprons, such as Emerald Mound, which is one large terrace with two smaller mounds on its summit; or Monks Mound, which has four separate levels and stands close to 100 feet (30 m) in height. Monks Mound had at least ten separate periods of mound construction over a 200-year period. Some of the terraces and aprons on the mound seem to have been added to stop slumping of the enormous mound. [6]
Although the mounds were primarily meant as substructure mounds for buildings or activities, sometimes burials did occur there. Intrusive burials occurred when a grave was dug into a mound and the body or a bundle of defleshed, disarticulated bones was deposited into it. Mound C at Etowah has been found to have more than 100 intrusive burials into the final layer of the mound, with many grave goods added, such as Mississippian copper plates (Etowah plates), monolithic stone axes, ceremonial pottery and carved whelk shell gorgets. Also interred in this mound was a paired set of white marble Mississippian stone statues. [3]
A long-standing interpretation of Mississippian mounds comes from Vernon James Knight, who stated that the Mississippian platform mounds were one of the three "sacra", or objects of sacred display, of the Mississippian religion – also see Earth/fertility cult and Southeastern Ceremonial Complex. He based his theory on analogy to ethnographic and historic data on related Native American tribal groups in the Southeastern United States.
Knight suggests a microcosmic ritual organization based around a "native earth" autochthony, agriculture, fertility, and purification scheme, in which mounds and the site layout replicate cosmology. Mound rebuilding episodes are construed as rituals of burial and renewal, while the four-sided construction acts to replicate the flat earth and the four quarters of the earth. [7] [8]
The use of platform mounds is documented elsewhere in the world, including:

Etowah Indian Mounds (9BR1) are a 54-acre (220,000 m2) archaeological site in Bartow County, Georgia, south of Cartersville. Built and occupied in three phases, from 1000–1550 CE, the prehistoric site is located on the north shore of the Etowah River.

Monks Mound is the largest Pre-Columbian earthwork in the Americas and the largest pyramid north of Mesoamerica. The beginning of its construction dates from 900 to 955 CE. Located at the Cahokia Mounds UNESCO World Heritage Site near Collinsville, Illinois, the mound size was calculated in 1988 as about 100 feet (30 m) high, 955 feet (291 m) long including the access ramp at the southern end, and 775 feet (236 m) wide. This makes Monks Mound roughly the same size at its base as the Great Pyramid of Giza. The perimeter of its base is larger than the Pyramid of the Sun at Teotihuacan. As a platform mound, the earthwork supported a wooden structure on the summit.

Lake Jackson Mounds Archaeological State Park (8LE1) is one of the most important archaeological sites in Florida, the capital of chiefdom and ceremonial center of the Fort Walton Culture inhabited from 1050–1500. The complex originally included seven earthwork mounds, a public plaza and numerous individual village residences.

A step pyramid or stepped pyramid is an architectural structure that uses flat platforms, or steps, receding from the ground up, to achieve a completed shape similar to a geometric pyramid. Step pyramids are structures which characterized several cultures throughout history, in several locations throughout the world. These pyramids typically are large and made of several layers of stone. The term refers to pyramids of similar design that emerged separately from one another, as there are no firmly established connections between the different civilizations that built them.

Spiro Mounds is an Indigenous archaeological site located in present-day eastern Oklahoma. The site was built by people from the Arkansas Valley Caddoan culture. that remains from an American Indian culture that was part of the major northern Caddoan Mississippian culture. The 80-acre site is located within a floodplain on the southern side of the Arkansas River. The modern town of Spiro developed approximately seven miles to the south.

Town Creek Indian Mound is a prehistoric Native American archaeological site located near present-day Mount Gilead, Montgomery County, North Carolina, in the United States. The site, whose main features are a platform mound with a surrounding village and wooden defensive palisade, was built by the Pee Dee, a South Appalachian Mississippian culture people that developed in the region as early as 980 CE. They thrived in the Pee Dee River region of North and South Carolina during the Pre-Columbian era. The Town Creek site was an important ceremonial site occupied from about 1150—1400 CE. It was abandoned for unknown reasons. It is the only ceremonial mound and village center of the Pee Dee located within North Carolina.

The Kincaid Mounds Historic Site c. 1050–1400 CE, is a Mississippian culture archaeological site located at the southern tip of present-day U.S. state of Illinois, along the Ohio River. Kincaid Mounds has been notable for both its significant role in native North American prehistory and for the central role the site has played in the development of modern archaeological techniques. The site had at least 11 substructure platform mounds, and 8 other monuments.
The Pisgah phase is an archaeological phase of the South Appalachian Mississippian culture in Southeast North America. It is associated with the Appalachian Summit area of southeastern Tennessee, Western North Carolina, and northwestern South Carolina in what is now the United States.

