
A carpet is a textile floor covering typically consisting of an upper layer of pile attached to a backing. The pile was traditionally made from wool, but since the 20th century synthetic fibers such as polypropylene, nylon, or polyester have often been used, as these fibers are less expensive than wool. The pile usually consists of twisted tufts that are typically heat-treated to maintain their structure. The term carpet is often used in a similar context to the term rug, but rugs are typically considered to be smaller than a room and not attached to the floor.

Tibetan rug making is an ancient, traditional craft. Tibetan rugs are traditionally made from Tibetan highland sheep's wool, called changpel. Tibetans use rugs for many purposes ranging from flooring to wall hanging to horse saddles, though the most common use is as a seating carpet. A typical sleeping carpet measuring around 3 ft × 5 ft is called a khaden.

A Persian carpet, Persian rug, or Iranian carpet is a heavy textile made for a wide variety of utilitarian and symbolic purposes and produced in Iran, for home use, local sale, and export. Carpet weaving is an essential part of Persian culture and Iranian art. Within the group of Oriental rugs produced by the countries of the "rug belt", the Persian carpet stands out by the variety and elaborateness of its manifold designs.

A kilim is a flat tapestry-woven carpet or rug traditionally produced in countries of the former Persian Empire, including Iran, but also in the Balkans and the Turkic countries. Kilims can be purely decorative or can function as prayer rugs. Modern kilims are popular floor coverings in Western households.

Gabbeh or gabba carpets are a traditional variety of Persian carpet. Gabbeh is known as gava in Kurdish and Luri and is also called khersak (خرسک) in Bakhtiari, literally meaning a "bear's cub". Traditionally a sleeping rug, a gabbeh is a hand-woven pile rug of coarse quality and medium size characterized by an abstract design that relies upon open fields of color and a playfulness with geometry. This type of rug is popular among the populations of the Zagros Mountains of Iran, including Kurdish, Luri and Qashqai people. The gabbeh is usually crafted by women.

Knot density is a traditional measure for quality of handmade or knotted pile carpets. It refers to the number of knots, or knot count, per unit of surface area - typically either per square inch (kpsi) or per square centimeter (kpsc), but also per decimeter or meter. Number of knots per unit area is directly proportional to the quality of carpet. Density may vary from 25 to 1,000 knots per square inch or higher, where ≤80 kpsi is poor quality, 120 to 330 kpsi is medium to good, and ≥330 kpsi is very good quality. The inverse, knot ratio, is also used to compare characteristics. Knot density = warp×weft while knot ratio = warp/weft. For comparison: 100,000/square meter = 1,000/square decimeter = 65/square inch = 179/gereh.

Uşak carpets, Ushak carpets or Oushak Carpets are Turkish carpets that use a particular family of designs, called by convention after the city of Uşak, Turkey – one of the larger towns in Western Anatolia, which was a major center of rug production from the early days of the Ottoman Empire, into the early 20th century.
An oriental rug is a heavy textile made for a wide variety of utilitarian and symbolic purposes and produced in "Oriental countries" for home use, local sale, and export.

Bergama Carpet refers to handwoven Turkish carpets, made in the Bergama district in the Izmir Province of northwest Turkey. As a market place for the surrounding villages, the name of Bergama is used as a trade name to define the provenience.

Anatolian rug or Turkish carpet is a term of convenience, commonly used today to denote rugs and carpets woven in Anatolia and its adjacent regions. Geographically, its area of production can be compared to the territories which were historically dominated by the Ottoman Empire. It denotes a knotted, pile-woven floor or wall covering which is produced for home use, local sale, and export, and religious purpose. Together with the flat-woven kilim, Anatolian rugs represent an essential part of the regional culture, which is officially understood as the Culture of Turkey today, and derives from the ethnic, religious and cultural pluralism of one of the most ancient centres of human civilisation.

Hereke carpets are Turkish handmade carpets produced and sold in Hereke, a coastal town in Turkey. For a long time, they were produced only in Hereke, 60 km from Istanbul. The materials used are silk, a combination of wool and cotton, and sometimes gold or silver threads.

