
The glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as the ninth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IX, or simply CN IX, is a cranial nerve that exits the brainstem from the sides of the upper medulla, just anterior to the vagus nerve. Being a mixed nerve (sensorimotor), it carries afferent sensory and efferent motor information. The motor division of the glossopharyngeal nerve is derived from the basal plate of the embryonic medulla oblongata, whereas the sensory division originates from the cranial neural crest.

The abdominal aorta is the largest artery in the abdominal cavity. As part of the aorta, it is a direct continuation of the descending aorta.

The otic ganglion is a small parasympathetic ganglion located immediately below the foramen ovale in the infratemporal fossa and on the medial surface of the mandibular nerve. It is functionally associated with the glossopharyngeal nerve and innervates the parotid gland for salivation.
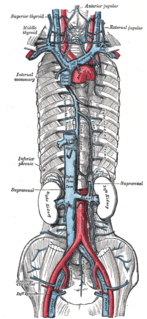
The inferior phrenic veins drain the diaphragm and follow the course of the inferior phrenic arteries;

The inferior phrenic arteries are two small vessels which supply the diaphragm. They present much variety in their origin.

The cardiac plexus is a plexus of nerves situated at the base of the heart that innervates the heart.

The lesser petrosal nerve is the general visceral efferent (GVE) component of the glossopharyngeal nerve, carrying parasympathetic preganglionic fibers from the tympanic plexus to the parotid gland. It synapses in the otic ganglion, from where the postganglionic fibers emerge.

The celiac ganglia or coeliac ganglia are two large irregularly shaped masses of nerve tissue in the upper abdomen. Part of the sympathetic subdivision of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), the two celiac ganglia are the largest ganglia in the ANS, and they innervate most of the digestive tract.

The superior ganglion of the glossopharyngeal nerve is a sensory ganglion of the peripheral nervous system. It is located within the jugular foramen where the glossopharyngeal nerve exits the skull. It is smaller than and superior to the inferior ganglion of the glossopharyngeal nerve.

The subclavian nerve, also known as the nerve to the subclavius, is small branch of the upper trunk of the brachial plexus. It contains axons from C5 and C6. The subclavian nerve innervates the subclavius muscle.

The superior mesenteric plexus is a continuation of the lower part of the celiac plexus, receiving a branch from the junction of the right vagus nerve with the plexus.

The inferior cervical ganglion is situated between the base of the transverse process of the last cervical vertebra and the neck of the first rib, on the medial side of the costocervical artery.

The suprarenal plexus is formed by branches from the celiac plexus, from the celiac ganglion, and from the phrenic and greater splanchnic nerves, a ganglion being formed at the point of junction with the latter nerve.

The hepatic plexus, the largest offset from the celiac plexus, receives filaments from the left vagus and right phrenic nerves.

The esophageal plexus is formed by nerve fibers from two sources, branches of the vagus nerve, and visceral branches of the sympathetic trunk. The esophageal plexus and the cardiac plexus contain the same types of fibers and are both considered thoracic autonomic plexus.

The superior cardiac nerve arises by two or more branches from the superior cervical ganglion, and occasionally receives a filament from the trunk between the first and second cervical ganglia. It runs down the neck behind the common carotid artery, and in front of the Longus colli muscle; and crosses in front of the inferior thyroid artery, and recurrent nerve. The course of the nerves on the two sides then differs.

The superior suprarenal artery is an artery in the abdomen. It is a branch of the inferior phrenic artery, itself a branch of the aorta. It supplies the adrenal gland.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The ciliary ganglion is a parasympathetic ganglion located just behind the eye in the posterior orbit. Three types of axons enter the ciliary ganglion but only the preganglionic parasympathetic axons synapse there. The entering axons are arranged into three roots of the ciliary ganglion, which join enter the posterior surface of the ganglion.













