| Philometra | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Philometra fasciati | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Nematoda |
| Class: | Secernentea |
| Order: | Camallanida |
| Family: | Philometridae |
| Genus: | Philometra Costa, 1845 |
| Species | |
See text | |
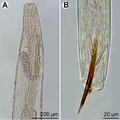
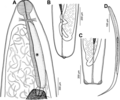
Philometra is a genus of nematodes, which are parasites of marine and freshwater fishes. [1] The genus was erected by Oronzio Gabriele Costa in 1845.
Contents
Species in this genus are worldwide. They parasitize the body cavities, tissues and ovaries of both marine and freshwater fishes. When still in the larval stages, these worms move to the body cavities or subcutaneous tissues in the host. This migration can cause damage to skeletal joints, result in internal bleeding, and inflame visceral organs. Emaciation and lowered growth rates may result from this.
Infestation produces nodules under the skin. When the worms are in the adult or juvenile stage, these nodules may be visible between the rays of the fins or may cause the scales to raise up. Larger nodules may be the result of gravid females which may rupture the skin surface. Once ruptured, the female parasite disintegrates [2] . This allows the release of the live larvae into the water. This wound on the fish then heals, leaving almost no scarring.
Species of Philometra require two hosts to complete their life cycle. After the larval worms are released from the host fish, they are ingested by copepods which act as an intermediate host. Once inside the copepod, the larvae molt several times. Fish may then eat the infested copepod.