
Copepods are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat. Some species are planktonic, some are benthic, a number of species have parasitic phases, and some continental species may live in limnoterrestrial habitats and other wet terrestrial places, such as swamps, under leaf fall in wet forests, bogs, springs, ephemeral ponds, puddles, damp moss, or water-filled recesses of plants (phytotelmata) such as bromeliads and pitcher plants. Many live underground in marine and freshwater caves, sinkholes, or stream beds. Copepods are sometimes used as biodiversity indicators.

Tantulocarida is a highly specialised group of parasitic crustaceans that consists of about 33 species, treated as a class in superclass Multicrustacea. They are typically ectoparasites that infest copepods, isopods, tanaids, amphipods and ostracods.

The family Argulidae, whose members are commonly known as carp lice or fish lice, are parasitic crustaceans in the class Ichthyostraca. It is the only family in the monotypic subclass Branchiura and the order Arguloida, although a second family, Dipteropeltidae, has been proposed. Although they are thought to be primitive forms, they have no fossil record.

Sea lice are copepods of the family Caligidae within the order Siphonostomatoida. They are marine ectoparasites that feed on the mucus, epidermal tissue, and blood of host fish. The roughly 559 species in 37 genera include around 162 Lepeophtheirus and 268 Caligus species.
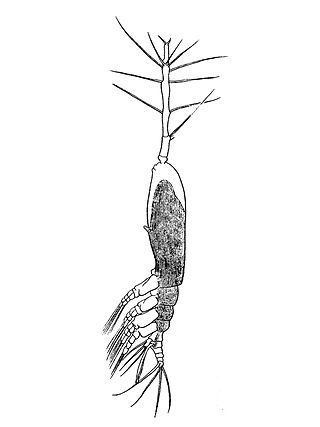
Monstrilloida is an order of copepods with a cosmopolitan distribution in the world's oceans. The order contains a single family, Monstrillidae. The name of the first ever described genus Monstrilla is derived from latin, meaning "tiny monster", because the lack of usual diagnostic features of copepods puzzled early taxonomists.
Hamaticolax unisagittatus is a species of parasitic copepod belonging to the family Bomolochidae. It is a parasite on the gills of the common snook and has only been recorded in coastal waters off Rio de Janeiro State. In one study over half of the host fish sampled in this area carried this parasite.
Shiinoidae is a family of parasitic copepods found on marine teleosts.

Pennellidae is a family of parasitic copepods. When anchored on a host, they have a portion of the body on the outside of the host, whereas the remaining anterior part of the parasite is hidden inside tissues of the host.

Lernaeocera branchialis, sometimes called cod worm, is a parasite of marine fish, found mainly in the North Atlantic. It is a marine copepod which starts life as a small pelagic crustacean larva. It is among the largest of copepods, ranging in size from 2 to 3 millimetres when it matures as a copepodid larva to more than 40 mm as a sessile adult.

Lernaeopodidae is a family of parasitic copepods. The females are typically large and fleshy, and attach to the host permanently using a plug made of chitin called the bulla. The males cling on to the females using their antennae. They parasitize both marine and freshwater fish. Some lernaeopodids, including Clavella and Salmincola, can have negative impacts on fish in aquaculture.
Pennella balaenopterae is a large ectoparasitic copepod specialising in parasitising marine mammals. It is the largest member of the genus Pennella, the other species of which are parasites of larger marine fish.

Argulus foliaceus, also known as the common fish louse, is a species of fish lice in the family Argulidae. It is "the most common and widespread native argulid in the Palaearctic" and "one of the most widespread crustacean ectoparasites of freshwater fish in the world", considering its distribution and range of hosts. It can cause the severe disease state argulosis in a wide variety of fish species. It is responsible for epizootic outbreaks that have led to the collapse of aquaculture operations. Fish lice are not related to lice, which are insects.

Lepeophtheirus pectoralis is a species of parasitic copepod from the northeast Atlantic Ocean, and the type species of the genus Lepeophtheirus. It is a parasite of flatfish, with the European flounder, the plaice, and the dab as the most frequent hosts. It feeds on the mucus, skin, and blood of the fish, with egg-producing females infecting the pectoral and pelvic fins of the host, while immature individuals and males are found on the rest of the body.

Peniculisa is a genus of marine parasitic copepods in the family Pennellidae.
Cardiodectes bellottii is a species of copepods in the family Pennellidae. It is a parasite of fish. It is found in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans as well as the Mediterranean Sea; specimens from the Pacific were formerly treated as a separate species, Cardiodectes medusaeus.
Pennella exocoeti is a large ectoparasitic copepod, a specialist parasite of flying fish. The adult female copepod clings to the fish's gills or skin and feeds on its body fluids.

Lernaeenicus sprattae is a species of copepod in the family Pennellidae. It is a parasite of the European sprat and certain other fish and is sometimes known as the sprat eye-maggot.

Peniculus hokutoae is a species of parasitic pennellid copepod. It was described in 2018 from a single female. The type-host is the myctophid fish Symbolophorus evermanni and the type-locality is off Japan. The Japanese name of this species is hokuto-kozutsu-hijikimushi.
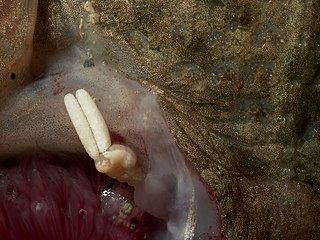
Acanthochondria cornuta is a species of parasitic copepod from the northeast Atlantic Ocean, and the type species of the genus Acanthochondria. It infects the gills of several species of flatfish, particularly the European flounder. Copepodids and immature females infect the holobranch of the host, while adult females prefer the pseudobranch and the internal wall, suggesting they migrate upstream in the gills of the host as they mature.
Ergasilus curticrus is a freshwater parasitic copepod named in 2015. Described from the Orinoco river basin, it was found solely to be hosted by individuals of the Characiform fish species Bryconops giacopinii. Of those located in South America, it is one of only five species in its genus to be found outside of Brazil.













