
Eulipotyphla is an order of mammals suggested by molecular methods of phylogenetic reconstruction, which includes the laurasiatherian members of the now-invalid polyphyletic order Lipotyphla, but not the afrotherian members.
Gymnures, also called hairy hedgehogs or moonrats, are mammals belonging to the subfamily Galericinae, in the family Erinaceidae and the order Eulipotyphla. Gymnures resemble rats but are not closely related as they are not rodents; they are instead closely related to hedgehogs, which also belong to Erinaceidae. They are thought to have appeared in Eastern Asia before their closest relatives, and changed little from the original ancestor, which is thought to have been also the ancestor of the shrews.

Erinaceidae is a family in the order Eulipotyphla, consisting of the hedgehogs and moonrats. Until recently, it was assigned to the order Erinaceomorpha, which has been subsumed with the paraphyletic Soricomorpha into Eulipotyphla. Eulipotyphla has been shown to be monophyletic; Soricomorpha is paraphyletic because Soricidae shared a more recent common ancestor with Erinaceidae than with other soricomorphs.
Hylomys is a small genus of the family Erinaceidae. Hylomys species, like all species in the subfamily Galericinae, are known as gymnures or moonrats. Their closest relatives include the fossil Lantanotherium and Thaiagymnura and the living Neotetracus and Neohylomys. Members of this genus are found in Southeast Asia and Eastern Asia.

The Javan short-tailed gymnure is a small mammal from the family of the Erinaceidae. The scientific name of the species is first published by Salomon Müller in 1840. This species used to include the dorsalis, maxi, and peguensis subspecies, but these have now been elevated to species of their own: the Bornean short-tailed gymnure, Max's short-tailed gymnure, and the northern short-tailed gymnure. In addition, two new species were created from two other populations of H. suillus. The range of this species is now limited to Java.

The dwarf gymnure is a gymnure found only at Mount Kerinci, Sumatra, Indonesia. It is listed by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as a critically endangered species due to a restricted range.

The moonrat is a southeast Asian species of mammal in the family Erinaceidae. It is the only species in the genus Echinosorex. The moonrat is a fairly small, primarily carnivorous animal which, despite its name, is not closely related to rats or other rodents. The scientific name is sometimes given as Echinosorex gymnurus, but this is incorrect.

Soricomorpha is a formerly used taxon within the class of mammals. In the past it formed a significant group within the former order Insectivora. However, Insectivora was shown to be polyphyletic and various new orders were split off from it, including Afrosoricida, Macroscelidea, and Erinaceomorpha, with the four remaining extant and recent families of Soricomorpha shown here then being treated as a separate order. Insectivora was left empty and disbanded.

The Hainan gymnure or Hainan moonrat is a species of mammal in the family Erinaceidae. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical dry forests. It was thought to be endemic to the island of Hainan, China, where it is threatened due to habitat loss, but in 2018 was found to also occur in, and be rather common, in Northern Vietnam.

The shrew gymnure, or shrew hedgehog, is a species of mammal in the family Erinaceidae and is the only extant species in the genus Neotetracus. It is found in China, Myanmar, and Vietnam.
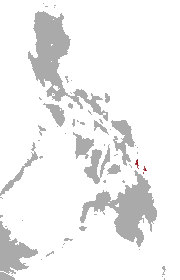
The Dinagat gymnure is a species of mammal in the family Erinaceidae. It is endemic to the Philippines.

Podogymnura truei, also known as the Mindanao gymnure, Mindanao moonrat, or Mindanao wood shrew, is a mammal of the family Erinaceidae. It is endemic to the Mindanao islands of the Philippines. Erinaceidae is a family of small mammals that include the gymnures, also known as the silky furred moonrats, and the hedgehogs. Animals belonging to this family are significant because they are among the oldest known placental mammals that are alive. Gymnures are relatives of hedgehogs but lack the prickly spines. Four species are categorized in the genus Podogymnura: P. aureospinula, P. intermedia, P. minima, and P. truei. All share a close resemblance to the moonrat Echinosorex gymnura, which is commonly found on the Borneo, Sumatra, and the Malay Peninsulas.

The long-eared gymnure is a eulipotyphlan that is found in Laos. This specific type of gymnure has long ears and a long skull compared to that of others. It is also recognized for its broad forefeet, stout claws, and naked hindfeet. While it was previously lumped in with the dwarf and short-tailed gymnures of the genus Hylomys, it is now placed in its own genus Otohylomys.
The eastern Mindanao gymnure is a species of gymnure in the genus Podogymnura. It is known only from Mount Hamiguitan and Mount Kampalili, two mountains in the eastern part of the island of Mindanao in the Philippines. It was first named in 2023 by a team of researchers led by Danilo Balete.