A knotted-pile carpet is a carpet containing raised surfaces, or piles, from the cut off ends of knots woven between the warp and weft. The Ghiordes/Turkish knot and the Senneh/Persian knot, typical of Anatolian carpets and Persian carpets, are the two primary knots. A flat or tapestry woven carpet, without pile, is a kilim. A pile carpet is influenced by width and number of warp and weft, pile height, knots used, and knot density.

Ryijy is a woven Finnish long-tufted tapestry or knotted-pile carpet hanging.
Iranian handicrafts are handicraft or handmade crafted works originating from Iran.

A Turkmen rug is a type of handmade floor-covering textile traditionally originating in Central Asia. It is useful to distinguish between the original Turkmen tribal rugs and the rugs produced in large numbers for export mainly in Pakistan and Iran today. The original Turkmen rugs were produced by the Turkmen tribes who are the main ethnic group in Turkmenistan and are also found in Afghanistan and Iran. They are used for various purposes, including tent rugs, door hangings and bags of various sizes.

Kerman carpets are one of the traditional classifications of Persian carpets. Kerman is both a city and a province located in south central Iran. The term also sometimes describes a type which may have been made elsewhere. Typical manufacturing techniques use an asymmetrical knot on cotton foundation, but less frequent examples incorporate silk or part silk piles, or silk foundations with wool pile.
Moroccan rugs are the weaves, carpets, and textiles that have been traditionally hand-woven in Morocco. Rugs have been woven by the indigenous people of Morocco since the Paleolithic Era. Traditionally, Moroccan rugs have been woven by tribal peoples for their utility rather than for decorative purposes. Twentieth-century Moroccan rugs are widely collected in the West, and are almost always woven by tribes people who do not seek nor possess formal artistic training.
Varamin carpets and rugs or Veramin carpets and rugs are carpets and rugs woven in city of Varamin and its surrounding area, southeast of Tehran. Many rug and carpet experts see Varamins as being among those Persian carpets most authentic in terms of traditional style and motif.
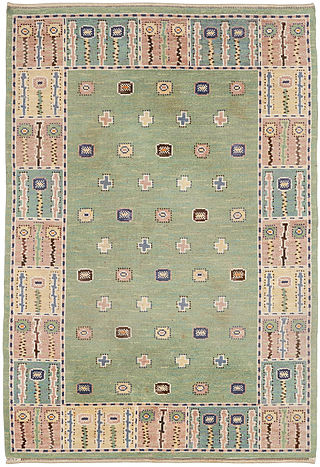
Carpets and rugs have been handmade in Sweden for centuries, taking on many different forms and functions over the course of time. Rugs woven in the traditional Oriental manner, especially in the Ottoman Empire and points east, were originally brought to Sweden over trade routes as early as the early Middle Ages. In the centuries that followed, Swedish rug-makers often infused their works with themes and motifs traditionally found in Oriental rugs. Eventually, Swedish rug-makers would begin to use Oriental rug-making techniques, but themes and motifs more consistent with the artistic and cultural heritage of Sweden. By the early modern periods, rugs had long been an important avenue of art – especially folk art – in Swedish culture. By the beginning of the twentieth century, the craft was seen as being an important artistic and cultural practice throughout Sweden, and designers began to make rugs that had a broad international appeal. Swedish rugs from the mid-twentieth century remain among the most desirable and sought after in the rug world.
Chobi rugs CHOBI is a widely used commercial term used for hand made carpets from Afghanistan and to a diminished extent in the NWFP region of Afghanistan/Pakistan border. This term has been used since the displacement and return of refugees during and after the Soviet Afghan war in the 1980s. The uprooting of weaving populations effected traditional all wool weaving which had previously been almost exclusively based on Turkmen designs with an all wool structure in red tones as expressed by Afghan carpets. Strong demand for furnishing concepts from the west to produce Persian style patterns most notably the concept of Ziegler carpets proved a good commercial success and a well made robust product using increasingly cotton as a foundation resulted. Following a western lead in tase since late 1980s the business has since 2000 fallen to a considerable degree to being administered via Pakistan merchants given the ease of export from Pakistan. Afghan weavers had largely returned to Afghanistan from Pakistan refugee camps during late 20th cent however since the Taliban/ Pashtuns take over of Afghanistan in 2021 disruption to weaving has again occurred.
















