
Plant pathology or phytopathology is the scientific study of plant diseases caused by pathogens and environmental conditions. Plant pathology involves the study of pathogen identification, disease etiology, disease cycles, economic impact, plant disease epidemiology, plant disease resistance, how plant diseases affect humans and animals, pathosystem genetics, and management of plant diseases.
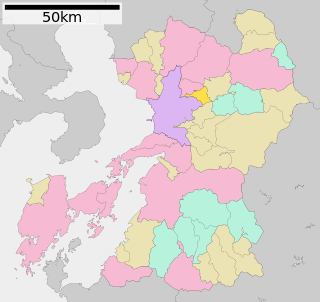
Kikuyō is a town located in Kikuchi District, Kumamoto Prefecture, Japan.

Agrobacterium is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria established by H. J. Conn that uses horizontal gene transfer to cause tumors in plants. Agrobacterium tumefaciens is the most commonly studied species in this genus. Agrobacterium is well known for its ability to transfer DNA between itself and plants, and for this reason it has become an important tool for genetic engineering.
Mathematical models can project how infectious diseases progress to show the likely outcome of an epidemic and help inform public health and plant health interventions. Models use basic assumptions or collected statistics along with mathematics to find parameters for various infectious diseases and use those parameters to calculate the effects of different interventions, like mass vaccination programs. The modelling can help decide which intervention(s) to avoid and which to trial, or can predict future growth patterns, etc.

Kenichi Hagiwara was a Japanese singer and actor.

Pure red cell aplasia (PRCA) or erythroblastopenia refers to a type of aplastic anemia affecting the precursors to red blood cells but usually not to white blood cells. In PRCA, the bone marrow ceases to produce red blood cells. There are multiple etiologies that can cause PRCA. The condition has been first described by Paul Kaznelson in 1922.

Rhizobium rhizogenes is a Gram-negative soil bacterium that produces hairy root disease in dicotyledonous plants. R. rhizogenes induces the formation of proliferative multiple-branched adventitious roots at the site of infection, so-called 'hairy roots'. It also induces galls.

Hans M. Heybroek was a Dutch botanist best known for his research into the genus Ulmus at the Dorschkamp Research Institute for Forestry & Landscape Planning. Until his retirement in 1992, he was responsible for the raising and release of numerous elm hybrid cultivars, notably 'Columella'. Specializing in phytopathology, Heybroek also investigated the Coral Spot fungus Nectria cinnabarina in elm. In 1960 he travelled to the Kashmir to search for a frost-hardy form of the Himalayan Elm Ulmus wallichiana as a source of anti-fungal genes for use in the Dutch elm research programme.
Septoria menthae is a fungal plant pathogen infecting mint. It is the causal organism of mint leafspot.
Sclerotium cinnamomi is a fungal plant pathogen in the family Typhulaceae. It can cause 2–5 mm crusty black sclerotia on decaying plant matter.

Sarocladium oryzae (Sawada) is a plant pathogen causing the Sheath rot disease of rice and Bamboo blight of Bambusoideae spp. in Asia.
GA-binding protein alpha chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GABPA gene.

Imakita Kōsen was a Japanese Rinzai Zen rōshi and Neo-Confucianist.

Leptosphaerulina is a genus of fungi in the class Dothideomycetes. The relationship of this taxon to other taxa within the class was unknown in 2007 until it was placed within the Didymellaceae family in the Pleosporales order. The genus was first described by Australian plant pathologist Daniel McAlpine in 1902.

Apiforol is a chemical compound belonging to the flavan-4ol class of flavonoids.
Kentaro Sawada is a former Japanese football player. He played for Japan national team.

Rebirth is a 2011 Japanese drama film directed by Izuru Narushima, based on author Mitsuyo Kakuta's novel. The film was a critical success, winning 10 awards at the 35th Japan Academy Prize, including Best Picture, Best Director, Best Leading Actress, Best Supporting Actress, and Best Script.

Phytophthora plurivora is a very aggressive soil-borne plant pathogen, with worldwide distribution and a wide variety of hosts.

Erwin Frink Smith was an American plant pathologist with the United States Department of Agriculture. He played a major role in demonstrating that bacteria could cause plant disease.

Keisuke Sawada is a professional Japanese baseball player. He plays pitcher for the Chiba Lotte Marines. Previous he play for the Orix Buffaloes.















