Related Research Articles

Mayapan is a Pre-Columbian Maya site a couple of kilometers south of the town of Telchaquillo in Municipality of Tecoh, approximately 40 km south-east of Mérida and 100 km west of Chichen Itza; in the state of Yucatán, Mexico. Mayapan was the political and cultural capital of the Maya in the Yucatán Peninsula during the Late Post-Classic period from the 1220s until the 1440s. Estimates of the total city population are 15,000–17,000 people, and the site has more than 4,000 structures within the city walls, and additional dwellings outside.

Baja California Sur, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California Sur, is the least populated state and the 31st admitted state of the 32 federal entities which comprise the 31 States of Mexico. It is also the ninth-largest Mexican state in terms of area.

Edward Palmer was a self-taught British botanist and an early American archaeologist.

The Pericú were the aboriginal inhabitants of the Cape Region, the southernmost portion of Baja California Sur, Mexico. They have been linguistically and culturally extinct since the late 18th century.
Sigismundo Taraval (1700–1763) was a pioneering Jesuit missionary in Baja California who wrote important historical accounts of the peninsula.
The San Dieguito complex is an archaeological pattern left by early Holocene inhabitants of Southern California and surrounding portions of the Southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico. Radiocarbon dating places a 10,200 BP (8200 BCE) date consideration.

The Spanish missions in Baja California were a large number of religious outposts established by Catholic religious orders, the Jesuits, the Franciscans and the Dominicans, between 1683 and 1834 to spread the Christian doctrine among the Native Americans or Indians living on the Baja California peninsula. The missions gave Spain a valuable toehold in the frontier land, and introduced European livestock, fruits, vegetables, and industry into the region. The Indians were severely impacted by the introduction of European diseases such as smallpox and measles and by 1800 their numbers were a fraction of what they had been before the arrival of the Spanish.
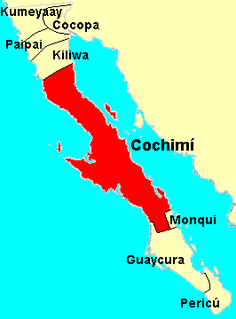
The Cochimí were the indigenous inhabitants of the central part of the Baja California peninsula, from El Rosario in the north to San Javier in the south. Information on Cochimí customs and beliefs has been preserved in the brief observations by explorers but, above all, in the writings of the Jesuits. Particularly important and detailed are the works of Miguel Venegas and Miguel del Barco (1973).
This article refers to the archaeologist. For others with the name Malcolm Rogers, please see Malcolm Rogers (disambiguation).

Mission Santiago was founded by the Italian Jesuit Ignacio María Nápoli in 1724 and financed by the Marqués de Villapuente de la Peña and his wife the Marquesa de las Torres de Rada, at the native settlement of Aiñiní, about 40 kilometers north of San José del Cabo in the Cape Region of Baja California Sur, Mexico.
The archaeological La Jolla complex represents a prehistoric culture oriented toward coastal resources that prevailed during the middle Holocene period between c. 8000 BC and AD 500 in southwestern California and northwestern Baja California.
The Comondú Complex is an archaeological pattern dating from the late prehistoric period in northern Baja California Sur and southern Baja California. It is associated with the historic Cochimí people of the peninsula.
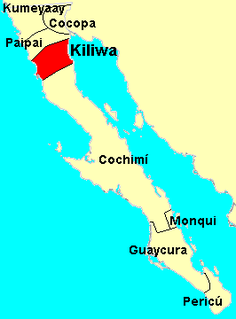
The Kiliwa are an indigenous people of Mexico living in northern Baja California. Historically they occupied a territory lying between the Cochimí on the south and the Paipai on the north, and extending from San Felipe on the Gulf of California to San Quintín on the Pacific coast. Their traditional language is the Kiliwa language.

The Paipai are an indigenous people of Mexico living in northern Baja California. Their traditional territory lies between the Kiliwa on the south and the Kumeyaay and Cocopa on the north, and extending from San Vicente near the Pacific coast nearly to the Colorado River's delta in the east. Today they are concentrated primarily at the multi-ethnic community of Santa Catarina in Baja California's Sierra de Juárez.

El Vallecito is an archaeological site located in the city of La Rumorosa, in the Tecate Municipality, Baja California, Mexico.
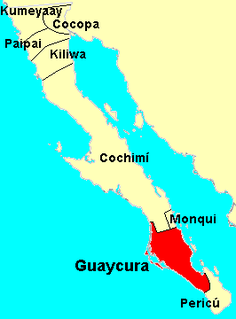
Waikuri is an extinct language of southern Baja California spoken by the Waikuri or Guaycura people. The Jesuit priest Baegert documented words, sentences and texts in the language between 1751 and 1768.

Colha, Belize is a Maya archaeological site located in northern portion of the country, about 52 km. north of Belize City, near the town of Orange Walk. The site is one of the earliest in the Maya region and remains important to the archaeological record of the Maya culture well into the Postclassic Period. According to Palma Buttles, “Archaeological evidence from Colha allows for the interpretation occupation from the Early Preceramic (3400-1900B.C.) to Middle Postclassic with population peaks occurring in the Late Preclassic and again in the Late Classic ”. These peaks in population are directly related to the presence of stone tool workshops at the site. Colha's proximity to an important source of high quality chert that is found in the Cenozoic limestone of the region and well traveled trade routes was utilized by the inhabitants to develop a niche in the Maya trade market that may have extended to the Greater Antilles. During the Late Preclassic and Late Classic periods, Colha served as a primary supplier of worked stone tools for the region. It has been estimated that the 36 workshops at Colha produced nearly 4 million chert and obsidian tools and eccentrics that were dispersed throughout Mesoamerica during the Maya era. This made it an important player in the trade of essential good throughout the area.

Baking Pot is a Maya archaeological site located in the Belize River Valley on the southern bank of the river, northeast of modern-day town of San Ignacio in the Cayo District of Belize; it is 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) downstream from the Barton Ramie and Lower Dover archaeological sites. Baking Pot is associated with an extensive amount of research into Maya settlements, community-based archaeology, and of agricultural production; the site possesses lithic workshops, and possible evidence of cash-cropping cacao as well as a long occupation from the Preclassic through to the Postclassic period.
William Clifford Massey (1917–1974) was an anthropologist who played a key role in the study of the prehistory of the Baja California Peninsula in Mexico. His scientific contributions included archaeological surveys, excavations, and the documentation of previous collections, as well as detailed analyses of ethnohistoric and linguistic evidence bearing of the region's prehistory.
Harumi Fujita is a Japanese researcher of Mexican archaeology, who has specialized in pre-classical period of the northern states of Baja California and Baja California Sur. Her research has shown that fishing cultures had arisen in the area at the end of the Pleistocene period, indicating an occupation from at least 11,000 years ago. In a cave shelf known as the Babisuri Shelter, radiocarbon dating indicated the area may have been occupied 40,000 years ago.
References
- Fujita, Harumi. 2006. "The Cape Region". In The Prehistory of Baja California: Advances in the Archaeology of the Forgotten Peninsula, edited by Don Laylander and Jerry D. Moore, pp. 82–98.
- Massey, William C. 1955. Culture History in the Cape Region of Baja California, Mexico. Unpublished Ph.D. dissertation, University of California, Berkeley.
- Massey, William C. 1966. "Archaeology and Ethnohistory of Lower California". In Archaeological Frontiers and External Connections, edited by Gordon F. Ekholm and Gordon R. Willey, pp. 38–58. Handbook of Middle American Indians, Vol. 4. University of Texas Press, Austin.
