
Phytophthora is a genus of plant-damaging oomycetes, whose member species are capable of causing enormous economic losses on crops worldwide, as well as environmental damage in natural ecosystems. The cell wall of Phytophthora is made up of cellulose. The genus was first described by Heinrich Anton de Bary in 1875. Approximately 210 species have been described, although 100–500 undiscovered Phytophthora species are estimated to exist.

Phytophthora cinnamomi, also known as cinnamon fungus, is a soil-borne water mould that produces an infection which causes a condition in plants variously called "dieback", "root rot", or, "ink disease".
Phytophthora sojae is an oomycete and a soil-borne plant pathogen that causes stem and root rot of soybean. This is a prevalent disease in most soybean growing regions, and a major cause of crop loss. In wet conditions the pathogen produces zoospores that move in water and are attracted to soybean roots. Zoospores can attach to roots, germinate, and infect the plant tissues. Diseased roots develop lesions that may spread up the stem and eventually kill the entire plant. Phytophthora sojae also produces oospores that can remain dormant in the soil over the winter, or longer, and germinate when conditions are favourable. Oospores may also be spread by animals or machinery.

Phytophthora palmivora is an oomycete that causes bud-rot of palms, fruit-rot or kole-roga of coconut and areca nut. These are among the most serious diseases caused by fungi and moulds in South India. It occurs almost every year in Malnad, Mysore, North & South Kanara, Malabar and other areas. Similar diseases of palms are also known to occur in Sri Lanka, Mauritius, and Sumatra. The causative organism was first identified as P. palmivora by Edwin John Butler in 1917.
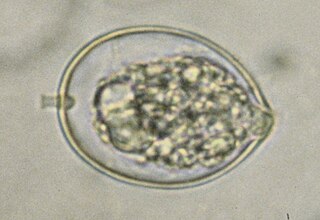
Phytophthora cactorum is a fungal-like plant pathogen belonging to the Oomycota phylum. It is the causal agent of root rot on rhododendron and many other species, as well as leather rot of strawberries.

Phytophthora medicaginis is an oomycete plant pathogen that causes root rot in alfalfa and chickpea. It is a major disease of these plants and is found wherever they are grown. P. medicaginis causes failure of stand establishment because of seedling death. Phytophthora medicaginis is part of a species complex with Phytophthora megasperma.
Phytophthora nicotianae or black shank is an oomycete belonging to the order Peronosporales and family Peronosporaceae.
Pythium irregulare is a soil borne oomycete plant pathogen. Oomycetes, also known as "water molds", are fungal-like protists. They are fungal-like because of their similar life cycles, but differ in that the resting stage is diploid, they have coenocytic hyphae, a larger genome, cellulose in their cell walls instead of chitin, and contain zoospores and oospores.
Pythium aphanidermatum is a soil borne plant pathogen. Pythium is a genus in the class Oomycetes, which are also known as water molds. Oomycetes are not true fungi, as their cell walls are made of cellulose instead of chitin, they are diploid in their vegetative state, and they form coenocytic hyphae. Also, they reproduce asexually with motile biflagelette zoospores that require water to move towards and infect a host. Sexually, they reproduce with structures called antheridia, oogonia, and oospores.
Pythium graminicola is a plant pathogen infecting cereals.
Pythium volutum is a plant pathogen infecting wheat, barley, and turfgrass. It is known to be sensitive to some of the compounds typically present in selective media commonly used for isolating Pythium spp., so isolation may require alternative methods.
Phytophthora fragariae is a fungus-like (oomycete) plant pathogen that causes red stele, otherwise known as Lanarkshire disease, in strawberries. Symptoms of red stele can include a red core in the roots, wilting of leaves, reduced flowering, stunting, and bitter fruit. The pathogen is spread via zoospores swimming through water present in the soil, released from sporangia.
Phytophthora megakarya is an oomycete plant pathogen that causes black pod disease in cocoa trees in west and central Africa. This pathogen can cause detrimental loss of yield in the economically important cocoa industry, worth approximately $70 billion annually. It can damage any part of the tree, causing total yield losses which can easily reach 20-25%. A mixture of chemical and cultural controls, as well as choosing resistant plant varieties, are often necessary to control this pathogen.

Phytophthora kernoviae is a plant pathogen that mainly infects European beech and Rhododendron ponticum. It was first identified in 2003 in Cornwall, UK when scientists were surveying for the presence of Phytophthora ramorum. This made it the third new Phytophthora species to be found in the UK in a decade. It was named Phytophthora kernoviae after the ancient name for Cornwall, Kernow. It causes large stem lesions on beech and necrosis of stems and leaves of Rhododendron ponticum. It is self-fertile. It has also been isolated from Quercus robur and Liriodendron tulipifera. The original paper describing the species, stated it can infect Magnolia and Camellia species, Pieris formosa, Gevuina avellana, Michelia doltsopa and Quercus ilex. Since then many other plants have been identified as natural hosts of the pathogen. Molecular analysis has revealed that an infection on Pinus radiata, recorded in New Zealand in 1950, was caused by P. kernoviae. The pathogen was also noted on Drimys winteri, Gevuina avellana, Ilex aquifolium, Quercus ilex, Vaccinium myrtillus, Hedera helix, Podocarpus salignas.
Phytophthora quercina is a papillate homothallic soil-borne plant pathogen causing root rot of oak tree species in Europe. It is associated with necrotic fine roots.
Buckeye rot of tomato is caused by three species of pathogens in the genus Phytophthora: P. nicotianae var. parasitica, P. capsici, and P. drechsleri. It is an oomycete that thrives in warm, wet conditions and lives in the soil. It is characterized by a bull’s eye pattern of dark brown rotting on the tomato fruit, and affects fruit that is close to, or lying on the soil. The easiest management is to keep the plant out of contact with the soil, although other chemical methods can be very effective. This disease commonly occurs in the southeast and south central areas of the United States. The disease has affected a large portion of crop yield in the United States as well as India. The relatively small genome size of Phytophthora parasitica compared to Phytophthora infestans gives researchers the unique ability to further examine its ability to cause disease.
Phytophthora lacustris is an oomycete plant pathogen.
Black rot on orchids is caused by Pythium and Phytophthora species. Black rot targets a variety of orchids but Cattleya orchids are especially susceptible. Pythium ultimum and Phytophthora cactorum are known to cause black rot in orchids.
Cranberry Root Rot (CRR) is a disease in cranberries that can cause a decline in yield.