The Plaquemine culture was an archaeological culture centered on the Lower Mississippi River valley. It had a deep history in the area stretching back through the earlier Coles Creek and Troyville cultures to the Marksville culture. The Natchez and related Taensa peoples were their historic period descendants. The type site for the culture is the Medora site in Louisiana; while other examples include the Anna, Emerald, Holly Bluff, and Winterville sites in Mississippi.
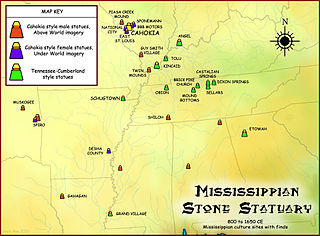
The Mississippian stone statuary are artifacts of polished stone in the shape of human figurines made by members of the Mississippian culture and found in archaeological sites in the American Midwest and Southeast. Two distinct styles exist; the first is a style of carved flint clay found over a wide geographical area but believed to be from the American Bottom area and manufactured at the Cahokia site specifically; the second is a variety of carved and polished locally available stone primarily found in the Tennessee-Cumberland region and northern Georgia. Early European explorers reported seeing stone and wooden statues in native temples, but the first documented modern discovery was made in 1790 in Kentucky, and given as a gift to Thomas Jefferson.
The Wilbanks Site (9CK5) is a Late Mississippian culture Native American archaeological site in Cherokee County, Georgia, United States. The site was located about midway between the towns of Cartersville, Georgia to the west, and Canton, Georgia to the east. It was on the south bank of the Etowah River, but is now submerged underneath Lake Allatoona, under roughly 80–90 feet of water.
The Chauga Mound (38OC1) is an archaeological site once located on the northern bank of the Tugaloo River, about 1,200 feet (370 m) north of the mouth of the Chauga River in present-day Oconee County, South Carolina. The earthen platform mound and former village site were inundated by creation of Lake Hartwell after construction of the Hartwell Dam on the Savannah River, which was completed in 1962.
The Dyar site (9GE5) is an archaeological site in Greene County, Georgia, in the north central Piedmont physiographical region. The site covers an area of 2.5 hectares. It was inhabited almost continuously from 1100 to 1600 by a local variation of the Mississippian culture known as the South Appalachian Mississippian culture. Although submerged under Lake Oconee, the site is still important as one of the first explorations of a large Mississippian culture mound. The Dyar site is thought to have been one of the principal towns of the paramount chiefdom of Ocute, perhaps Cofaqui.
The Lamar mounds and village site (9BI2) is an important archaeological site on the banks of the Ocmulgee River in Bibb County, Georgia, several miles to the southeast of the Ocmulgee mound site. Both mound sites are part of the Ocmulgee Mounds National Historical Park, a national park and historic district created in 1936 and run by the U.S. National Park Service. Historians and archaeologists have theorized that the site is the location of the main village of the Ichisi encountered by the Hernando de Soto expedition in 1539.
The Mill Cove Complex is a group of prehistoric archaeological sites located in Duval County, Florida built by people of the St. Johns culture approximately 900 to 1250 CE. The site encompasses two sand mounds, Grant Mound (8DU14) and the contemporaneous Shields Mound (8DU12) located 750 metres (0.47 mi) away, and an area in between the two which is full of St. Johns culture midden deposits.

Mississippian copper plates, or plaques, are plain and repousséd plates of beaten copper crafted by peoples of the various regional expressions of the Mississippian culture between 800 and 1600 CE. They have been found as artifacts in archaeological sites in the American Midwest and Southeast. The plates, found as far afield as Florida, Georgia, Illinois, Mississippi, Oklahoma, Tennessee, and Wisconsin, were instrumental in the development of the archaeological concept known as the Southeastern Ceremonial Complex. Some of the more notable examples are representations of raptorial birds and avian-themed dancing warriors.
Mound 34 is a small platform mound located roughly 400 metres (1,300 ft) to the east of Monks Mound at Cahokia Mounds near Collinsville, Illinois. Excavations near Mound 34 from 2002 to 2010 revealed the remains of a copper workshop, although the one of a kind discovery had been previously found in the late 1950s by archaeologist Gregory Perino, but lost for 60 years. It is so far the only remains of a copper workshop found at a Mississippian culture archaeological site.

Mound 72 is a small ridgetop mound located roughly 850 meters (2,790 ft) to the south of Monks Mound at Cahokia Mounds near Collinsville, Illinois. Early in the site's history, the location began as a circle of 48 large wooden posts known as a "woodhenge". The woodhenge was later dismantled and a series of mortuary houses, platform mounds, mass burials and eventually the ridgetop mound erected in its place. The mound was the location of the "beaded burial", an elaborate burial of an elite personage thought to have been one of the rulers of Cahokia, accompanied by the graves of several hundred retainers and sacrificial victims.
The Emmons Cemetery Site, also known as the Emmons Site, is a Middle Mississippian culture archaeological site located in Kerton Township, Fulton County, Illinois, on the edge of a bluff overlooking the Illinois River to its east. The location was a used as a cemetery and several unique and rare items were found interred with the burials.
Long Swamp Site is a 4-acre (16,000 m2) archaeological site in Cherokee County, Georgia, United States, on the north shore of the Etowah River near St Rt 372. The site consists of a South Appalachian Mississippian culture village with a palisade and a platform mound.