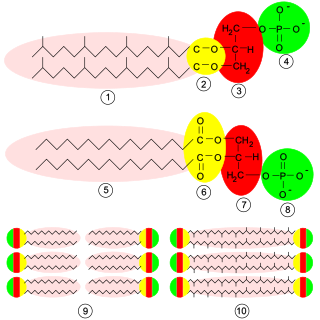
Glycerophospholipids or phosphoglycerides are glycerol-based phospholipids. They are the main component of biological membranes. Two major classes are known: those for bacteria and eukaryotes and a separate family for archaea.

Phospholipase A1 (EC 3.1.1.32; systematic name: phosphatidylcholine 1-acylhydrolase) encoded by the PLA1A gene is a phospholipase enzyme which removes the 1-acyl group:
Diglyceride acyltransferase, DGAT, catalyzes the formation of triglycerides from diacylglycerol and fatty acyl-CoA. The reaction catalyzed by DGAT is considered the terminal and only committed step in triglyceride synthesis. The conversion is essential for intestinal absorption and adipose tissue formation.
The enzyme glycosylphosphatidylinositol diacylglycerol-lyase catalyzes the reaction

The enzyme phosphatidate phosphatase (PAP, EC 3.1.3.4) is a key regulatory enzyme in lipid metabolism, catalyzing the conversion of phosphatidate to diacylglycerol:
In enzymology, a 2-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2-acylglycerol O-acyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an acyl-[acyl-carrier-protein]-phospholipid O-acyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a diacylglycerol-sterol O-acyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glycerophospholipid acyltransferase (CoA-dependent) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a long-chain-alcohol O-fatty-acyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a triacylglycerol---sterol O-acyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a CDP-diacylglycerol—inositol 3-phosphatidyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a CDP-diacylglycerol—serine O-phosphatidyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
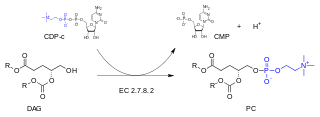
In enzymology, a diacylglycerol cholinephosphotransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an ethanolaminephosphotransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

2-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholines are a class of phospholipids that are intermediates in the metabolism of lipids. Because they result from the hydrolysis of an acyl group from the sn-1 position of phosphatidylcholine, they are also called 1-lysophosphatidylcholine. The synthesis of phosphatidylcholines with specific fatty acids occurs through the synthesis of 1-lysoPC. The formation of various other lipids generates 1-lysoPC as a by-product.

A diglyceride, or diacylglycerol (DAG), is a glyceride consisting of two fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through ester linkages. Two possible forms exist, 1,2-diacylglycerols and 1,3-diacylglycerols. DAGs can act as surfactants and are commonly used as emulsifiers in processed foods. DAG-enriched oil has been investigated extensively as a fat substitute due to its ability to suppress the accumulation of body fat; with total annual sales of approximately USD 200 million in Japan since its introduction in the late 1990s till 2009.

Diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DGAT1 gene.

Diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 2 (DGAT2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DGAT2 gene.









