
Butyric acid, also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, is a straight-chain alkyl carboxylic acid with the chemical formula CH3CH2CH2CO2H. It is an oily, colorless liquid with an unpleasant odor. Isobutyric acid is an isomer. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. The acid does not occur widely in nature, but its esters are widespread. It is a common industrial chemical and an important component in the mammalian gut.

Amyl nitrate is the chemical compound with the formula CH3(CH2)4ONO2. This molecule consists of the 5-carbon amyl group attached to a nitrate functional group. It is the ester of amyl alcohol and nitric acid.
1-Pentanol,, is an organic compound with the formula CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2OH and is classified as a primary alcohol. It is a colourless liquid with a distinctive aroma. It is one of 8 isomeric alcohols with the formula C5H11OH. It is used as a solvent, a biological drying agent and in the synthesis of some fragrance compounds. It is also a common component of fusel alcohols, the undesirable byproducts of alcoholic fermentation.

Ethyl butyrate, also known as ethyl butanoate, or butyric ether, is an ester with the chemical formula CH3CH2CH2COOCH2CH3. It is soluble in propylene glycol, paraffin oil, and kerosene. It has a fruity odor, similar to pineapple, and is a key ingredient used as a flavor enhancer in processed orange juices. It also occurs naturally in many fruits, albeit at lower concentrations.

Valeric acid or pentanoic acid is a straight-chain alkyl carboxylic acid with the chemical formula CH3(CH2)3COOH. Like other low-molecular-weight carboxylic acids, it has an unpleasant odor. It is found in the perennial flowering plant Valeriana officinalis, from which it gets its name. Its primary use is in the synthesis of its esters. Salts and esters of valeric acid are known as valerates or pentanoates. Volatile esters of valeric acid tend to have pleasant odors and are used in perfumes and cosmetics. Several, including ethyl valerate and pentyl valerate are used as food additives because of their fruity flavors.
Pentyl pentanoate (C4H9COOC5H11) is an ester used in dilute solution to replicate the scent or flavour of apple, and sometimes pineapple. It is referred to as pentyl valerate or amyl pentanoate using classical nomenclature. it can be used for a variety of chemical uses, such as in the production of flavoured products, like sweets.

Methyl butyrate, also known under the systematic name methyl butanoate, is the methyl ester of butyric acid. Like most esters, it has a fruity odor, in this case resembling apples or pineapples. At room temperature, it is a colorless liquid with low solubility in water, upon which it floats to form an oily layer. Although it is flammable, it has a relatively low vapor pressure, so it can be safely handled at room temperature without special safety precautions.
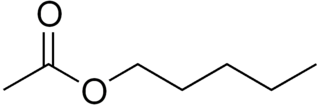
Amyl acetate (pentyl acetate) is an organic compound and an ester with the chemical formula CH3COO[CH2]4CH3 and the molecular weight 130.19 g/mol. It is colorless and has a scent similar to bananas and apples. The compound is the condensation product of acetic acid and 1-pentanol. However, esters formed from other pentanol isomers (amyl alcohols), or mixtures of pentanols, are often referred to as amyl acetate. The symptoms of exposure to amyl acetate in humans are dermatitis, central nervous system depression, narcosis and irritation to the eyes and nose.

Pentyl is a five-carbon alkyl group or substituent with chemical formula -C5H11. It is the substituent form of the alkane pentane.
Pentyl propanoate is an organic ester formed by the condensation of pentan-1-ol and propanoic acid. It is a colorless liquid with an apple-like odor, that floats on water.

An extract (essence) is a substance made by extracting a part of a raw material, often by using a solvent such as ethanol, oil or water. Extracts may be sold as tinctures, absolutes or in powder form.
The molecular formula C5H11NO2 may refer to:
The molecular formula C8H16O2 may refer to:
The molecular formula C9H18O2 (molar mass: 158.24 g/mol) may refer to:
Pentyl hexanoate (C5H11COO.C5H11) is an ester found in apple and pineapple fruits. It is closely related to pentyl butyrate and pentyl pentanoate, both of which are also present in fruits.

sec-Amyl acetate is an organic compound and an ester. It is formed in an esterification reaction of sec-amyl alcohol (2-pentanol) and acetic acid. It is a colorless liquid.

A GABA analogue is a compound which is an analogue or derivative of the neurotransmitter gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA).

6-Amyl-α-pyrone, also 6-pentyl-2-pyrone or 6PP, is an unsaturated lactone molecule. It contains two double bonds in the ring and a pentyl substituent at carbon adjacent to the ring oxygen. It is a colorless liquid which possesses characteristic coconut aroma, produced biologically by Trichoderma species. It is found in animal foods, peach, and heated beef.











