| Pinus occidentalis | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Pinus occidentalis in Jarabacoa, Dominican Republic | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Gymnospermae |
| Division: | Pinophyta |
| Class: | Pinopsida |
| Order: | Pinales |
| Family: | Pinaceae |
| Genus: | Pinus |
| Subgenus: | P. subg. Pinus |
| Section: | P. sect. Trifoliae |
| Subsection: | P. subsect. Australes |
| Species: | P. occidentalis |
| Binomial name | |
| Pinus occidentalis | |
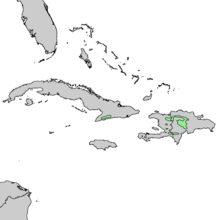 | |
| Natural range of Pinus occidentalis | |
Pinus occidentalis, also known as the Hispaniolan pine, [1] Hispaniola pine [2] or pino criollo, [3] is a pine tree endemic to the island of Hispaniola [4] (split between the Dominican Republic and Haiti).
