
Huperzia is a genus of lycophyte plants, sometimes known as the firmosses or fir clubmosses; the Flora of North America calls them gemma fir-mosses. This genus was originally included in the related genus Lycopodium, from which it differs in having undifferentiated sporangial leaves, and the sporangia not formed into apical cones. The common name firmoss, used for some of the north temperate species, refers to their superficial resemblance to branches of fir (Abies), a conifer. As of 2020, two very different circumscriptions of the genus were in use. In the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016, Huperzia is one of three genera in the subfamily Huperzioideae of the family Lycopodiaceae. Most species in the subfamily are placed in the genus Phlegmariurus. Huperzia is left with about 25 species, although not all have been formally transferred to other genera. Other sources recognize only Huperzia, which then has about 340 species.
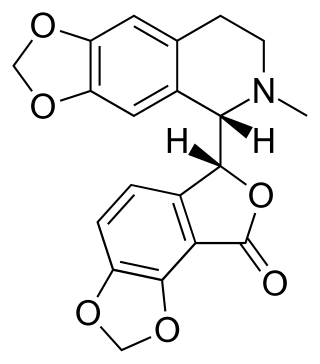
Bicuculline is a phthalide-isoquinoline compound that is a light-sensitive competitive antagonist of GABAA receptors. It was originally identified in 1932 in plant alkaloid extracts and has been isolated from Dicentra cucullaria, Adlumia fungosa, and several Corydalis species. Since it blocks the inhibitory action of GABA receptors, the action of bicuculline mimics epilepsy; it also causes convulsions. This property is utilized in laboratories around the world in the in vitro study of epilepsy, generally in hippocampal or cortical neurons in prepared brain slices from rodents. This compound is also routinely used to isolate glutamatergic receptor function.

Sphaeropteris medullaris, synonym Cyathea medullaris, commonly known as mamaku or black tree fern, is a large tree fern up to 20 m tall. It is distributed across the south-west Pacific from Fiji to Pitcairn Island. Its other Māori names include katātā, kōrau, or pītau.

Sphaeropteris is a genus of tree fern in the family Cyatheaceae. It has been treated as a subgenus within the genus Cyathea, but is accepted in the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016.

Dennstaedtia is a mostly tropical and subtropical genus of ferns described as a genus in 1801. hayscented fern, or cup ferns, are common names for some species in this genus. Its best-known member is probably the temperate North-American hay-scented fern, Dennstaedtia punctilobula, which forms extensive clonal ground-cover colonies on level surfaces in the Appalachian area.

Tmesipteris, the hanging fork ferns, is a genus of ferns, one of two genera in the family Psilotaceae, order Psilotales . Tmesipteris is restricted to certain lands in the Southern Pacific, notably Australia, New Zealand and New Caledonia. In New Zealand this hanging epiphyte is common in the warm temperate rain forests of both main islands, where it can normally be found as short spiky dark-green fronds, often with lighter bag-like sporangia at the bases of some of its "leaves". The plant possesses no true leaves; what appear to be leaves are flattened stems. The fronds emerge directly from the fibrous root-mats which clad the trunks of mature tree ferns such as Dicksonia and Cyathea. Tmesipteris is from the Greek language, meaning a "cut fern", referring to the truncated leaf tips.
Johann Jakob Bernhardi was a German doctor and botanist.

Kickxia is a genus of plants in the plantain family (Plantaginaceae). It includes several species known commonly as cancerworts or fluellins. Species are mostly native to Europe, Central Asia, and Africa, with two, K. elatine and K. spuria, well-established as invasive elsewhere.

Tithonia is a genus of flowering plants in the tribe Heliantheae within the family Asteraceae.

Cystopteridaceae is a family of ferns in the order Polypodiales. In the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016 (PPG I), the family is placed in the suborder Aspleniineae of the order Polypodiales, and includes three genera. Alternatively, it may be treated as the subfamily Cystopteridoideae of a very broadly defined family Aspleniaceae.

Dicranopteris (forkedfern) is a genus of tropical ferns of the family Gleicheniaceae. There are about 20 described species.

Solanum villosum, the hairy nightshade, red nightshade or woolly nightshade, is a sprawling annual weed in Europe, western Asia, northern Africa and is also naturalized in Australia and North America.

Viscaria vulgaris, the sticky catchfly or clammy campion, is a flowering plant in the family Caryophyllaceae.

Viscaria is a genus of flowering plants in the family Caryophyllaceae, native to Canada, Greenland, Iceland, Europe, Kazakhstan, and western Siberia. Molecular studies attempting to resolve relationships in the tribe Sileneae have found that Viscaria is closely genetically related to the genus Atocion, but is quite distinct from it morphologically.

Falkia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Convolvulaceae, native to southern Africa, eastern Africa, and the Arabian Peninsula. They are creeping perennial herbs.

Veratrum lobelianum is a species of flowering plant belonging to the family Melanthiaceae.

Hypochaeris maculata is a species of flowering plant belonging to the family Asteraceae, it’s common name is spotted cat's-ear.

Potentilla thuringiaca is a species of flowering plant belonging to the family Rosaceae.
Cysticapnos is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Papaveraceae.
Sphaeropteris lunulata is a species of tree fern in the family Cyatheaceae, native from Sulawesi in Malesia and the Bismarck Archipelago in Papuasia to the western Pacific. It was first described by Georg Forster in 1786 as Polypodium lunulatum and transferred to Sphaeropteris by Rolla Tryon in 1970.

















